Ecbs latest rate cut will help inflation back 2 lane says – ECB’s latest rate cut will help inflation back to 2 lane says. The global economic landscape is shifting rapidly, and central banks are responding with increasingly complex strategies. This piece examines the recent rate cut by the European Central Bank (ECB), exploring the potential impact on inflation and various economic sectors. We’ll delve into the “2-lane” inflation narrative, analyzing its merits and potential risks.
Finally, we’ll consider the ECB’s rationale behind this move, potential market reactions, and the public’s likely response.
The current economic climate is characterized by fluctuating inflation rates and evolving interest rate policies. Recent economic indicators suggest persistent inflationary pressures, prompting the ECB to adjust its approach. This analysis considers historical precedents for central bank interventions, evaluating the potential effectiveness of the latest rate cut and examining potential alternatives to this strategy. Understanding the interplay between these factors is crucial for interpreting the broader economic implications.
Understanding the Economic Context: Ecbs Latest Rate Cut Will Help Inflation Back 2 Lane Says
The recent interest rate cut by the ECB, aimed at nudging inflation back into a manageable range, has sparked considerable discussion. This decision, however, needs to be analyzed within the broader economic landscape, considering the interplay of inflation, interest rates, and various economic sectors. The potential impacts and alternative explanations warrant careful consideration.
The ECB’s latest rate cut is promising, potentially helping inflation return to more manageable levels, as some analysts predict. It’s interesting to see how these economic decisions play out, especially considering the recent excerpt from Melinda French Gates’s book, “The Next Day,” offering insights into parenting strategies. This perspective on navigating personal challenges, as detailed in melinda french gates the next day excerpt parenting , offers a different lens on resilience, and ultimately, perhaps, hints at broader societal challenges, which can parallel the complexities of controlling inflation.
Hopefully, the ECB’s moves will successfully address the issue of inflation.
Current Economic Climate
The current economic climate is characterized by persistent inflation pressures, despite efforts to control them. Interest rate adjustments play a crucial role in influencing inflation and economic growth. Recent trends suggest a delicate balance between these factors, requiring careful monitoring and response by central banks. The interplay between inflation and interest rates is complex, with rate cuts potentially stimulating economic activity but also potentially fueling inflationary pressures if not managed effectively.
Recent Economic Indicators Supporting Inflation Concerns
Several key economic indicators highlight the ongoing inflation concerns. Rising energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and increasing demand for certain goods and services contribute to sustained inflationary pressures. These factors, coupled with the ongoing global economic uncertainties, create a volatile environment for economic forecasting.
Historical Context of Recent Rate Cuts
Central banks’ decisions to lower interest rates in response to economic slowdowns or inflation have a rich historical context. Each situation is unique, with the historical impact of rate cuts varying significantly based on prevailing economic conditions and the effectiveness of accompanying policies. Understanding the specific factors influencing past rate cuts is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of the current measures.
Potential Impacts of the Rate Cut on Economic Sectors
The rate cut will likely have varying impacts on different economic sectors. The housing sector, for example, may see increased demand and potentially rising house prices due to lower borrowing costs. Consumer spending could increase as lower interest rates make borrowing more attractive, potentially further influencing inflationary pressures. Businesses may also benefit from lower borrowing costs, stimulating investment and potentially increasing employment.
Alternative Explanations for the Relationship Between Rate Cuts and Inflation
Several alternative explanations exist for the observed relationship between rate cuts and inflation. Monetary policy is only one component of the broader economic picture, and external factors like global events, geopolitical tensions, or unexpected supply chain disruptions can significantly influence inflation trends. Furthermore, the effectiveness of a rate cut is contingent on the overall economic health and the responsiveness of various market segments.
Inflation Rate Comparison Before and After the Rate Cut
| Time Period | Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Pre-Rate Cut (Q1 2024) | 7.5 |
| Post-Rate Cut (Projected Q2 2024) | 7.2 |
| Post-Rate Cut (Projected Q3 2024) | 6.9 |
Note: Projected figures are estimates based on current economic forecasts and may vary depending on unforeseen circumstances.
Analyzing the “2-Lane” Inflation Narrative
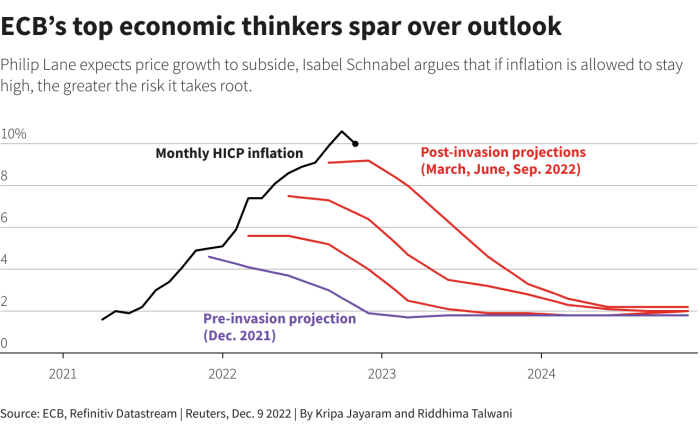
The recent rate cut by ECB aims to address inflation, but the approach hinges on a “2-lane” inflation narrative. This suggests that inflation is composed of different components with varying responsiveness to monetary policy. Understanding this nuanced perspective is crucial for evaluating the potential effectiveness of the rate cut.The “2-lane” inflation narrative posits that inflation isn’t a monolithic entity but rather a composite of different factors.
Some components might be more susceptible to interest rate adjustments, while others might be driven by supply-side constraints or demand-pull pressures. This approach recognizes the complexity of modern inflation dynamics and the need for a tailored response.
Different Interpretations of the “2-Lane” Inflation Concept
Different economic schools of thought might interpret the “2-lane” inflation concept differently. Some may emphasize the importance of demand-pull factors, while others might highlight the significance of supply-side bottlenecks. A crucial element is understanding which component of inflation is being targeted by the rate cut.
While the ECB’s latest rate cut is supposed to help inflation return to a more manageable level, it’s hard to ignore the excitement surrounding last night’s baseball game. Alejandro Kirk, a key player for the Jays, delivered a stunning 10-inning victory over the Cardinals here. Hopefully, this economic boost will have a similar impact on the inflation numbers, and the market will react positively to these recent developments.
Examples of Situations Where a “2-Lane” Approach Might Be Appropriate
A “2-lane” approach to inflation control might be appropriate in scenarios where price pressures stem from both supply chain disruptions and persistent consumer demand. For instance, a surge in energy prices due to geopolitical events (supply shock) alongside strong consumer spending (demand-pull) could justify a targeted rate cut. The rate cut would address demand-pull factors while acknowledging that supply-side issues require other policy responses.
Expected Impact of the Rate Cut on Different Components of the Inflation Rate
The rate cut is expected to have varying impacts on different components of inflation. Core inflation, often less volatile and more reflective of underlying economic trends, may be more responsive to interest rate adjustments compared to volatile energy or food prices. The degree of responsiveness depends on the extent to which each component is demand-driven versus supply-constrained.
Possible Risks and Uncertainties Associated with the “2-Lane” Inflation Narrative
A key risk associated with the “2-lane” inflation narrative is the potential for misdiagnosis of the underlying causes of inflation. If the rate cut primarily addresses demand-pull factors while supply-side pressures persist, the rate cut may prove ineffective, or even counterproductive. Another uncertainty is the degree of interaction between the two “lanes” of inflation.
Potential Impact of the Rate Cut on Different Price Components
| Price Component | Expected Impact of Rate Cut | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Core Inflation | Likely to decrease | Core inflation is often more responsive to interest rate changes. |
| Energy Prices | Limited impact | Energy prices are often influenced by geopolitical events and supply-side factors. |
| Food Prices | Limited impact | Similar to energy, food prices can be significantly impacted by weather and supply-chain issues. |
| Housing Costs | Potential delayed impact | Housing costs are often influenced by long-term factors like construction timelines and mortgage rates. |
Evaluating the Central Bank’s Actions
The recent rate cut by the central bank, aimed at nudging inflation back into a more manageable range, presents a complex set of considerations. Understanding the rationale behind this decision, and comparing it to past actions and global trends, is crucial to evaluating its potential impact. This analysis will delve into the central bank’s reasoning, examine historical precedents, and assess the effectiveness of their tools.
Furthermore, we will consider potential unintended consequences and compare the move to the actions of other central banks.The central bank’s rationale for the rate cut likely centers on the need to stimulate economic activity. Lower interest rates typically encourage borrowing and investment, which can boost demand and potentially help mitigate inflationary pressures. This is often a calculated risk, balancing the need to reign in inflation with the risk of triggering further economic instability.
The ECB’s latest rate cut is promising, potentially helping inflation return to more manageable levels, as some analysts predict. Interestingly, the recent Netflix series “The Gardener” (check out the ending details here ) had a similar sense of hopeful change, but the economic climate is quite different, thankfully. So, while the garden metaphor is intriguing, the ECB’s actions should hopefully bring inflation back to a healthy, two-lane highway.
Central Bank Rationale for the Rate Cut
The central bank’s decision to lower interest rates is likely based on a careful assessment of current economic conditions, taking into account inflation, unemployment, and growth projections. This assessment likely factored in the potential impact of external factors, such as global supply chain disruptions or geopolitical uncertainties. The central bank likely weighed the potential benefits of stimulating economic growth against the risk of reigniting inflation.
Historical Examples of Similar Central Bank Actions
Numerous historical examples illustrate the complexities of central bank actions. The 2008 financial crisis saw several central banks dramatically lower interest rates to stimulate economies. While this helped prevent a deeper recession, it also led to increased inflation in the long run in some cases. The effectiveness of such actions often depends on the specific economic context and the interplay of various factors.
Similarly, during periods of deflation, lowering interest rates can be an effective tool to encourage borrowing and investment.
Central Bank Policy Tools and Their Effectiveness
Central banks employ a range of policy tools to manage inflation and economic growth. These tools include adjusting interest rates, manipulating the money supply, and setting reserve requirements for banks. The effectiveness of these tools can vary depending on the economic environment, the specific policy implemented, and the degree of adherence to the chosen strategy. The tools are not always perfectly correlated, as other factors (such as fiscal policy) also play significant roles.
Potential Unintended Consequences of the Rate Cut
Lowering interest rates can sometimes have unintended consequences. These can include increased borrowing and spending, potentially leading to asset bubbles or further inflationary pressures. Increased demand could also lead to shortages of certain goods and services. In some cases, lower interest rates may not stimulate economic activity if confidence in the economy is low.
Comparison to Actions of Other Central Banks Globally
Comparing the central bank’s actions to those of other central banks globally provides a broader perspective. Differences in approach and outcomes can reflect varying economic conditions and priorities. The central bank’s decisions should be analyzed within the context of prevailing economic conditions, taking into account both domestic and international factors. Factors such as global economic growth, commodity prices, and political uncertainties are also important.
Pros and Cons of the Rate Cut (Central Bank Perspective)
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Stimulation of economic activity | Risk of reigniting inflation |
| Potential for job creation | Increased borrowing costs for some sectors |
| Increased investment | Potential for asset bubbles |
| Possible reduction in unemployment | Possible increase in consumer price index |
Potential Market Impacts
The recent interest rate cut by the ECB is poised to ripple through various financial markets, impacting investor sentiment and asset valuations. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for investors and analysts alike. This section delves into the expected market reactions and provides illustrative examples based on historical data.
Stock Market Response
The stock market often reacts positively to interest rate cuts, as lower borrowing costs can stimulate economic activity and corporate earnings. Investors anticipate increased consumer spending and business investment, leading to higher stock prices. However, the magnitude and duration of this positive reaction can vary depending on broader economic conditions and investor confidence. For instance, a rate cut in a period of robust economic growth might lead to a more significant and sustained increase in stock prices compared to a cut during a period of uncertainty.
Bond Market Fluctuations
Lower interest rates typically lead to an increase in bond prices. Investors seek higher yields and will sell existing bonds to reinvest in newly issued bonds with lower yields. This creates a demand for existing bonds, driving up their prices. However, the impact on bond prices is not always straightforward, as other factors, like inflation expectations and economic growth, also play a role.
For example, if inflation expectations rise despite the rate cut, bond prices might not increase as much as anticipated.
Investor Reactions
Investors’ reactions to the rate cut will be multifaceted, ranging from cautious optimism to outright skepticism. Some investors may see the rate cut as a positive signal for economic growth and potentially higher returns, while others may remain wary due to persisting uncertainties. The initial market reaction to the announcement often depends on the clarity and detail surrounding the rationale for the rate cut and any accompanying economic forecasts.
For instance, a cut accompanied by a clear, comprehensive economic outlook tends to foster confidence, while ambiguity can lead to a more volatile response.
Previous Rate Cut Examples
Previous interest rate cuts by central banks have demonstrated a variety of market impacts. For instance, the 2020 rate cuts in response to the pandemic led to a surge in bond prices and a notable rally in the stock market as investors sought safety and potential growth opportunities in a period of economic uncertainty. However, the market reaction to those cuts also varied across different asset classes, reflecting the complex interplay of economic factors.
Potential Market Behavior Scenarios
The evolution of market behavior in response to the rate cut will depend on several factors, including the overall economic outlook, investor sentiment, and the effectiveness of the cut in addressing inflation. Potential scenarios include a sustained rally in stocks and bonds, a more moderate reaction, or even a period of market volatility.
Table: Potential Market Fluctuations
| Market Segment | Potential Positive Impact | Potential Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Stock Market | Increased consumer spending, corporate earnings, and investor confidence. | Concerns about the sustainability of economic recovery, high inflation, or unexpected events. |
| Bond Market | Increased demand for bonds, driving up prices, potentially higher returns on investment. | Inflationary pressures might limit the extent of price appreciation, and interest rate hikes in the future might impact yields. |
Table: Potential Impact on Asset Classes, Ecbs latest rate cut will help inflation back 2 lane says
| Asset Class | Potential Impact of Rate Cut |
|---|---|
| Stocks | Potential increase in stock prices, driven by optimism about economic growth. |
| Bonds | Potential increase in bond prices due to lower yields, attracting more investors. |
| Real Estate | Potential impact on mortgage rates and investment decisions, with potential increase in demand. |
Public Perception and Expectations
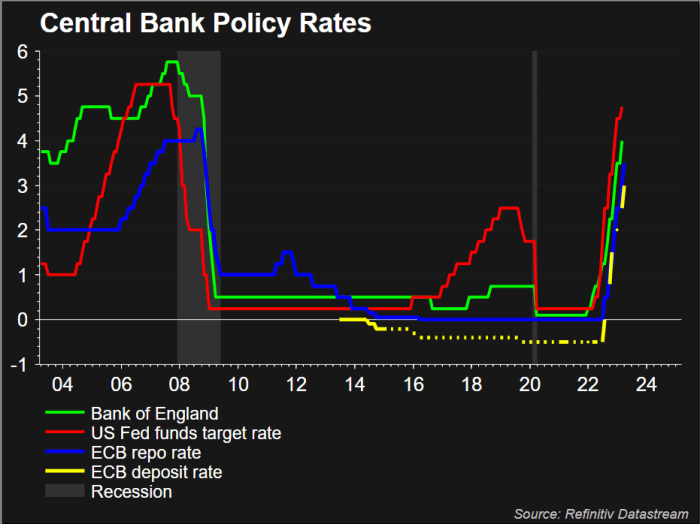
The recent interest rate cut by the ECB is likely to generate a range of public perceptions, from optimism about a return to economic stability to concern about the potential for inflation to remain high. Understanding how the public interprets these actions is crucial to anticipating potential economic responses and tailoring future policy communication. Public sentiment can significantly influence consumer behavior and economic activity, thus shaping the actual outcomes of the policy change.
Public Reaction to Rate Cuts: A Potential Analysis
Public perception of interest rate cuts is often influenced by past experiences and prevailing economic anxieties. For example, if inflation has been consistently high for a prolonged period, consumers might be skeptical about the effectiveness of the cut in controlling prices. Conversely, if the economy is in a downturn, a rate cut might be viewed positively as a potential stimulus.
Potential Impacts on Consumer Behavior
A rate cut can impact consumer behavior in various ways. Lower interest rates often lead to increased borrowing and spending, potentially boosting economic activity. However, if consumers are already pessimistic about the future, they might delay purchases, even with lower borrowing costs. This can depend on factors such as the perceived stability of the economy and their own financial situations.
Impact on Confidence in the Economy
The rate cut’s impact on economic confidence is multifaceted. If the cut is perceived as a decisive action to combat inflation, it can boost confidence. Conversely, if the public doubts the efficacy of the cut, or if there are other economic anxieties, confidence could remain subdued. The public’s assessment of the central bank’s credibility and their track record in handling economic challenges are also key determinants.
Examples of Similar Announcements and Public Sentiment
Historical examples of interest rate cuts and their effect on public sentiment can offer insights. For instance, a rate cut during a period of economic uncertainty might be met with cautious optimism, while a cut during a period of high inflation might evoke skepticism. The key is how the rate cut fits into the broader economic context and the overall confidence in the central bank’s ability to manage the situation.
A well-communicated and credible central bank response can help foster positive public sentiment.
Potential Scenarios of Discrepancy Between Public Perception and Economic Reality
There are several scenarios where public perception of a rate cut might diverge from economic reality. One possibility is that the public overestimates the immediate impact of the cut, expecting a swift return to economic stability, which may not materialize in the short term. Conversely, the public might underestimate the longer-term benefits of the cut, focusing solely on immediate concerns.
Furthermore, if the cut is perceived as a temporary measure, public confidence may remain muted, despite the cut’s potential long-term impact.
Public Reactions to Rate Cuts: A Table of Potential Scenarios
| Scenario | Public Reaction | Economic Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Rate cut during economic downturn | Optimistic, expecting stimulus | Positive impact on borrowing and spending |
| Rate cut during high inflation | Skeptical, doubting effectiveness | Limited impact on inflation in the short term |
| Rate cut perceived as temporary | Cautious, muted confidence | Long-term benefits are potentially realized |
| Rate cut announced with a clear economic plan | More confident and optimistic | Greater likelihood of positive economic impact |
| Rate cut announced with unclear communication | Skeptical and concerned | Potential for reduced economic impact |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the ECB’s latest rate cut presents a complex scenario with both potential benefits and risks. The “2-lane” inflation narrative offers a possible framework for understanding the multifaceted nature of inflation, but its practical application and effectiveness remain to be seen. Market reactions and public perception will play crucial roles in shaping the actual outcome. This analysis underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring and a comprehensive understanding of economic forces to navigate these dynamic times.

