UK public AI law poll reveals a fascinating interplay between public opinion and the development of AI regulations. This exploration delves into public perceptions of AI in the UK, examining different demographics and their varying levels of trust and concern. The poll reveals public attitudes towards AI applications in sectors like healthcare, finance, and transportation, highlighting common themes and anxieties about AI ethics and safety.
Furthermore, it explores public awareness of existing and proposed AI laws, pinpointing potential gaps and misconceptions.
The poll also scrutinizes public concerns regarding AI law implementation, categorizing anxieties and offering potential solutions. It investigates how public opinion has shaped current AI lawmaking, showcasing mechanisms for public feedback and engagement. The study also looks into future trends, predicting potential shifts in public opinion and the evolution of public concerns. Finally, it analyzes public sentiment towards specific AI applications in different sectors, such as healthcare and autonomous vehicles, and how these opinions have influenced policy discussions.
Public Perception of AI in the UK
Public opinion on artificial intelligence (AI) in the UK is complex and multifaceted, reflecting a range of concerns and hopes about its future impact. While some view AI as a powerful tool for progress, others harbour anxieties about its potential risks. Understanding these nuances is crucial for developing responsible AI policies and strategies.Public opinion polls consistently reveal a mixed public perception of AI, with some sectors demonstrating greater trust than others.
This reflects varying levels of public understanding and experience with different AI applications. Concerns about job displacement, ethical dilemmas, and the potential for misuse are frequently raised.
Public Opinion Polls and Demographics
Public opinion polls on AI in the UK reveal varied attitudes across different demographic groups. Age, educational attainment, and socioeconomic status often correlate with differing levels of trust and concern. Younger generations, often more familiar with AI technologies, may exhibit a more positive outlook, contrasting with older generations who might harbor more apprehension about the unknown. Similarly, individuals with higher levels of education may have a more nuanced understanding of AI capabilities, potentially leading to more balanced opinions.
Socioeconomic factors also play a role, with those facing potential job displacement often expressing greater concerns about AI’s impact on employment.
Public Trust and Concerns in Different Sectors
Public trust and concerns about AI vary significantly across different sectors. In healthcare, concerns about data privacy and algorithmic bias are often raised, while in finance, worries about fraud and security are prominent. The transportation sector, however, often sees AI as a means to enhance safety and efficiency, leading to more positive perceptions. These sector-specific differences highlight the need for tailored approaches to address public concerns and build trust in AI applications.
Themes and Patterns in Public Responses
Recurring themes emerge in public responses concerning AI ethics and safety. Concerns about job displacement, data privacy, and algorithmic bias frequently appear across various polls and surveys. The public often expresses a desire for transparency and accountability in AI systems, particularly when dealing with sensitive information or critical decisions. There is also a recurring interest in ensuring AI is developed and used ethically, addressing potential societal harms and biases.
These common themes provide valuable insights for policymakers and developers to address the public’s concerns.
The UK public AI law poll is fascinating, but it got me thinking about the practical implications for graduates. Finding sponsorship and mentorship opportunities is crucial for career advancement, and a great resource for this is the sponsorship mentorship jobs graduates essay. Ultimately, a well-defined AI legal framework in the UK is essential to guide these emerging opportunities and ensure fair practices for all.
Public Attitudes Towards AI
| Demographics | Concerns | Support Levels |
|---|---|---|
| Younger Generations (18-35) | Job displacement, lack of transparency, potential misuse | Higher support for AI applications in areas like entertainment and communication |
| Older Generations (55+) | Job displacement, lack of control over AI systems, ethical implications of AI use | Lower support for AI applications, especially in sensitive areas like healthcare and finance |
| Higher Education | Algorithmic bias, data security, ethical considerations | More nuanced views on AI, potentially greater support for AI in research and development |
| Lower Socioeconomic Status | Job displacement, fear of automation, lack of access to AI benefits | Lower support for AI applications that may directly impact employment |
| Healthcare | Data privacy, algorithmic bias, potential for errors in diagnoses | Moderate support, with concerns about patient safety and accountability |
| Finance | Fraud, security risks, potential for misuse of financial data | Mixed support, with concerns about the reliability and trustworthiness of AI systems |
| Transportation | Safety concerns, reliability of autonomous systems, job displacement | Higher support for AI applications in transportation, with a focus on enhanced safety and efficiency |
AI Law and Regulation in the UK
The UK’s approach to AI regulation is evolving rapidly, responding to the increasing complexity and societal impact of artificial intelligence. While there isn’t a single, comprehensive AI Act like some other jurisdictions, the UK’s strategy focuses on leveraging existing legislation and developing targeted policies to manage the risks and opportunities presented by AI. This approach seeks to strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring public safety and trust.The current UK framework for AI regulation draws from a range of existing laws, primarily those concerning data protection, consumer protection, and safety.
The government is actively exploring specific regulations to address the unique challenges posed by AI in various sectors. This proactive approach is intended to ensure the UK remains a global leader in AI development while safeguarding against potential harms.
Existing Legal Framework
The UK’s legal framework for AI is not explicitly focused on AI as a specific technology. Instead, existing laws and regulations are applied to AI systems as appropriate. This includes data protection laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which has significant implications for AI systems that process personal data. Further, consumer protection laws are also relevant to AI systems that impact consumers, and health and safety laws are pertinent to AI systems used in areas like manufacturing and healthcare.
These laws often serve as a basis for addressing potential issues raised by AI.
Comparison with Other Countries
The EU’s approach to AI regulation, with its proposed AI Act, is more comprehensive and explicitly addresses AI as a technology. The UK’s approach, while less prescriptive, focuses on a more sector-specific and adaptable regulatory strategy. This means that the UK aims to address specific issues as they arise, using a more nuanced and potentially faster method. While the EU’s comprehensive approach offers a clear set of rules, the UK’s targeted approach may allow for more rapid adaptation to evolving AI technologies and industry practices.
The UK public’s AI law poll reveals interesting trends, but it’s fascinating to consider how other historical events, like the potential Alcatraz Trump rebuild, an open prison island with judges and immigration costs, influence public opinion. This history highlights the complex interplay of public perception, political agendas, and the legal framework. Ultimately, these broader issues all contribute to the larger conversation around responsible AI development and implementation in the UK.
Potential Impact on Sectors
The impact of AI regulation on various sectors will be significant. For example, in healthcare, AI-powered diagnostic tools may be subject to new safety and accuracy standards. In finance, AI-driven algorithmic trading could be regulated to prevent market manipulation. Furthermore, the creative industries, such as filmmaking and music production, might experience changes in copyright and intellectual property laws as AI tools become more integrated into these fields.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Different Legal Frameworks
| Legal Framework | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| UK | Flexibility, adaptability to evolving technologies, potential for faster implementation of sector-specific regulations. | Potential lack of clarity and consistency across sectors, reliance on existing laws that may not fully address the unique characteristics of AI. |
| EU | Comprehensive approach, clear standards for AI systems, potential for harmonization of regulations across member states. | Potential for bureaucratic hurdles, slower implementation compared to the UK’s sector-specific approach, potential for overly restrictive measures that stifle innovation. |
Public Awareness of AI Law
Public perception of AI is evolving rapidly, but public awareness of the specific laws and regulations governing its development and use in the UK remains a crucial factor in successful implementation and ethical application. Understanding the public’s grasp of these regulations is essential for tailoring future policy and education initiatives. This understanding can reveal gaps in knowledge and misconceptions that may impede the public’s trust and participation in the AI landscape.Public awareness of AI law in the UK is uneven, with some understanding of broad principles but limited knowledge of the intricacies of specific legislation.
This lack of in-depth understanding can lead to misinterpretations of the intended purpose and scope of the regulations. It’s vital to address these knowledge gaps through targeted education and outreach programs.
Public Understanding of Key AI Concepts
The public’s understanding of fundamental AI concepts like bias, transparency, and accountability is a crucial precursor to understanding AI laws. While there may be a basic awareness of these concepts, the application of these ideas to specific legal frameworks is often not well-understood. This demonstrates the need for more accessible and engaging educational resources that explain these complex ideas in simpler terms.
Misconceptions and Gaps in Knowledge, Uk public ai law poll
Several misconceptions regarding AI law persist among the public. A common misconception is that existing regulations are insufficient to address the rapidly evolving nature of AI technologies. Furthermore, some believe AI laws are overly complex and difficult to understand, leading to a feeling of disconnect and alienation from the legal processes. Another misconception is that AI laws are primarily focused on regulating specific industries or sectors, rather than their broader societal implications.
Public Perception of Effectiveness and Clarity
Public perception of the effectiveness and clarity of UK AI laws is mixed. Some feel that the regulations are too vague or lack specific guidelines, while others believe they are comprehensive enough to address current challenges. A significant portion of the public may not fully understand how the laws interact with specific applications of AI, like facial recognition or autonomous vehicles.
This highlights the need for clearer, more accessible explanations of the legal frameworks.
Public Awareness Levels by Demographics
Public awareness of AI laws varies significantly across different demographics. This disparity underscores the importance of tailoring awareness campaigns to specific groups.
| Demographic Group | Awareness Level (Estimated) | Potential Reasons for Variation |
|---|---|---|
| Young Adults (18-25) | Moderate | Exposure to AI through social media and technology, potential interest in careers related to AI |
| Middle-Aged Adults (35-54) | Low | Less direct exposure to AI technologies in daily life, potential concerns about job displacement |
| Older Adults (65+) | Very Low | Limited experience with digital technologies, potential confusion about AI concepts |
| High-Income Earners | Moderate to High | Potential greater exposure to AI through work or personal interests |
| Low-Income Earners | Low | Potential lack of access to information or resources |
“Public understanding of AI law is a prerequisite for informed engagement and responsible development of the technology.”
Public Concerns Regarding AI Law
The burgeoning field of artificial intelligence (AI) presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. As AI systems become more integrated into our daily lives, the need for robust and well-defined legal frameworks becomes paramount. However, the public often harbors concerns about how these laws will be implemented and what impact they will have on their lives. These concerns warrant careful consideration and proactive engagement to ensure public trust and acceptance of AI regulation.
Public Anxiety Regarding Job Displacement
Public apprehension about AI’s potential impact on employment is substantial. The automation of tasks previously performed by humans, driven by AI algorithms, raises legitimate fears about job losses across various sectors. This concern isn’t theoretical; examples of companies automating tasks, leading to job reductions, are readily available.
The UK public’s views on AI law are fascinating, but it’s interesting to consider how different geopolitical issues might influence those opinions. For example, the recent ceasefire plan proposed by Ehud Barak and Trump, as detailed in this article , might subtly affect how people perceive the need for strong AI regulations. Ultimately, understanding the public’s take on AI law requires a nuanced perspective that considers a broader range of global factors.
- Concerns about the potential for mass unemployment are widespread, particularly among workers in industries where AI could easily automate tasks.
- The need for retraining and upskilling programs to adapt to the changing job market is recognized as crucial, but the public is uncertain about the extent to which existing initiatives will be sufficient to mitigate job displacement.
- The potential for AI to exacerbate existing inequalities in the labor market is a significant concern, particularly for lower-skilled workers. Existing biases in AI algorithms could potentially widen the gap between the highest-paid and lowest-paid workers.
Public Concerns Regarding Privacy and Security
The collection and use of personal data by AI systems are a major source of public concern. As AI systems learn from vast datasets of personal information, the potential for misuse and breaches of privacy is a serious concern.
| Category | Concern | Potential Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Privacy | Concerns about the collection, storage, and use of personal data by AI systems. The potential for misuse and breaches of privacy are real, particularly in cases where data security is lacking or where AI algorithms are not transparent. | Stronger data protection regulations, increased transparency about data usage, and robust security measures for AI systems are essential. |
| Security | Concerns about the security of AI systems themselves, particularly in critical infrastructure, including potential vulnerabilities to hacking or malicious attacks. The use of AI in security systems, for example, raises concerns about the potential for errors and bias in these systems. | Investment in cybersecurity for AI systems, rigorous testing and validation procedures, and the development of robust security protocols are critical. |
Public Anticipation of AI Law’s Impact on Daily Life
The public is curious about how AI laws will affect their everyday lives, and whether they will create an environment that is more or less secure. The introduction of AI laws often prompts speculation about the possible consequences. The public anticipates changes in everything from banking to healthcare to transportation.
- Concerns about the fairness and equity of AI systems in various sectors, including the justice system and financial services, are widespread.
- The potential for AI to create a more efficient and convenient society is balanced against the potential for misuse and unintended consequences.
- Public anticipation of AI law’s impact often focuses on practical concerns, such as how it will affect their access to services and products, the accuracy and reliability of AI-powered tools, and the protection of their personal data.
Public Input and Engagement with AI Lawmaking

Public opinion plays a crucial role in shaping AI law. Understanding public concerns and preferences is vital for developing effective and acceptable regulations. This section explores how public opinion polls inform AI lawmaking in the UK, the mechanisms for public feedback, and the process for public participation.Public perception surveys and polls provide valuable insights into public anxieties, expectations, and desired safeguards related to AI.
These data points inform policy decisions, ensuring that regulations address the most pressing public concerns and reflect the values of the citizenry. This proactive approach fosters public trust and legitimacy in the AI regulatory framework.
Mechanisms for Public Feedback
Public input is essential for creating effective and inclusive AI laws. Various avenues facilitate public feedback and engagement with the development of AI legislation. These channels allow individuals to express their views and concerns directly to lawmakers, shaping the trajectory of AI regulation.
- Public consultations: Formal consultations, often published on government websites, allow the public to submit written responses to proposed regulations or draft laws. These consultations are usually accompanied by detailed documents, outlining the background, rationale, and potential impacts of the proposed regulations. The process encourages a broad range of perspectives, encompassing diverse sectors and demographics, leading to a more nuanced understanding of the issues.
- Online platforms and surveys: Government agencies and independent organizations frequently utilize online platforms and surveys to gather public opinions. These digital tools provide convenient access for citizens to share their views and respond to questionnaires. The wide reach and accessibility of these online platforms allow for a significant volume of feedback.
- Public hearings and forums: Organised public hearings and forums provide a platform for public discussion and testimony. These events allow individuals and groups to directly engage with lawmakers, policymakers, and experts, allowing for a deeper exploration of the issues. These gatherings often feature presentations by AI experts, followed by open discussion and questions.
- Citizen advisory groups: Forming citizen advisory groups is a direct way to gather and incorporate public feedback into the AI lawmaking process. These groups are typically composed of members from diverse backgrounds, representing various societal viewpoints and interests. This participatory approach can be highly effective in generating a comprehensive understanding of the public’s concerns.
Detailed Procedure for Public Participation
A structured procedure facilitates public engagement in AI lawmaking processes. This ensures that public input is considered and incorporated systematically.
- Identifying the Need for Public Input: Government bodies and AI regulatory bodies assess whether public input is needed for a particular piece of legislation or regulation. This evaluation is crucial to determine the most appropriate method for public engagement.
- Developing a Consultation Plan: A clear plan outlining the scope, objectives, and duration of the public consultation process is essential. This plan must define the specific issues to be addressed and the desired outcomes.
- Disseminating Information: Ensuring that information regarding the proposed legislation or regulation reaches the public is crucial. This includes widely distributing relevant documents and details on the proposed regulations through various channels, including official websites, social media, and news outlets.
- Facilitating Public Feedback: Establishing various mechanisms for the public to submit their feedback, including online forms, email addresses, and designated postal addresses, is vital. The methods should be tailored to accessibility needs and cater to a broad spectrum of participants.
- Analyzing Public Feedback: Gathering, collating, and analyzing the submitted feedback is a critical step. This analysis helps policymakers identify key concerns, preferences, and priorities within the public. It’s important to ensure impartiality and avoid bias in the analysis.
- Incorporating Public Input: The feedback analysis informs policymakers in shaping the final legislation or regulation. Changes or adaptations are implemented based on public concerns and suggestions.
- Transparency and Communication: Publicly communicating the outcome of the consultation process and how public feedback was considered in the final decision is vital. This transparency fosters trust and legitimacy in the AI lawmaking process.
Prominent Examples of Public Engagement
Several initiatives demonstrate the importance of public engagement in AI lawmaking. These examples highlight how various stakeholders have been actively involved in shaping AI regulations.
- Government consultations on AI ethics and safety: Numerous consultations on AI ethics and safety have sought public input. These consultations demonstrate a commitment to including the public in the process of developing AI regulations.
- Industry initiatives on AI responsible development: Industry initiatives aimed at promoting responsible AI development often include public forums and workshops. These initiatives acknowledge the public’s interest in AI safety and ethics.
- Academic research on public perceptions of AI: Research initiatives focusing on public perceptions of AI contribute to a deeper understanding of public anxieties and expectations. This research is a crucial source of information for policy development.
Future Trends in Public Opinion and AI Law: Uk Public Ai Law Poll
The public’s understanding and acceptance of artificial intelligence (AI) are constantly evolving, impacting how they perceive AI-related laws and regulations. This dynamic relationship necessitates careful consideration of potential future shifts in public opinion, particularly as AI systems become more integrated into daily life. Anticipating these changes will be crucial in developing effective and sustainable AI legislation.Public concerns surrounding AI’s impact on jobs, privacy, and safety are likely to remain significant.
However, the specific nature of these concerns might evolve. As AI becomes more sophisticated and pervasive, new anxieties will emerge. The increasing automation of tasks could lead to a greater focus on the ethical implications of AI decision-making, potentially influencing public opinion regarding the need for clearer regulatory frameworks.
Potential Shifts in Public Opinion
Public opinion on AI and its associated laws is likely to shift in response to various factors, including technological advancements, public awareness campaigns, and real-world examples of AI’s impact. A key area of potential shift involves the perceived benefits of AI. Positive experiences with AI-powered tools in healthcare, education, or other sectors might lead to increased acceptance of its use and a willingness to embrace regulations.
Conversely, negative consequences, such as job displacement or algorithmic bias, could trigger a backlash, leading to more stringent regulatory demands.
Evolution of Public Concerns and Expectations
Public concerns regarding AI will likely evolve alongside technological advancements. Initial concerns about job displacement might give way to more nuanced concerns about the ethical implications of AI decision-making, algorithmic bias, and the potential for misuse. Increased awareness of AI’s impact on privacy and data security is expected, with a potential rise in the demand for robust data protection regulations.
The public will likely expect more transparency and accountability from AI systems and their developers.
The Anticipated Role of Public Input
Public input will play a critical role in shaping future AI law and regulation. The effectiveness of AI regulations hinges on public understanding and support. Active public engagement in consultations and debates will be vital in ensuring that AI laws reflect the public’s needs and concerns. This includes fostering dialogue between policymakers, technology developers, and the public.
Timeline of Potential Future Developments
| Year | Potential Development |
|---|---|
| 2024-2026 | Initial public debates about AI’s impact on jobs and economic inequality. Increased calls for regulatory frameworks to address bias and safety concerns. |
| 2027-2029 | Rise in awareness of AI’s impact on privacy and data security. Public demand for stronger data protection laws and regulations on data collection and usage. |
| 2030-2032 | Growing concerns about the ethical implications of AI decision-making. Emphasis on explainability and accountability for AI systems. |
| 2033-2035 | Potential for significant shifts in public opinion based on real-world examples of successful and unsuccessful AI deployments. A more nuanced understanding of the benefits and risks of AI. |
Public Opinion on Specific AI Applications
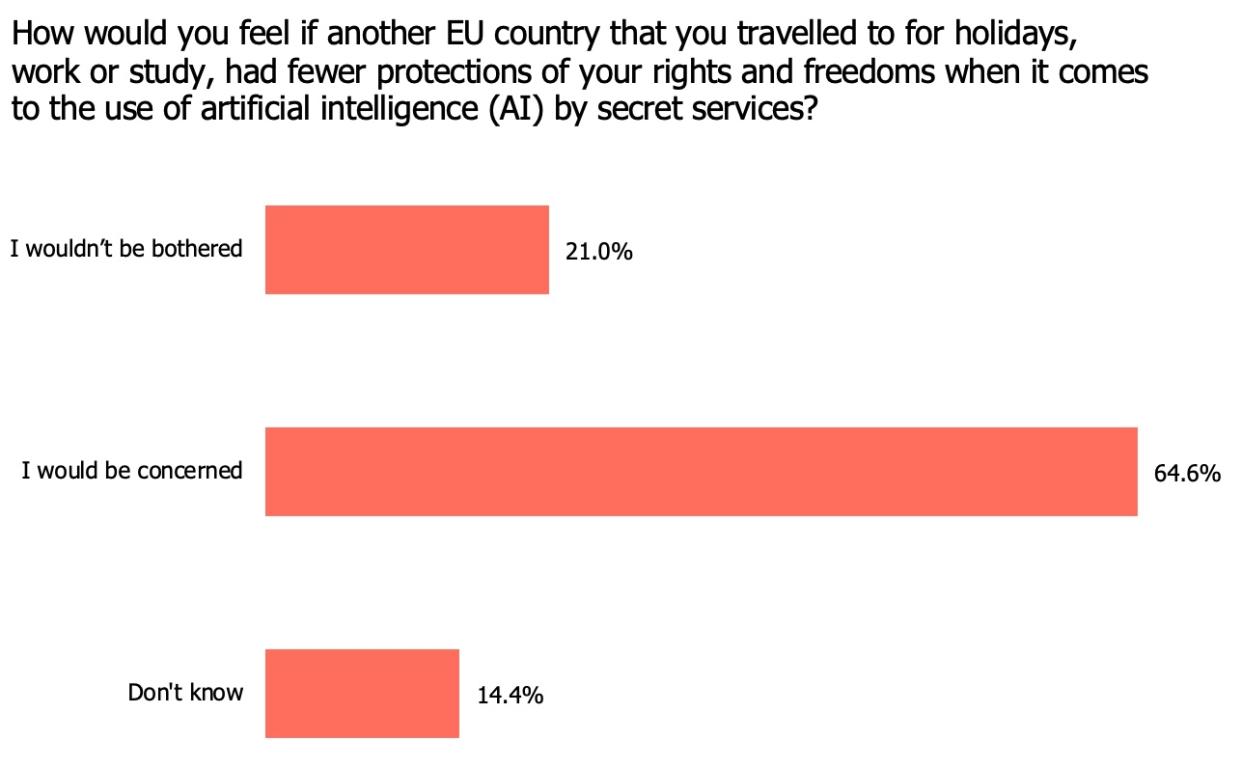
Public perception of AI is multifaceted and often shaped by the specific application. Concerns and hopes surrounding AI vary greatly depending on the sector in which it’s deployed. Understanding these nuanced perspectives is crucial for developing responsible AI policies.Public opinion polls reveal a complex relationship between the public and AI. While some applications evoke excitement and anticipation, others elicit apprehension and distrust.
This varied response necessitates a nuanced approach to AI regulation, one that considers public sentiment alongside technical feasibility and societal impact.
Public Sentiment on AI in Healthcare
Public opinion polls consistently demonstrate a high level of trust in AI’s potential to enhance healthcare. Patients and medical professionals alike recognize the potential for AI to accelerate diagnosis, personalize treatment plans, and improve overall efficiency. However, concerns about data privacy and the potential for algorithmic bias remain significant. For instance, studies suggest a willingness to accept AI-assisted diagnoses, provided that the system’s accuracy and transparency are rigorously demonstrated.
Public Opinion on Autonomous Vehicles
The public’s view on autonomous vehicles is often divided. While many recognize the potential for increased safety and efficiency, concerns persist regarding liability in case of accidents, the reliability of the systems, and the potential displacement of human drivers. Surveys have shown a correlation between public acceptance and the perceived safety and reliability of the technology. Furthermore, the perceived lack of human control in critical situations is a key factor shaping public opinion.
The increasing availability of real-world test cases and the implementation of robust safety protocols are vital in building public trust.
Public Opinion on AI in Finance
Public opinion on AI in finance is marked by a mix of optimism and apprehension. The potential for AI to improve fraud detection, personalize financial services, and automate tasks is widely acknowledged. However, concerns about financial security, data breaches, and the potential for algorithmic bias in loan approvals or investment recommendations are frequently raised. For example, public perception polls often highlight the need for greater transparency and accountability in AI-driven financial systems.
Comparison of Public Sentiment Towards Different AI Applications
| AI Application | Public Trust | Primary Concerns | Policy Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | High, but tempered by concerns about data privacy and bias | Data privacy, algorithmic bias, lack of transparency | Focus on explainable AI, robust data security measures, and ethical guidelines for AI use in healthcare |
| Autonomous Vehicles | Moderate, dependent on perceived safety and reliability | Liability in accidents, loss of human control, potential job displacement | Prioritize safety protocols, develop clear liability frameworks, and address public concerns about job displacement |
| Finance | Moderate, with concerns about financial security and algorithmic bias | Financial security, data breaches, potential for algorithmic bias | Implement strict security measures, ensure transparency in AI algorithms, and develop ethical guidelines for AI use in finance |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the UK public AI law poll provides a comprehensive snapshot of public sentiment surrounding AI law and regulation in the UK. The data collected reveals a complex picture of public opinion, ranging from support to concerns about the ethical implications and societal impact of AI. Understanding these perspectives is crucial for shaping future AI laws and regulations in a way that balances technological advancement with public needs and concerns.

