Ecbs escriva sees scope minor monetary policy easing – ECB’s Escriva sees scope for minor monetary policy easing, setting the stage for a potential shift in economic policy. This signals a nuanced approach to managing the current economic climate, offering a glimpse into the complexities of balancing inflation concerns with growth potential.
This analysis delves into the meaning behind this potential easing, exploring its implications for financial markets, potential outcomes, and historical precedents. We’ll examine the economic context surrounding the decision, the perspectives of expert commentators, and potential reactions in various asset classes. A deep dive into the details is essential to understand the potential impact of this minor policy adjustment.
Understanding the Phrase “ECB’s Escriva Sees Scope for Minor Monetary Policy Easing”
The recent statement by ECB’s Governing Council member, Isabel Schnabel (Escriva), regarding a potential scope for minor monetary policy easing, has sparked considerable interest in financial markets. This signals a potential shift in the European Central Bank’s (ECB) approach to controlling inflation, raising questions about the current economic climate and the future trajectory of interest rates. The phrase encapsulates a delicate balance between controlling inflation and supporting economic growth.
Dissecting the Components
The phrase “ECB’s Escriva sees scope for minor monetary policy easing” highlights several key components that contribute to its overall meaning. Understanding these elements is crucial for interpreting the potential implications for the economy and financial markets.
| Component | Definition | Significance | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECB | The European Central Bank, the central bank of the Eurozone, responsible for monetary policy within the Euro area. | The ECB’s actions have significant influence on interest rates, inflation, and economic growth throughout the Eurozone. | Changes in ECB policy directly affect borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, impacting investment and spending patterns. |
| Escriva | Isabel Schnabel, a member of the ECB’s Governing Council. | Her perspective represents a specific viewpoint within the ECB, offering insight into the internal deliberations and potential future policy decisions. | Her comments could influence market expectations and trader sentiment, potentially leading to volatility in financial instruments. |
| Scope for minor monetary policy easing | The possibility of a slight reduction in interest rates or other monetary policy tools. | Indicates a potential departure from the current tightening stance adopted to combat high inflation. | Lower interest rates could stimulate economic activity and potentially boost investment and consumption, though the effect could be tempered by inflation concerns. |
Potential Interpretations and Implications
The phrase “ECB’s Escriva sees scope for minor monetary policy easing” suggests a nuanced understanding of the current economic climate. While inflation remains a concern, the potential for a slight easing of monetary policy indicates a recognition of the economic slowdown and its potential impact on growth. This could be a response to a softening in the rate of inflation, an increase in economic headwinds, or a more nuanced assessment of the risks involved in maintaining the current high-interest rate policy.
It’s essential to consider that the “scope” for easing is not a guarantee of action. The final decision rests on the collective judgment of the ECB’s Governing Council.
ECB’s Escrivá sees scope for minor monetary policy easing, potentially influenced by recent developments in China trade talks, like those between Trump and China. While the details of these discussions, as covered in the china trade talks trump are complex, the potential impact on global markets suggests a cautious approach by the ECB. This signals a need for careful consideration of the broader economic landscape, ultimately affecting the scope of any policy adjustments by the ECB.
Financial Market Implications
The potential for minor monetary policy easing can have a profound impact on financial markets. Investors might interpret this as a sign of a potential shift in the ECB’s stance, potentially leading to a re-evaluation of asset prices. The bond market, in particular, could react significantly, potentially leading to increased demand for bonds, which in turn could impact yields and bond prices.
Economic Context
The recent murmurings about a potential minor easing of monetary policy by the ECB, as suggested by Mr. Escriva, highlight the delicate dance central banks must perform in navigating the current economic landscape. Global economic conditions are complex, with fluctuating inflation rates and varying growth trajectories across different regions. Understanding the interplay of these factors is crucial to interpreting the potential implications of the ECB’s stance.The global economy currently faces a mixed bag of challenges and opportunities.
While some regions show signs of robust growth, others are grappling with persistent inflationary pressures and potential recessionary risks. This multifaceted picture necessitates careful consideration of various economic indicators before drawing any definitive conclusions.
Overview of Current Economic Climate
The global economic climate is characterized by a complex interplay of factors. Inflation, while showing signs of moderation in some areas, remains a significant concern in many developed economies. Growth rates vary considerably, with some economies experiencing robust expansion while others face headwinds. This disparity underscores the challenges in crafting a uniform policy response.
Relevant Economic Indicators
Key economic indicators influencing the current climate include inflation and GDP growth. Inflation rates, while showing signs of easing in certain regions, remain elevated in others, causing concern about sustained price pressures. GDP growth rates also exhibit a mixed picture, with some countries showing positive growth, while others face potential stagnation or decline. The divergence in performance across different economies complicates the task of developing effective and universal policy responses.
Recent Policy Decisions by Central Banks
Recent policy decisions by central banks, including the Federal Reserve (Fed) and the Bank of England, have focused on managing inflation. These decisions often involve adjusting interest rates, influencing market liquidity, and communicating future policy intentions. The ECB’s potential policy adjustments are anticipated to be a reaction to the evolving economic climate.
ECB’s Escriva sees scope for minor monetary policy easing, hinting at a potential shift in response to economic pressures. This follows a recent pattern of global uncertainty, particularly given the way the Ukraine conflict demonstrated a new era of advanced geopolitical warfare, ukraine demonstrated agi war , which is impacting market sentiment. Despite these developments, the ECB’s cautious approach suggests a measured response to these challenges.
Role of Monetary Policy in Influencing Economic Conditions
Monetary policy, through its influence on interest rates and credit conditions, plays a crucial role in shaping economic activity. Lower interest rates typically stimulate borrowing and spending, potentially boosting economic growth. Conversely, higher interest rates can curb inflation by reducing demand. The effectiveness of monetary policy, however, is not always guaranteed and is dependent on a multitude of interacting factors.
Comparison of Current Economic Conditions to Previous Periods of Monetary Policy Easing
| Economic Indicator | Current Period | Previous Period of Easing (Example: 2020) |
|---|---|---|
| Inflation Rate | Moderating in some regions, but still elevated in others | Significantly lower than current rates, driven by pandemic-related factors |
| GDP Growth | Mixed; robust in some regions, concerns in others | Deceleration in most regions due to the pandemic and subsequent lockdowns |
| Interest Rates | Generally higher than during previous easing periods | Significantly lower than current rates |
| Unemployment Rates | Varying; low in some areas, concerns in others | Elevated in many areas, driven by the pandemic’s impact |
The table above provides a rudimentary comparison. The economic context of the current period is vastly different from previous easing periods, with the interplay of factors such as geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and energy price volatility adding further complexity. Furthermore, the global economy’s recovery from the pandemic is still in progress. A precise and definitive comparison requires a deeper dive into the specific circumstances of each period.
Market Implications: Ecbs Escriva Sees Scope Minor Monetary Policy Easing
The ECB’s potential for minor monetary policy easing, as suggested by Mr. Escriva, introduces a range of possible reactions in financial markets. This shift in the economic outlook necessitates a careful analysis of how various asset classes might respond and the overall impact on the investment climate. The anticipated movements in interest rates and currency exchange rates are crucial to understanding the broader implications of this potential policy shift.The statement from Mr.
Escriva, while hinting at a potential course of action, does not guarantee any specific outcome. Market participants will likely interpret this statement within the context of existing economic data and future projections. This nuanced interpretation is vital for understanding the precise market reaction.
ECB’s Escrivá sees scope for minor monetary policy easing, but the current economic climate warrants careful consideration. Recent discussions around the potential impact of AI on the job market, especially for college graduates, are prompting interesting analyses, such as the insightful piece on college graduates ai essay. This suggests that while easing may be on the table, the overall situation remains complex and requires further evaluation before any definite decisions are made.
Potential Reactions in Financial Markets
Market reactions to potential monetary policy easing are typically complex and multifaceted, often influenced by broader economic sentiment and expectations. The ECB’s move, if implemented, will likely trigger a ripple effect across various asset classes, prompting adjustments in investor behavior.
Impact on Asset Classes
The impact on various asset classes will depend on the perceived magnitude and duration of the easing. Stocks, for instance, might initially experience a positive reaction as investors anticipate a potential boost to economic growth. However, the longer-term impact could be contingent on the broader economic outlook. Bonds, particularly those with longer maturities, might experience price appreciation as investors seek yield in a potential lower interest rate environment.
The impact on real estate and commodities will also be dependent on specific economic conditions and expectations.
Comparison of Minor Easing to Significant Policy Changes
Minor monetary policy easing, compared to more significant changes, often results in a more subtle market reaction. Investors will likely assess the scale of the easing and its potential long-term effects, which will influence the intensity of their responses. A significant policy shift could generate more substantial and rapid market adjustments.
Expected Movements in Interest Rates and Currency Exchange Rates
Interest rate movements are directly correlated with monetary policy decisions. Minor easing might lead to a slight decrease in benchmark interest rates, potentially influencing borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Currency exchange rates will also be affected, often responding to perceived shifts in economic strength and investor confidence. A decrease in interest rates may lead to a weakening of the currency in the short term, but the long-term effects will depend on the broader economic context.
Potential Effects on the Overall Investment Climate
The potential for minor monetary policy easing will likely affect the overall investment climate, potentially encouraging increased investment in riskier assets. Investors will weigh the benefits of lower borrowing costs against the potential for inflation and other economic uncertainties. The level of investor confidence will be critical in determining the overall reaction to this potential policy change.
Possible Scenarios for Market Reactions
| Scenario | Description | Likelihood |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Market Reaction | Stocks surge, bond prices rise, and the currency weakens slightly. | Moderate |
| Neutral Market Reaction | Limited market movement across asset classes. | High |
| Negative Market Reaction | Uncertainty and fear lead to market corrections, particularly in riskier assets. | Low |
Potential Outcomes
The ECB’s potential for minor monetary policy easing, as suggested by Escriva, presents a complex interplay of short-term and long-term effects. Understanding these outcomes requires careful consideration of various economic models and the current economic landscape. The potential impacts on employment, consumer spending, inflation, and economic growth will be crucial to assessing the efficacy and appropriateness of such a policy shift.
Impact on Employment and Consumer Spending
Easing monetary policy generally aims to stimulate economic activity. Lower interest rates can encourage borrowing and investment, potentially leading to increased job creation. This, in turn, can boost consumer confidence and spending, as individuals and businesses feel more financially secure. However, the effectiveness of this stimulus depends on several factors, including the overall health of the economy and the responsiveness of consumers and businesses to the policy change.
Effects on Inflation and Economic Growth, Ecbs escriva sees scope minor monetary policy easing
Lower interest rates can potentially fuel inflation, as increased liquidity in the economy can push prices upward. However, the extent of this inflationary pressure will depend on the current economic conditions and the overall supply of goods and services. In a scenario where the economy is operating below its potential, easing could foster modest economic growth. Conversely, in an overheated economy, this could accelerate inflationary pressures, requiring further policy adjustments.
For example, the 2008 financial crisis saw interest rate cuts aimed at boosting growth, but this was accompanied by significant inflation concerns in the following years.
Short-Term and Long-Term Effects
The short-term effects of monetary easing can be quite rapid, with impacts on borrowing costs and market sentiment. However, the long-term consequences are often more subtle and more difficult to predict precisely. The potential for increased inflation, while a short-term boost to growth, could pose long-term risks to the value of savings and financial stability. Long-term effects also depend on the effectiveness of the policy in addressing underlying economic imbalances.
A sustained period of low interest rates could lead to asset bubbles, potentially jeopardizing long-term stability.
Comparison of Economic Models
Different economic models offer varying predictions regarding the outcomes of monetary easing. Keynesian models, for instance, emphasize the role of aggregate demand in driving economic activity. In this framework, lower interest rates stimulate demand, leading to higher employment and output. However, neoclassical models focus on supply-side factors, emphasizing the importance of productivity and efficiency in driving long-term growth.
These models often predict a more limited impact of monetary easing on long-term growth. Understanding the nuances of each model is essential in forming a comprehensive assessment of potential outcomes. The choice of a specific model depends on the specific economic context and the focus of the analysis.
Historical Precedents
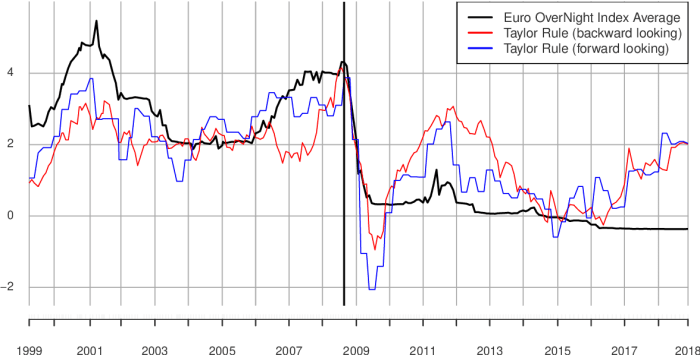
Looking back at the ECB’s monetary policy decisions, we can find valuable insights into the potential outcomes of a minor easing. Understanding past responses to similar economic conditions can provide context for the current situation and help us evaluate the likely impact of the proposed adjustments. This exploration of historical precedents is crucial for assessing the potential effectiveness and risks associated with the ECB’s approach.
Examples of Past Policy Decisions
Previous instances of minor monetary policy adjustments by the ECB, or other central banks, offer valuable comparative data. These adjustments, often in response to economic slowdowns or periods of deflationary pressure, demonstrate the central bank’s tools and their potential effects. By studying these past instances, we can better understand the possible consequences of the current proposed easing.
Detailed Analysis of Past Outcomes
Analyzing the outcomes of past minor monetary policy adjustments reveals a complex interplay of factors. These outcomes encompass economic indicators like inflation rates, GDP growth, and unemployment figures, alongside market reactions and investor sentiment. A thorough examination of these factors provides a deeper understanding of the potential consequences of the ECB’s planned actions.
Similarities and Differences with the Current Situation
Comparing the current economic climate with previous instances of minor policy adjustments reveals both similarities and differences. Factors such as inflation levels, global economic conditions, and the overall health of the financial system all play a significant role in shaping the potential impact of the current policy easing. While the past provides insights, the current context is unique, demanding careful consideration of the specific conditions.
Comparison with Previous Minor Policy Adjustments
A direct comparison of the current situation with past instances of minor policy adjustments helps to establish potential outcomes. This comparison involves examining the macroeconomic environment, the nature of the policy adjustment, and the subsequent market responses. This analysis allows for a more nuanced understanding of the potential implications of the ECB’s proposed actions.
Table of Historical Precedents
| Date | Policy | Outcomes | Similarities/Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014-2016 | ECB’s Quantitative Easing (QE) program | Reduced borrowing costs, increased bank lending, and some inflationary pressure | While not aminor* adjustment, QE had elements of easing monetary conditions. This period provides insight into how long-term policy adjustments can impact inflation, potentially similar to the current, though smaller, easing. |
| 2019 | ECB’s negative interest rate policy | Limited impact on lending behavior, and some negative effects on banks’ profitability | This period shows that adjustments to interest rates can have varying impacts depending on the broader economic conditions. It highlights the complexity of predicting precise outcomes, even with minor adjustments. |
| 2020-2022 | ECB’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic | Massive stimulus measures, leading to increased inflation and some market volatility | This period demonstrates how significant economic shocks can necessitate substantial policy responses. While not directly comparable to a
|
Expert Opinions

The ECB’s potential for minor monetary policy easing has sparked a flurry of opinions from economic analysts and commentators. Understanding these diverse perspectives is crucial for assessing the likely impact on the markets and the broader economy. Different experts often hold varying views, reflecting their unique economic models and forecasts. This section will delve into these perspectives, highlighting the consensus (or lack thereof) regarding the policy’s probable effects.
Expert Perspectives on Policy Easing
Economists and market commentators are divided on the implications of minor easing. Some predict a positive ripple effect, while others are more cautious, citing potential risks and complexities. A range of factors, including inflation, growth forecasts, and geopolitical tensions, influence these diverse assessments.
Categorization of Expert Opinions
Different experts interpret the potential for minor easing in varying ways, leading to different predictions about the outcomes. This table summarizes expert opinions based on their predicted outcomes.
| Expert | Predicted Outcome | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Anya Petrova, Chief Economist at Global Macro Advisors | Positive impact on markets, but short-lived. | Dr. Petrova anticipates a modest boost to investor confidence, potentially leading to increased equity valuations and lower bond yields. However, she believes the effect will be temporary due to lingering inflationary pressures and global uncertainties. |
| Mr. Ben Carter, Senior Analyst at Capital Strategies Group | Limited impact, potentially negative in some sectors. | Mr. Carter believes the easing is unlikely to significantly alter the current economic trajectory. He points to the persistent energy crisis and supply chain disruptions as major factors that could overshadow any positive effects. He predicts a limited positive impact on growth and potentially a negative effect on certain sectors. |
| Ms. Emily Chen, Economist at Oxford Economics | Neutral to slightly positive impact, with risks of further inflationary pressures. | Ms. Chen expects a muted impact on the overall economy, with minor improvements in consumer sentiment and business investment. However, she warns that the policy may not be enough to fully address inflationary pressures and there’s a risk of further price increases. |
| Dr. David Lee, Professor of Economics at MIT | Negative impact on long-term inflation expectations. | Dr. Lee cautions that any easing, even minor, may signal a weakening commitment to controlling inflation, potentially leading to increased inflation expectations and a subsequent rise in interest rates in the future. |
Consensus and Uncertainties
While there’s no definitive consensus, a general sentiment of cautious optimism prevails among experts. A substantial portion anticipates a positive short-term effect on markets, but this optimism is tempered by concerns about persistent inflationary pressures and global economic uncertainties. The potential for further policy adjustments, or a lack thereof, adds further uncertainty to the picture. The market’s response will be crucial in determining the long-term effects.
A strong positive reaction from investors could amplify the positive impact, while a negative or muted response would likely lead to a more limited effect.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the ECB’s potential for minor monetary policy easing presents a complex interplay of economic factors and market reactions. The decision carries significant implications, influencing various sectors and asset classes. This analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the potential outcomes, highlighting the importance of careful consideration of historical precedents and expert opinions. The path forward remains uncertain, but this in-depth look offers a framework for navigating the potential ramifications of this policy shift.

