Trump tariffs biggest clean energy impacts have had a significant and multifaceted effect on the global clean energy sector. This exploration delves into the historical context of Trump’s trade policies, examining the specific industries and goods targeted by these tariffs. We’ll analyze the arguments for and against these policies, and their contrasting effects on different sectors of the economy, including clean energy.
This analysis will also highlight the profound impacts on the manufacturing and development of clean energy technology, including solar panels, wind turbines, and energy-efficient products.
The tariffs have demonstrably affected the clean energy industry, impacting everything from raw material procurement to the financial health of companies and workers. We’ll examine the ripple effects on the supply chain, looking at the potential for long-term economic growth in clean energy, both with and without tariffs. Ultimately, we’ll discuss potential alternative policies to mitigate the negative impacts and promote a more sustainable future for clean energy.
Trump Tariffs
The Trump administration’s trade policies, heavily reliant on tariffs, significantly impacted global markets and domestic industries. These policies, while aiming to protect American interests, sparked considerable debate and controversy, raising questions about their effectiveness and long-term consequences. This analysis explores the history, specifics, justifications, and opposing arguments surrounding these tariffs.
Overview of Trump’s Trade Policies
Donald Trump’s trade policies, particularly the use of tariffs, were a defining feature of his presidency. He frequently cited national security and economic concerns as justifications for these measures. These actions prompted a wide range of responses, from support among certain segments of the population to strong opposition from international partners and domestic critics.
Specific Industries and Goods Targeted
Tariffs were applied to a broad range of imported goods, impacting various industries. Notable targets included steel, aluminum, solar panels, washing machines, and agricultural products from countries like China, Mexico, and Canada. These tariffs aimed to reduce imports and encourage domestic production.
Trump’s tariffs definitely had a ripple effect on clean energy, impacting various sectors. Interestingly, a recent interview with Jean-Noël Barrot, focusing on France’s ocean policy and its intersection with Trump’s actions, jean noel barrot interview france oceans trump , hints at how global trade disputes can indirectly influence green energy development. The complexities of international relations, however, still leave the exact nature of these impacts open to interpretation, especially in the context of clean energy.
Stated Justifications for Imposing Tariffs
Proponents of these tariffs often argued that they were necessary to protect American industries from unfair competition, safeguard national security, and encourage domestic job creation. They claimed that these tariffs would reduce trade imbalances and force other countries to adopt more favorable trade practices. The goal was to strengthen American manufacturing and reduce reliance on foreign imports.
Arguments Against Tariffs from Opposing Viewpoints
Critics argued that tariffs imposed by the US led to retaliatory tariffs from other countries, creating trade wars that harmed American businesses and consumers. Increased costs and reduced supply were also common concerns, impacting businesses that relied on imported goods and consumers paying higher prices. Furthermore, these policies often faced criticism for negatively impacting international relations and undermining global trade agreements.
Impact on Different Sectors of the Economy
The following table presents a comparative analysis of the impacts of tariffs on different sectors of the economy. The analysis highlights the potential for tariffs to affect various industries, from agriculture to manufacturing, and the importance of considering these broader impacts.
| Sector | Potential Positive Impacts | Potential Negative Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Increased domestic production, potential job creation | Higher input costs, reduced competitiveness in export markets, supply chain disruptions |
| Agriculture | Protection for domestic farmers, potential increase in farm income | Reduced exports, retaliatory tariffs from other countries, impacting farmers dependent on international markets |
| Consumers | Potential lower prices for domestically produced goods (if domestic production expands) | Higher prices for imported goods, reduced choices in products |
| International Relations | Potential to exert leverage in trade negotiations | Escalation of trade disputes, strained relations with other countries |
Tariffs and Renewable Energy Sources

Tariffs, often imposed for protectionist or strategic reasons, can have significant and sometimes unforeseen consequences across various sectors, including renewable energy. Understanding these impacts is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike to make informed decisions and mitigate potential risks. The implications for the manufacturing and deployment of solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy technologies are complex and merit careful consideration.The imposition of tariffs on raw materials used in renewable energy production can significantly affect the cost of these components.
This, in turn, can impact the overall price of renewable energy systems, potentially hindering their widespread adoption. The cascading effect of tariffs on global supply chains can also impact the competitiveness of renewable energy technologies in the market.
Impact on Solar Panel Manufacturing
Tariffs on raw materials, such as polysilicon, used in solar panel manufacturing, can increase production costs. This can lead to higher prices for solar panels, making them less competitive compared to traditional energy sources. For example, if a tariff is placed on imported polysilicon, domestic solar panel manufacturers might face higher input costs, potentially impacting their profitability and competitiveness.
Ultimately, this could slow the adoption of solar energy, especially in markets where cost is a significant factor.
Comparison of Tariff Impacts on Renewable Energy Sources
The impact of tariffs varies across different renewable energy sources depending on their specific supply chains and reliance on imported components. Solar energy, for instance, is heavily reliant on imported polysilicon and other materials, making it more vulnerable to tariff increases. Wind energy, while also reliant on international trade for some components, may not be as susceptible to the same degree, given the variety of materials involved.
The complexity of supply chains, as well as the extent to which components are sourced internationally, is a key factor in determining the impact of tariffs.
Role of International Trade in Renewable Energy Supply Chains
International trade plays a crucial role in the supply chains of renewable energy components. Many critical raw materials and manufacturing processes are distributed globally. For example, specialized equipment or advanced manufacturing techniques might be concentrated in certain countries. This intricate network of international trade allows for the efficient production and distribution of renewable energy components at competitive prices.
Disruptions to this network, such as tariffs, can have a significant impact on the availability and cost of these components.
Potential Effects on Research and Development Efforts
Tariffs can negatively impact research and development efforts in renewable energy technologies. Increased production costs can discourage investment in research and development for new, more efficient technologies, potentially hindering the long-term progress of the renewable energy sector. Moreover, the uncertainty surrounding tariffs can deter companies from investing in new projects or expanding existing ones, slowing down innovation and deployment.
For instance, a company might postpone investing in a new solar panel technology if tariffs on critical materials make it difficult to produce and sell the technology at a profitable price.
Vulnerability of Renewable Energy Sources to Tariffs
| Renewable Energy Source | Potential Vulnerability to Tariffs |
|---|---|
| Solar | High, heavily reliant on imported raw materials like polysilicon and other components. |
| Wind | Moderate, dependence on international trade for specific components, but potentially less than solar. |
| Hydropower | Low, generally relies less on international trade for key components. |
| Geothermal | Low, typically relies on locally sourced materials and processes. |
| Biomass | Variable, depends on the specific biomass feedstock and processing methods. |
This table provides a general overview of the potential vulnerability of different renewable energy sources to tariffs. The specific level of vulnerability can vary depending on the specific tariffs imposed and the complexity of the supply chain for each technology.
Tariffs and Energy Efficiency
Tariffs, often implemented for protectionist or strategic reasons, can have unforeseen consequences on various sectors, including energy efficiency. The imposition of tariffs on energy-efficient goods can impact both consumers and manufacturers, potentially altering the market landscape and affecting the overall energy consumption patterns. This analysis examines the specific impact of tariffs on the importation of energy-efficient goods and equipment, their potential effect on consumer access, and the broader implications for energy efficiency standards.The interplay between tariffs and energy efficiency is complex.
While tariffs might aim to boost domestic production of certain goods, they can simultaneously raise prices for consumers, potentially discouraging the adoption of energy-efficient products. This, in turn, could lead to higher overall energy consumption and environmental concerns. Furthermore, the impact of tariffs on the supply chain for energy-efficient products needs careful consideration, as disruptions could affect availability and affordability.
Influence on Importation of Energy-Efficient Goods, Trump tariffs biggest clean energy impacts
Tariffs directly influence the cost of imported energy-efficient goods and equipment. Increased tariffs make these products more expensive for importers and, consequently, for consumers. This can discourage the purchase and use of energy-efficient alternatives, potentially leading to a shift toward less efficient options. For example, a 25% tariff on LED light bulbs would significantly increase their price, potentially making them less attractive compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, despite their energy savings.
Effects on Consumer Access to Energy-Efficient Products
The increased cost of energy-efficient products due to tariffs can limit consumer access. Lower-income households, particularly, might be disproportionately affected, as they may face a greater financial burden when choosing between energy-efficient options and less expensive, less efficient alternatives. This could lead to a widening gap in access to energy-saving technologies. For example, if the price of energy-efficient refrigerators increases substantially due to tariffs, consumers might choose models with lower energy efficiency ratings, leading to higher energy bills over time.
Energy Savings Associated with Energy-Efficient Products
Energy-efficient products offer substantial energy savings compared to their non-efficient counterparts. These savings can translate to significant cost reductions for consumers over the lifespan of the product. For instance, an energy-efficient washing machine can save hundreds of dollars on utility bills over its lifetime compared to a conventional model. Reliable data from independent research organizations and government agencies can provide concrete figures on the energy savings associated with different energy-efficient products.
Impact on Energy Efficiency Standards
Tariffs could indirectly influence energy efficiency standards. If tariffs make energy-efficient imports less competitive, it might reduce the incentive for manufacturers to adhere to stringent energy efficiency standards. This could result in lower overall energy efficiency levels in the market. Governments may need to implement countermeasures, such as targeted subsidies or incentives, to maintain the adoption of energy-efficient products.
Table: Potential Tariff Impact on Energy-Efficient Products
| Product | Potential Tariff Impact | Energy Savings (estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| LED Light Bulbs | Increased price, potentially reducing consumer adoption. | 70-90% compared to incandescent bulbs |
| Energy-Efficient Refrigerators | Increased price, impacting affordability for some consumers. | 20-40% compared to standard models |
| Energy-Star Certified Washing Machines | Increased price, potentially discouraging purchase. | 25-50% compared to conventional models |
| High-Efficiency Air Conditioners | Increased price, potentially limiting market penetration. | 20-35% compared to standard models |
Note: Estimated energy savings vary depending on product type, model, and usage patterns. The provided data is illustrative and should not be considered exhaustive.
International Trade Relations and Clean Energy
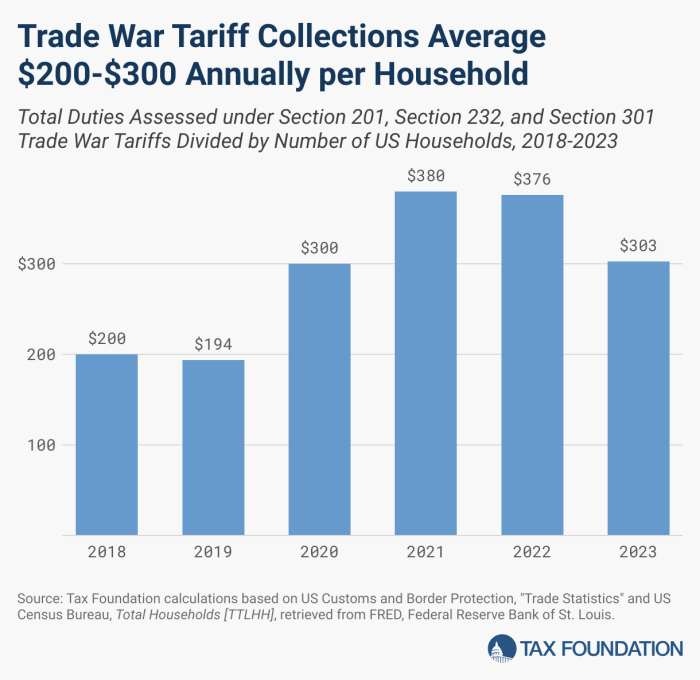
The global landscape of clean energy trade has undergone significant shifts in recent decades, with a growing emphasis on international cooperation and the development of sustainable energy solutions. Trump’s tariffs, however, introduced a degree of uncertainty and disruption, prompting a reassessment of international trade practices in this critical sector. Understanding the interplay between trade policies and clean energy is crucial for navigating the future of global sustainability efforts.The implementation of tariffs, particularly on solar panels and other clean energy technologies, had a substantial impact on the flow of goods and investment.
The resulting ripple effects can be seen in altered supply chains, shifting manufacturing locations, and modifications to international agreements. This analysis will delve into the specific impacts of these tariffs on international trade relations, including the implications for cooperation, investment, and the development of international standards.
Comparison of Global Clean Energy Trade Before and After Trump’s Tariffs
Prior to the implementation of Trump’s tariffs, international trade in clean energy technologies was characterized by increasing global cooperation. Countries were collaborating on research, development, and deployment initiatives. The flow of components and finished products was relatively unrestricted, fostering innovation and the spread of sustainable technologies across borders. The post-tariff landscape witnessed a shift towards protectionist measures, with countries potentially focusing on domestic production.
This change in trade dynamics had far-reaching implications for international cooperation and investment in clean energy projects.
Impact of Tariffs on International Cooperation in Clean Energy Development
The introduction of tariffs significantly hampered international cooperation in clean energy development. Joint research initiatives and technology sharing programs were negatively affected. Projects involving multiple nations faced logistical challenges and cost increases. The reduced collaboration hindered the rapid advancement of clean energy technologies and slowed down the global transition towards a more sustainable future.
Impact of Tariffs on Foreign Investment in Clean Energy Projects
Tariffs created an uncertain environment for foreign investment in clean energy projects. Companies considering investments in clean energy ventures were hesitant due to the potential for trade barriers and fluctuating market conditions. The reduced investment flow had a negative impact on the growth and development of clean energy infrastructure. Foreign investors were often concerned about the implications of tariffs for their supply chains and potential disruptions to their business operations.
In some cases, investments shifted to countries with more favorable trade policies.
Trump’s tariffs undeniably had significant, albeit largely negative, impacts on the burgeoning clean energy sector. The trade disputes, while seemingly unrelated, can be seen as a distraction from the larger geopolitical picture. For example, the way Trump and Putin have seemingly attempted to rebrand World War II victory narratives, as detailed in this article about trump putin brand wwii victory , highlights a troubling trend.
Ultimately, these kinds of actions and the ensuing economic fallout can hinder the development of sustainable solutions. These tariffs ultimately hindered progress in clean energy, a critical step toward a greener future.
Description of Potential Changes in International Standards and Regulations for Clean Energy Products
The introduction of tariffs prompted a reassessment of international standards and regulations for clean energy products. There were concerns about the potential for diverging standards, creating hurdles for international trade. Discussions regarding harmonization of standards and the establishment of common regulations gained momentum. Countries were actively exploring ways to mitigate the negative impact of tariffs and foster a more collaborative approach to clean energy trade.
Interconnectedness of International Trade in Clean Energy
International trade in clean energy is deeply interconnected. The supply chains for solar panels, wind turbines, and other clean energy technologies involve numerous countries. Tariffs imposed on one component or product can disrupt the entire supply chain, affecting manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers. The example of a solar panel illustrates this interconnectedness: the raw materials (silicon, glass, etc.) may originate from one country, the manufacturing process might occur in another, and the final product is often shipped to various markets globally.
This interconnectedness underscores the need for global cooperation and a consistent approach to trade policies in order to foster a sustainable and prosperous future.
Alternative Policy Scenarios
Navigating the complex interplay between tariffs and clean energy requires proactive policy adjustments. The current tariff regime’s effects on renewable energy sources, energy efficiency, and international trade relations warrant careful consideration of alternative approaches. These strategies must aim to mitigate negative impacts while fostering sustainable clean energy development.The potential benefits of alternative policies on clean energy development are significant, and the challenges of implementation are not insurmountable.
A strategic approach that addresses specific concerns and leverages existing opportunities is essential for achieving a positive outcome.
Trump’s tariffs definitely had a significant impact on clean energy, hindering domestic production and potentially boosting foreign competition. This sadly coincides with the passing of Gerry Connolly, a powerful advocate for federal workers, as seen in this article. The ripple effects of such policies on the clean energy sector, and the loss of passionate advocates like Connolly, are definitely worth considering as we move forward.
Alternative Tariff Structures
Various tariff structures can be implemented to encourage clean energy adoption while minimizing negative trade impacts. These structures may include differentiated tariffs based on the environmental performance of imported goods, offering incentives for cleaner production processes, or providing tax breaks for domestic clean energy technologies.
- Differentiated Tariffs: A tiered system could apply lower tariffs to goods meeting specific environmental standards, thus incentivizing cleaner production abroad and supporting global environmental goals. This would encourage countries to improve their environmental performance to access more favorable tariff rates.
- Incentivizing Cleaner Production: Government subsidies or tax breaks for companies that implement clean energy technologies in their production processes can encourage global adoption. This approach would create a positive feedback loop, where cleaner production is rewarded, and tariffs can be adjusted accordingly. The success of this approach relies on effective monitoring and verification mechanisms to ensure compliance.
- Tax Breaks for Domestic Clean Energy Technologies: Incentivizing domestic investment in clean energy can stimulate innovation and job creation within the country. These tax breaks could be targeted at specific technologies, such as solar panel manufacturing or wind turbine development, to foster rapid growth in these sectors.
Investment Incentives and Subsidies
Government investment in clean energy research and development, coupled with supportive policies, can foster innovation and drive down costs. Subsidies for clean energy technologies, including renewable energy and energy efficiency measures, can make them more competitive with traditional energy sources.
- Targeted Research and Development Funds: Investing in research and development of key clean energy technologies, such as advanced battery storage or next-generation solar panels, can significantly accelerate the transition to a cleaner energy future. This would be a crucial step to drive down the cost of these technologies and make them more accessible.
- Renewable Energy Portfolio Standards (RPS): Mandating a certain percentage of electricity generation from renewable sources can create a stable market for clean energy and encourage investment in renewable energy infrastructure. This approach ensures a consistent demand for clean energy, facilitating investment and growth in the sector.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Implementing stricter energy efficiency standards for buildings and appliances can lead to substantial reductions in energy consumption. This reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers carbon emissions, making a positive impact on the environment.
Framework for Evaluating Policy Effectiveness
A comprehensive framework is needed to assess the impact of alternative policies on clean energy. This framework should include metrics for measuring the effectiveness of tariffs, investment incentives, and other policies. Data on clean energy sector growth, job creation, emissions reductions, and international trade patterns should be collected and analyzed.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Defining clear and measurable KPIs, such as the percentage increase in renewable energy capacity, the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, and the number of jobs created in the clean energy sector, is critical for evaluating the effectiveness of policies.
- Longitudinal Data Collection: Data collection over a substantial period will provide valuable insights into the long-term effects of alternative policies. This data should cover various aspects of the clean energy sector, including investment trends, technological advancements, and market dynamics.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing the performance of clean energy sectors in countries implementing alternative policies with those in countries with less supportive policies can provide valuable insights into the efficacy of various approaches.
Potential Impacts of Different Tariff Rates
The potential impacts of different tariff rates on clean energy sectors vary considerably. Lower tariffs can increase imports of clean energy technologies, stimulating competition and potentially driving down prices. Higher tariffs can protect domestic industries but might also limit access to advanced technologies and hinder innovation.
| Tariff Rate | Impact on Clean Energy Sectors |
|---|---|
| Low | Increased imports, potential price reductions, increased competition. |
| Medium | Modest impact on imports, potential for some price adjustments, and impact on domestic industries. |
| High | Reduced imports, potential for higher domestic prices, potentially slowing innovation. |
Long-Term Implications: Trump Tariffs Biggest Clean Energy Impacts
Trump’s tariffs on clean energy components, while seemingly short-term, have far-reaching consequences for the global clean energy landscape. These policies have impacted supply chains, investment decisions, and the development of innovative technologies. The long-term effects, though complex and nuanced, are likely to shape the global energy transition for years to come.The tariffs’ lasting effects extend beyond immediate price increases.
They have introduced uncertainty into the market, discouraging long-term investments in clean energy infrastructure and potentially shifting the global balance of power in the renewable energy sector. This shift will affect not only established industries but also emerging companies and research institutions, potentially hindering innovation and limiting the potential for future economic growth.
Changes in the Global Clean Energy Landscape
The imposition of tariffs has disrupted established international trade flows in clean energy components. This disruption has incentivized some companies to relocate manufacturing facilities closer to their consumer markets, potentially altering the global distribution of clean energy technologies. Furthermore, the tariffs have encouraged domestic manufacturing of some components, but this approach may not be economically sustainable in the long term, and it could increase the cost of energy for consumers.
Potential for Long-Term Economic Growth in Clean Energy
Despite the challenges, the clean energy sector has demonstrated remarkable resilience. The global push for decarbonization continues, with many governments implementing policies to support renewable energy sources. This sustained demand for clean energy, coupled with advancements in technology, suggests that the sector has the potential for substantial long-term economic growth. Examples include increased government subsidies and tax incentives for renewable energy, as well as the development of new energy storage technologies.
Impact on Technological Advancements
Tariffs can affect the pace and direction of technological innovation. By hindering the free flow of components and expertise, tariffs may slow down the development of new technologies and hinder the adoption of innovative solutions. This could delay the achievement of significant cost reductions and the widespread adoption of clean energy solutions. For example, the limitation of access to specialized equipment might impede the development of more efficient solar panels or wind turbines.
Visual Representation of Projected Trajectory
Imagine two lines on a graph, both starting at a similar point representing current clean energy adoption levels. The line representing the trajectory with tariffs would initially show a slight decrease in adoption rate, potentially followed by a plateau. This is due to increased costs and uncertainty in the market. The line representing the trajectory without tariffs would show a more gradual and steady increase in adoption, potentially driven by sustained innovation and investment.
The difference between the two lines would highlight the potential for lost progress and reduced market competitiveness due to the tariffs.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, Trump’s tariffs have left an undeniable mark on the clean energy landscape. From the effects on specific renewable energy sources to the broader impact on international trade relations, the consequences are far-reaching and complex. While the stated justifications for these tariffs were multifaceted, their impact on the clean energy industry has been substantial, affecting both supply chains and economic growth.
The potential for long-term economic growth in clean energy is contingent on a nuanced understanding of these policies and their potential consequences.

