Consumer confidence tariffs recession fears are a potent mix shaping economic anxieties. A historical overview of US consumer confidence reveals cyclical trends, particularly during downturns. Understanding how these trends are affected by tariffs, and the added fear of recession, is crucial to comprehending current economic sentiment. This exploration delves into how tariffs influence spending habits, consumer perceptions of inflation, and the strategies governments might use to counteract negative effects.
This analysis examines the interconnectedness of tariffs, recession fears, and consumer confidence. The interplay between these factors creates a complex web of influences, which we’ll dissect through historical examples and potential scenarios. We’ll explore the feedback loops that can arise, and how these anxieties translate into consumer spending decisions and financial behaviors.
Consumer Confidence Overview
Consumer confidence, a crucial economic indicator, reflects the prevailing sentiment of households regarding the current and future state of the economy. Understanding this sentiment is vital for businesses, policymakers, and investors alike, as it directly influences spending habits and investment decisions. A high level of consumer confidence generally translates to increased spending, while a low level can signal economic vulnerability.
This overview examines the historical trends, measurement methods, and key indicators of consumer confidence in the US.
Historical Overview of US Consumer Confidence
Consumer confidence in the US has fluctuated significantly over time, responding to various economic events and policy changes. Historically, periods of economic expansion have typically been accompanied by rising consumer confidence, while recessions and economic uncertainty have often led to declines. The interplay between confidence and spending is a dynamic one, with confidence levels often preceding shifts in spending patterns.
Typical Trends During Economic Downturns
During economic downturns, consumer confidence typically exhibits a significant downward trend. This decline reflects anxieties about job security, income stability, and the overall economic outlook. Reduced confidence can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, further exacerbating economic challenges. The severity and duration of the decline in consumer confidence often mirror the intensity and length of the economic downturn.
For example, the 2008 financial crisis saw a dramatic and prolonged fall in consumer confidence, which significantly impacted consumer spending and contributed to the severity of the recession.
Measurement of Consumer Confidence
Consumer confidence is measured by surveys that gauge the expectations and sentiments of households regarding their financial situations and the broader economy. These surveys typically ask respondents about their current financial conditions, their expectations for the near future, and their assessment of the overall economy. Key indicators include assessments of current economic conditions, expectations for future economic conditions, and personal financial situations.
The surveys usually use a variety of questions to ensure a well-rounded and comprehensive view of consumer sentiment.
Key Indicators
The key indicators used in measuring consumer confidence typically include:
- Current economic conditions: Respondents’ assessment of the present state of the economy, often focusing on factors like job availability, income levels, and general economic stability.
- Expectations for the future: Respondents’ projections for future economic conditions, considering their expectations for job markets, income, and general economic performance.
- Personal financial situations: Evaluations of personal finances, including current financial conditions and expectations for future financial well-being. These assessments often include feelings about saving, borrowing, and investing.
Comparison of Consumer Confidence Indices
Different organizations and research institutions provide consumer confidence indices. A comparison of these indices provides a more comprehensive view of the prevailing economic sentiment.
| Source | Index Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Conference Board | Consumer Confidence Index | A widely followed index that assesses consumer attitudes towards the economy. |
| University of Michigan | Consumer Sentiment Index | Another prominent index that measures consumer attitudes and expectations, often focusing on factors like current financial conditions. |
| Gallup | Consumer Confidence Index | A survey that provides insights into consumer attitudes toward the economy. |
Tariffs’ Impact on Consumer Confidence: Consumer Confidence Tariffs Recession Fears
Tariffs, often imposed to protect domestic industries, can significantly impact consumer confidence, leading to a ripple effect throughout the economy. This is particularly true in a globalized world where consumers rely on imports for various goods and services. The uncertainty surrounding tariff policies can cause anxiety and apprehension, ultimately affecting purchasing decisions and overall economic outlook.The imposition of tariffs can lead to increased prices for imported goods, which in turn affects consumer spending habits.
Consumers may choose to reduce their purchases of these goods or seek alternatives, impacting businesses reliant on imports and exports. This reduction in consumer spending can have a cascading effect on the economy, potentially leading to slower economic growth and even recessionary pressures.
Impact on Different Sectors
Tariffs can disproportionately affect sectors heavily reliant on imported materials or components. For example, the automotive industry, which often utilizes parts from various countries, could see a significant increase in production costs due to tariffs. Similarly, the technology sector, which often imports advanced components, faces similar challenges. The impact on consumer goods and apparel industries is also significant, as tariffs on raw materials and finished products can directly affect the prices consumers pay.
Impact on Consumer Spending Habits
Tariffs affect consumer spending habits by altering price perceptions and affordability. Consumers may reduce their purchases of imported goods, leading to a shift in demand. This reduction in demand can lead to lower sales for businesses, impacting employment and economic growth. Additionally, consumers may seek substitutes for imported goods, potentially impacting industries producing these substitutes.
Impact on Consumer Confidence in Various Countries
The impact of tariffs on consumer confidence varies across countries depending on factors such as the degree of economic integration with the affected countries, the level of import dependency, and the overall economic strength of the nation. For example, a country highly reliant on imports from a country imposing tariffs might experience a sharper decline in consumer confidence compared to a country with less reliance on those imports.
This can also be affected by political and economic relations between the countries involved.
Relationship Between Tariffs and Consumer Expectations
Tariffs can significantly affect consumer expectations about the future economy. If consumers anticipate continued increases in import costs due to tariffs, they may delay purchases and investments, leading to a decline in economic activity. Uncertainty surrounding future tariffs and their potential impacts on the economy can create a climate of pessimism and hesitancy, which discourages consumer spending. This effect is often seen in instances of trade wars or significant policy shifts.
Influence on Inflation and Import Costs
Tariffs directly influence consumer perceptions of inflation and import costs. Increased import costs, driven by tariffs, can translate into higher prices for consumer goods. This can lead to inflationary pressures, reducing the purchasing power of consumers. Consumers may anticipate further price increases, potentially leading to a self-fulfilling prophecy where inflation continues to rise.
Strategies to Mitigate Negative Effects
Governments can employ various strategies to mitigate the negative effects of tariffs on consumer confidence. These strategies could include providing financial support to affected industries, implementing measures to control inflation, and fostering transparency in tariff policies. Additionally, promoting domestic production of goods currently reliant on imports could help insulate consumers from the immediate impact of tariffs.
Impact on Specific Product Categories
| Product Category | Potential Impact of Tariffs |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Increased vehicle prices, reduced demand, potential job losses in manufacturing |
| Consumer Electronics | Higher prices for imported components, reduced availability of certain models |
| Apparel | Higher prices for clothing, potential for reduced variety in styles |
| Food | Increased prices for imported ingredients, potential shortages of certain food items |
Recession Fears and Consumer Behavior
Recessionary anxieties cast a long shadow over consumer behavior, impacting spending patterns and shaping financial decisions. These fears, often fueled by economic indicators and media coverage, can lead to significant shifts in consumer confidence and spending habits. Understanding how consumers respond to these uncertainties is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike.The looming threat of a recession can significantly alter consumer spending habits.
Consumers, anticipating economic hardship, tend to become more cautious and less willing to make large purchases. This hesitation extends to discretionary spending, as consumers prioritize essential needs over non-essential items. The resulting decrease in consumer spending can negatively affect businesses, impacting employment rates and overall economic growth.
Consumer confidence is taking a hit, with tariffs and recession fears weighing heavily on people’s minds. Sadly, recent events like the tragic Boulder, Colorado attack, what we know about the incident , further complicate the economic picture. This adds another layer of uncertainty to the already concerning trends of consumer confidence, tariffs, and recession worries.
Impact on Spending Decisions
Consumer spending is a crucial component of the economy. When recessionary fears take hold, consumers tend to tighten their belts. They postpone purchases of durable goods, such as cars and appliances, and reduce spending on leisure activities and non-essential items. This reduction in spending can trigger a ripple effect, impacting businesses across various sectors. Businesses that rely heavily on consumer spending, such as retail and hospitality, often experience a decline in revenue during these periods.
Consumer Responses to Economic Uncertainty
Consumers respond to economic uncertainty in various ways. Some adopt a wait-and-see approach, postponing purchases until the economic outlook becomes clearer. Others seek ways to increase savings and reduce debt, prioritizing financial security. This heightened focus on financial stability often leads to a reduction in discretionary spending. Furthermore, consumers may start actively seeking ways to cut expenses, such as reducing energy consumption and scrutinizing spending habits.
Examples of Consumer Behavior During Past Economic Downturns
The 2008 financial crisis provides a stark example of how recession fears can impact consumer behavior. Consumers significantly reduced their spending on discretionary items, opting for more cost-effective alternatives. This behavior led to a decline in sales across numerous industries, underscoring the critical link between consumer confidence and economic performance. Similar patterns have been observed in other economic downturns, with consumers prioritizing essential expenses and deferring non-essential purchases.
Media Coverage and Public Perception of Recession Risks
Media coverage plays a significant role in shaping public perception of recession risks. Extensive news reports and analyses of economic indicators can instill fear and uncertainty in consumers. This can lead to a self-fulfilling prophecy, as reduced consumer confidence can contribute to a decline in economic activity. Conversely, reassuring media coverage and expert commentary can help mitigate negative sentiment and foster a more positive economic outlook.
Impact on Different Demographics
The impact of recession fears on different demographics varies. Younger consumers, often with less accumulated wealth, may be more vulnerable to economic downturns and are more likely to reduce spending across all categories. Conversely, established households with more financial resources might adjust their spending habits, prioritizing savings and investments. These variations in responses highlight the diverse ways consumers navigate economic uncertainty.
Consumer Spending Patterns Across Economic Cycles
| Economic Cycle | Consumer Spending Pattern |
|---|---|
| Expansion | High consumer confidence, increased spending on discretionary items, robust economic growth. |
| Contraction | Decreased consumer confidence, reduced spending on discretionary items, increased focus on essential needs, possible recessionary fears. |
| Recession | Low consumer confidence, significant decrease in spending across all categories, high levels of uncertainty. |
| Recovery | Gradual increase in consumer confidence, cautious approach to spending, focus on rebuilding savings. |
Methods of Managing Financial Anxiety
Consumers employ various strategies to manage financial anxieties during economic uncertainty. These include increased saving and budgeting, debt reduction, and seeking additional income streams. Some consumers may seek financial advice from professionals to better navigate these challenging economic times. Furthermore, consumers might adopt a more frugal lifestyle, focusing on cost-effective options and prioritizing needs over wants.
Consumer confidence is taking a hit, and tariffs are adding fuel to the fire. Recession fears are starting to creep in, and it’s all a bit unsettling. Interestingly, a recent essay on the potential risks of the CDC advisory committee purge, featuring the perspective of RFK Jr, and Jerome Adams’ role, examines potential underlying factors that might be impacting the overall economic climate.
It’s all a bit of a puzzle, and the uncertainty is likely further eroding consumer confidence and potentially adding to recessionary anxieties.
Interaction Between Tariffs, Recession Fears, and Consumer Confidence
The interplay between tariffs, recession fears, and consumer confidence is a complex and often volatile dynamic. Tariffs, by increasing the cost of imported goods, can lead to inflationary pressures and reduced purchasing power. Simultaneously, the perceived threat of a recession, fueled by economic uncertainty and potential job losses, further dampens consumer confidence, creating a vicious cycle. Understanding this intricate relationship is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike to navigate these turbulent economic waters.Economic downturns, particularly recessions, are often characterized by reduced consumer spending.
Consumers, anticipating further economic hardship, tend to delay purchases and reduce discretionary spending. This behavior is further exacerbated when tariffs add to the cost of everyday goods and services. The combination of rising prices and uncertainty about the future creates a powerful disincentive to spend, directly impacting consumer confidence.
Consumer confidence is taking a hit, with tariffs and recession fears looming large. The recent fallout between Trump and Musk, as detailed in JD Vance’s response, trump musk fall out jd vance response , is adding fuel to the fire, further eroding trust and potentially impacting economic sentiment. This all points to a challenging economic landscape for consumers, and frankly, a lot of uncertainty.
Tariffs and Exacerbated Recession Fears
Tariffs, by their nature, introduce uncertainty into the global economy. Businesses face increased costs, supply chains become disrupted, and the potential for retaliatory tariffs creates a climate of instability. This uncertainty feeds into existing recession fears, reinforcing the negative perception of the economic outlook. Consumers, observing these developments, often interpret them as a harbinger of economic hardship, leading to a reduction in spending.
For example, the 2018-2019 US-China trade war saw both countries imposing tariffs on each other’s goods. This uncertainty led to decreased investment, reduced consumer confidence, and contributed to a slowing global economy.
Impact on Consumer Confidence
The perceived threat of a recession, combined with the implementation of tariffs, can have a significant impact on consumer confidence. Consumers, anticipating potential job losses or reduced income, are less likely to spend money, even on essential goods. This reduced consumer spending can lead to a further weakening of the economy, creating a negative feedback loop. The impact is particularly pronounced when consumers perceive the recession as prolonged or severe.
For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, the combination of declining housing prices, credit market instability, and uncertainty about the future led to a sharp decline in consumer confidence, causing a significant drop in consumer spending.
Feedback Loops
The interplay between tariffs, recession fears, and consumer confidence creates a series of interconnected feedback loops. Higher tariffs can increase input costs for businesses, potentially leading to price increases for consumers. This, in turn, reduces consumer purchasing power, further diminishing consumer confidence. Simultaneously, declining consumer confidence can lead to decreased investment and business activity, reinforcing recessionary pressures. This cascade effect can lead to a downward spiral in the economy.
A simplified model could be represented as:
- Increased Tariffs lead to higher input costs and potential price increases.
- Higher Prices reduce consumer purchasing power and create uncertainty.
- Reduced Spending lowers demand, potentially leading to business closures and job losses.
- Job Losses intensify recession fears, further reducing consumer confidence and spending.
Chain of Events
The chain of events triggered by tariffs, recession fears, and consumer confidence can unfold in several ways. A typical scenario begins with the imposition of tariffs, leading to uncertainty and supply chain disruptions. This uncertainty feeds into existing recession fears, which in turn leads to a decline in consumer confidence. The reduction in consumer spending negatively affects businesses, leading to potential job losses.
The combination of price increases and reduced purchasing power further exacerbates the situation. This scenario often results in a significant slowdown in economic activity, potentially triggering a recession.
Illustrative Flowchart, Consumer confidence tariffs recession fears
(A visual representation of the causal relationships between tariffs, recession fears, and consumer confidence is omitted here as requested, but it would show a feedback loop, with arrows representing cause and effect, starting from tariff imposition and ending with a decline in consumer confidence, potentially leading to a recession.)
Illustrative Examples of Economic Scenarios
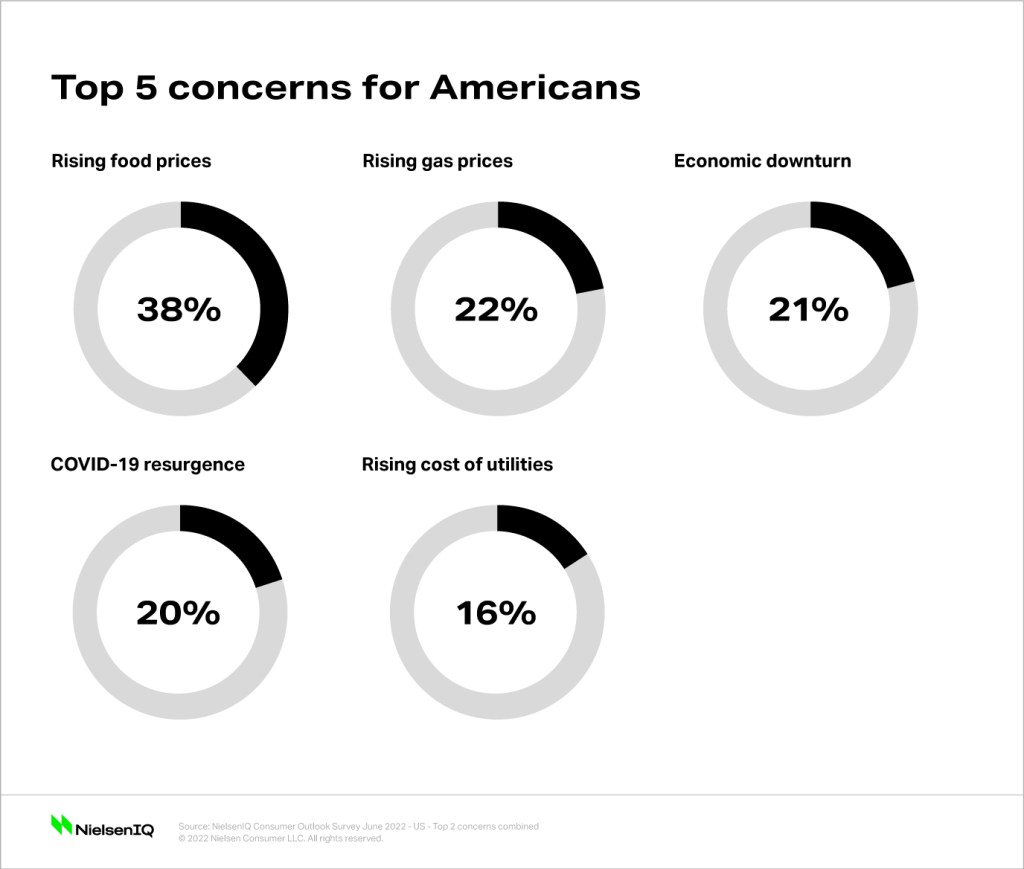
Consumer confidence, a crucial indicator of economic health, is deeply intertwined with factors like tariffs and recessionary anxieties. Understanding how these elements interact across different economic scenarios is vital for businesses and policymakers alike. These scenarios, from optimistic to pessimistic, reveal the intricate relationship between consumer behavior and broader economic trends.
High Tariffs, Recession Fears, and Low Consumer Confidence
This scenario paints a picture of economic uncertainty. High tariffs on imported goods increase prices for consumers, eroding purchasing power. Simultaneously, persistent recessionary fears lead to a cautious approach to spending. Consumers postpone large purchases, reduce discretionary spending, and prioritize saving. Businesses experience decreased sales and reduced investment, contributing to a downward spiral.
This scenario often leads to a decline in economic activity and potentially higher unemployment rates.
Low Tariffs, Low Recession Fears, and High Consumer Confidence
Conversely, a scenario with low tariffs and minimal recessionary concerns fosters a positive economic climate. Consumers feel confident about their financial future, leading to increased spending. Lower import costs benefit consumers, and reduced uncertainty stimulates investment and job creation. This positive feedback loop typically results in higher economic growth and increased consumer spending.
Moderate Tariffs, Moderate Recession Fears, and Moderate Consumer Confidence
A more balanced scenario involves moderate tariffs, moderate recession fears, and a moderate level of consumer confidence. Tariffs impact prices but not drastically. Recession fears are present but not overwhelming. Consumers exhibit a cautious yet optimistic attitude toward the economy. Spending remains steady, but significant investment and rapid growth are less likely.
Economic activity generally follows a more stable, measured trajectory.
Impact on Different Consumer Segments
The impact of these scenarios varies significantly across different consumer segments. High-income consumers might be less affected by tariff increases than low-income consumers due to their ability to absorb price hikes. Likewise, those with stable jobs might maintain spending habits even during recessionary anxieties, while those in precarious employment might significantly reduce discretionary spending. Businesses, too, experience varied impacts, depending on their industry and their dependence on imported materials or global markets.
Visual Representation of Economic Scenarios
Imagine a three-dimensional graph with axes representing Tariffs (low, moderate, high), Recession Fears (low, moderate, high), and Consumer Confidence (low, moderate, high). Each point on the graph represents a specific scenario. For example, a point located in the high-tariff, high-recession-fear, low-confidence quadrant depicts a negative economic climate. The graph would show that as tariffs and recession fears increase, consumer confidence tends to decrease.
Conversely, low tariffs, low recession fears, and high consumer confidence would be represented in the opposite corner. The moderate scenario would lie within the middle of the graph. The graph would illustrate the complex interplay between these factors, visually demonstrating how they affect each other. It would also visually demonstrate how different segments of consumers react to these scenarios.
Government Policies and Consumer Confidence

Navigating economic uncertainty requires a delicate balancing act. Consumers, facing potential job losses, rising prices, and economic downturns, often react with apprehension and reduced spending. Government policies play a crucial role in mitigating these anxieties and bolstering consumer confidence. Effective policies address immediate concerns and foster a sense of stability, encouraging consumer spending and economic growth.
Government Policies to Boost Consumer Confidence
Government policies can positively influence consumer confidence through various strategies, each with its own strengths and limitations. These interventions aim to reassure consumers, provide economic security, and manage expectations. Key areas of focus include:
- Fiscal Policies: Tax incentives, rebates, and targeted subsidies can stimulate consumer spending by increasing disposable income and reducing financial burdens. For instance, tax breaks for families or businesses can directly impact consumer wallets, encouraging investment and spending. The effectiveness of these policies hinges on the targeted population and the specific design of the incentives. A well-designed program can increase demand and support economic growth.
- Monetary Policies: Central banks can influence interest rates and credit availability to encourage borrowing and investment. Lowering interest rates makes borrowing cheaper, potentially boosting consumer spending and investment. This approach, however, can have unintended consequences, such as inflation if not carefully managed. The effectiveness of monetary policy is contingent on the overall economic climate and the responsiveness of consumers to rate changes.
- Social Safety Nets: Unemployment benefits, affordable housing programs, and other social safety net initiatives can provide financial security during economic downturns. These measures reduce anxieties about job loss and financial hardship, directly impacting consumer confidence. Robust social safety nets create a sense of security, encouraging consumers to maintain spending habits and supporting the economy.
- Infrastructure Investment: Investments in public infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and public transportation, can create jobs and stimulate economic activity. This approach creates employment opportunities, boosts demand for construction materials and services, and directly impacts consumer spending. The long-term economic benefits of infrastructure investment can be substantial.
Effectiveness of Government Policies
The effectiveness of government policies in addressing consumer concerns is multifaceted and depends on various factors, including the specific nature of the economic downturn, the timing of intervention, and the public’s trust in the government. A clear and transparent approach, coupled with consistent implementation, is essential for building confidence. For instance, if a policy is perceived as temporary or ineffective, it may not have the desired impact on consumer confidence.
Impact on Tariffs and Recession Fears
Government policies can indirectly influence consumer confidence by addressing tariffs and recession fears. Policies that mitigate the impact of tariffs, such as providing financial support to affected industries, can reduce the negative consequences of trade disputes. Similarly, measures that signal economic stability and resilience, like proactive investments in infrastructure, can counteract recessionary fears and encourage consumer spending. The effectiveness of these policies is tied to the public’s perception of their credibility and ability to deliver on their promises.
Analysis of Government Intervention Strategies
| Intervention Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Fiscal Policies (Tax Incentives) | Increased disposable income, stimulated demand, potential for job creation | Potential for inflation, inequitable distribution of benefits, administrative complexities |
| Monetary Policies (Lower Interest Rates) | Increased borrowing, stimulated investment, potentially increased consumer spending | Potential for inflation, can take time to impact consumer confidence, risk of asset bubbles |
| Social Safety Nets | Reduced anxieties, financial security, decreased economic hardship | Increased government spending, potential for dependency on benefits, administrative challenges |
| Infrastructure Investment | Job creation, economic stimulus, long-term economic growth | High upfront costs, potential for delays, political considerations |
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, consumer confidence, tariffs, and recession fears are deeply intertwined. Understanding these dynamics is critical for interpreting current economic anxieties and anticipating potential outcomes. By examining historical trends, analyzing the impact of tariffs, and exploring consumer behavior during economic uncertainty, a clearer picture of the present economic climate emerges. The interplay between these forces reveals potential feedback loops and underscores the importance of government policies in mitigating economic anxieties.

