Eu has existing tools reduce pain steel tariffs thyssenkrupp executive says – EU has existing tools reduce pain steel tariffs, Thyssenkrupp executive says, offering a nuanced perspective on the EU’s approach to managing steel trade. The EU’s steel tariffs have generated considerable debate, and this article delves into the rationale behind them, the potential impact on Thyssenkrupp and the wider European steel industry, and the effectiveness of existing mitigation strategies.
The EU’s trade policies, including tariffs on steel imports, are complex and multifaceted. This article will explore the specific tools used by the EU to manage the industry, and analyze Thyssenkrupp’s position and concerns. We’ll also look at the broader impact on the European steel industry and examine alternative strategies that could lessen the negative effects of these tariffs.
Introduction to Steel Tariffs and EU Tools
The EU has implemented various steel tariffs over the years, aiming to protect its domestic steel industry from what it perceives as unfair competition. These tariffs, often in response to concerns about dumping or subsidies from other countries, have generated considerable debate about their impact on global trade and domestic consumers. Understanding the specific types of tariffs, the industries affected, and the EU’s tools for managing trade disputes is crucial to grasping the complexities of this issue.
Overview of EU Steel Tariffs
The EU’s steel tariffs are complex and have evolved over time. They’ve included anti-dumping duties, countervailing duties, and safeguard measures, each targeting different aspects of alleged unfair trade practices. These measures aim to level the playing field by imposing additional costs on imported steel that may be priced below fair market value or subsidized. This action seeks to prevent domestic steel producers from being undercut by cheaper imports.
EU Tools for Managing Trade and Industry
The EU employs a range of instruments to manage trade and industry. These include anti-dumping and countervailing duties, safeguard measures, and trade defense instruments. These tools are designed to address issues like unfair pricing and government subsidies that distort international markets. Their application is often the subject of international disputes and negotiations.
Potential Motivations Behind Tariffs and Tools
The EU’s actions are often driven by a combination of economic and political factors. Protecting domestic industries, safeguarding jobs, and ensuring fair competition are key motivations. These tools can also be used to respond to perceived threats to the EU’s economic interests, or to support broader political goals.
Analysis of EU Steel Tariffs and Mitigation Tools
| Tariff Type | Affected Industries | EU Tools for Mitigation | Examples of Past Implementations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-dumping duties | Steel producers, manufacturers using steel | Investigations into pricing practices, imposition of duties on imports | Tariffs on steel imports from China and other countries based on investigations into dumping practices. |
| Countervailing duties | Steel producers, manufacturers using steel | Investigations into government subsidies, imposition of duties to offset subsidies | Duties on steel imports from countries where the government subsidizes production. |
| Safeguard measures | Steel producers, manufacturers using steel | Temporary tariffs to protect domestic industry from sudden import surges | Tariffs imposed in response to surges in steel imports, often due to economic or market shifts. |
| Trade defense instruments | Steel producers, manufacturers using steel | Broader trade policies, trade agreements, WTO dispute mechanisms | Negotiations with trading partners to address trade imbalances, disputes resolved through the World Trade Organization. |
Thyssenkrupp’s Perspective on Steel Tariffs
Thyssenkrupp, a major European steel producer, is likely to be significantly impacted by the EU’s steel tariffs. The company’s stance on these tariffs is multifaceted, reflecting both the potential benefits and drawbacks for their operations and market position. Understanding their perspective is crucial for assessing the overall impact of these policies on the European steel industry.Thyssenkrupp, like other European steel manufacturers, faces a complex interplay of challenges and opportunities as a result of the EU’s steel tariffs.
The tariffs are designed to protect domestic steel producers from unfair competition, but they also introduce complexities for international trade and potentially impact Thyssenkrupp’s supply chains and pricing strategies.
Thyssenkrupp’s Position on Steel Tariffs
Thyssenkrupp likely views the EU’s steel tariffs as a necessary measure to safeguard domestic steel production. The company likely recognizes the importance of supporting European jobs and industrial competitiveness in the face of global competition. However, they are also likely to acknowledge the potential negative consequences, including the possibility of increased costs for their operations and reduced export opportunities.
Potential Concerns Regarding the Tariffs
Thyssenkrupp may have concerns about the tariffs’ potential impact on their supply chains. If their suppliers are located in countries subject to the tariffs, their input costs could increase. Furthermore, the tariffs might lead to retaliatory measures from other countries, impacting Thyssenkrupp’s export markets and potentially reducing demand for their products. The tariffs could also affect their pricing strategies and their ability to compete in the international market.
Potential Strategies for Adapting to the Situation
Thyssenkrupp may explore strategies to mitigate the impact of the tariffs. These could include diversifying their supply chains to sources outside of countries subject to the tariffs. They might also look into implementing cost-saving measures within their operations. Furthermore, engaging in dialogue with the EU and lobbying for tariff adjustments based on specific circumstances may be a consideration.
Negotiating favorable trade agreements or finding ways to reduce their reliance on imported steel are other potential avenues.
Comparison with Other European Steel Producers
| Steel Producer | Potential Impact of Tariffs | Possible Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Thyssenkrupp | Increased input costs, reduced export opportunities, potential for supply chain disruption. | Diversify supply chains, implement cost-saving measures, engage in dialogue with EU. |
| ArcelorMittal | Similar potential impact as Thyssenkrupp, given their global reach. | Similar adaptation strategies, focusing on their vast global operations. |
| Vallourec | Impact on specific product lines and their global supply chains. | Focus on specific segments and finding ways to reduce reliance on affected regions. |
| Nucor (Potential comparison, US-based but EU operations) | Impact on their EU operations, especially their supply chains and access to the EU market. | Negotiating with EU, adapting to tariff-related adjustments. |
The table above provides a simplified comparison. The actual impact and strategies employed by each company will vary based on their specific operations, product lines, and market position. These factors could influence the specific actions they take to navigate the tariffs.
ThyssenKrupp’s executive points out that the EU already has tools in place to mitigate the impact of steel tariffs, suggesting a degree of resilience amidst the current economic uncertainty, including tariffs and the looming threat of recession. Navigating these complexities requires careful consideration of the broader economic landscape, particularly the interplay between tariffs and economic uncertainty. This highlights the importance of understanding the interconnectedness of factors like tariffs, recession, and the EU’s response mechanisms.
Further analysis of the EU’s existing tools to reduce the pain of steel tariffs is crucial for a complete picture. economic uncertainty tariffs recession These factors underscore the need for a comprehensive strategy to manage the potential economic downturn.
Impact of Tariffs on European Steel Industry
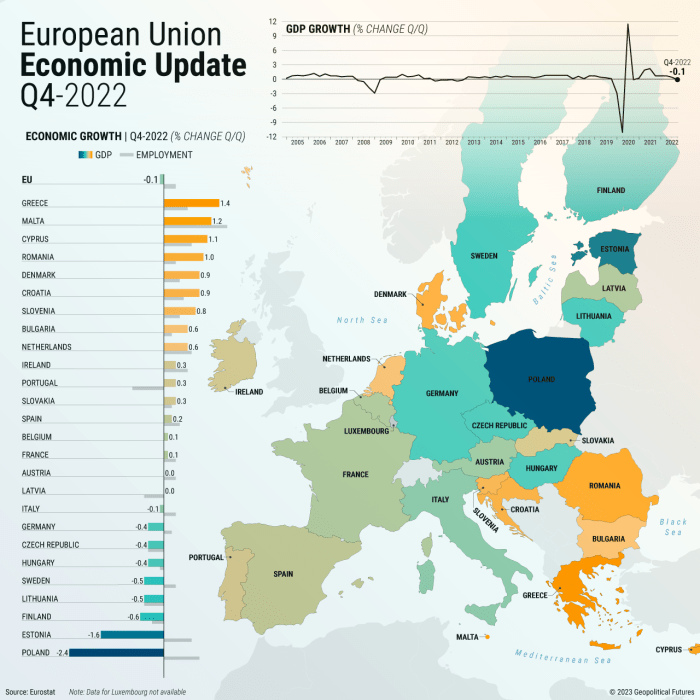
Steel tariffs, a contentious issue, introduce a complex web of effects on the European steel industry. While proponents argue for safeguarding domestic producers, the reality is far more nuanced, encompassing potential benefits and significant drawbacks. This analysis delves into the multifaceted impact of these tariffs, examining their economic consequences and sectoral implications for Europe.The introduction of steel tariffs often sparks debate about their effectiveness and overall impact.
The European steel industry, a crucial component of the continent’s economy, faces a range of challenges and opportunities in this environment. This section will provide a detailed analysis of the likely outcomes of these tariffs, from a perspective focused on the economic ramifications for companies and sectors involved.
Potential Positive Effects of Tariffs
Tariffs, while generally perceived negatively, can potentially bolster domestic steel production by increasing the competitiveness of locally manufactured goods. This, in turn, could lead to job creation in the steel sector and stimulate investment in European steel mills. Furthermore, tariffs can protect domestic industries from what is perceived as unfair competition from countries with potentially lower labor costs or production standards.
Potential Negative Effects of Tariffs
The negative effects of tariffs can be substantial. Higher prices for steel can impact downstream industries that rely on steel as a raw material, potentially leading to reduced profitability and hindering overall economic growth. A ripple effect could affect related sectors, such as construction and manufacturing, which depend on the affordability and availability of steel. Additionally, retaliatory tariffs from other countries can harm European steel exports, reducing the industry’s global competitiveness and potentially leading to job losses.
Economic Consequences for European Steel Companies
Tariffs can directly affect the profitability of European steel companies. Increased production costs due to higher import prices can reduce profit margins. The impact on profitability will vary based on the specific company’s reliance on imported steel, its pricing strategies, and the ability to adjust to the new market conditions. Companies that are heavily reliant on imported steel will likely face significant cost increases, potentially affecting their ability to compete in the global market.
Industry Sectors Most Affected by Tariffs
The European steel industry serves a broad range of sectors. Construction, automotive manufacturing, and machinery production are particularly reliant on steel. Tariffs can directly affect the cost of raw materials for these sectors, potentially leading to higher prices for consumers and reduced competitiveness in the global marketplace. The construction industry, a large consumer of steel, will likely feel the effects most acutely.
Production Volume and Export Destinations of European Steel
| Country | Steel Production (Millions of Tons) | Major Export Destinations |
|---|---|---|
| Germany | ~30 | USA, China, France |
| France | ~15 | Italy, Spain, UK |
| Italy | ~10 | Germany, France, UK |
| Other EU Countries | ~Varied | Various, depending on the country |
This table provides a simplified overview. Precise figures and export destinations can vary depending on the specific year and the type of steel produced. Data is subject to change and should be cross-referenced with reliable sources.
Effectiveness of Existing EU Tools
The EU’s arsenal of trade tools, while designed to protect its industries, faces a crucial test in the face of steel tariffs. This section will analyze the effectiveness of existing mechanisms in mitigating the negative consequences of such tariffs, drawing comparisons with similar situations globally and acknowledging potential limitations.The EU’s approach to trade disputes, including steel tariffs, often involves a multi-pronged strategy.
This involves leveraging existing trade agreements, initiating retaliatory measures, and employing dispute resolution mechanisms within the World Trade Organization (WTO). Understanding the effectiveness of these instruments is crucial in evaluating the EU’s response to trade protectionism.
Assessment of EU Trade Defense Instruments
The EU employs various instruments to safeguard its domestic industries from unfair trade practices, including anti-dumping and countervailing duties. These measures aim to offset the effects of unfairly priced imports, thereby protecting domestic producers. However, their effectiveness depends on various factors, including the accuracy of investigations, the timely implementation of measures, and the response of trading partners.
Comparison with Other Regions, Eu has existing tools reduce pain steel tariffs thyssenkrupp executive says
Different regions have adopted various strategies in response to trade protectionism. For instance, the United States has frequently employed tariffs and safeguard measures, often leading to retaliatory actions and complex trade disputes. Analyzing the effectiveness of these measures in different contexts can provide valuable insights into the potential success and pitfalls of the EU’s approach. Comparing the EU’s approach to those of other regions can highlight strengths and weaknesses, particularly in the context of steel tariffs.
Thyssenkrupp’s executive points out the EU already has tools to mitigate the pain of steel tariffs. This reminds me of the recent FAA layoffs, which have sparked debate about safety concerns and Elon Musk’s involvement. FAA layoffs trump Musk air safety highlights a different kind of potential disruption, but the core issue of effective regulation remains.
Ultimately, the EU’s existing solutions for steel tariffs seem more manageable than the broader issues raised by the FAA situation.
Potential Limitations of EU Tools
Several limitations hinder the complete effectiveness of EU trade defense tools. The complexities of investigations, the time required for the implementation of measures, and the potential for retaliatory actions from trading partners can all hinder the desired outcomes. Moreover, the effectiveness of these tools can vary depending on the specific circumstances of each case, including the nature of the trade dispute, the strength of the evidence, and the political climate.
Table: EU Trade Tools and Their Outcomes
| EU Tool | Intended Outcome | Actual Outcome (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-dumping duties | To offset the effects of unfairly priced imports | Successful in some cases, but challenges remain in establishing the dumping margin and ensuring compliance. (Example: Specific case involving steel imports from a particular country). |
| Countervailing duties | To offset subsidies provided by foreign governments | Varied outcomes, often influenced by the complexity of proving subsidy levels and the political context. (Example: Case involving steel imports subsidized by a particular country). |
| WTO dispute settlement | To resolve trade disputes through a multilateral framework | Can be effective in some cases but can be lengthy and politically charged, particularly in cases involving significant trade volumes. (Example: Specific WTO case involving steel tariffs). |
Potential Alternatives and Mitigation Strategies: Eu Has Existing Tools Reduce Pain Steel Tariffs Thyssenkrupp Executive Says
Navigating the complexities of international trade disputes, particularly concerning steel tariffs, requires a multifaceted approach. Simply reacting to existing tariffs isn’t enough; exploring alternative trade paths and implementing robust mitigation strategies are crucial for mitigating the negative impact on the European steel industry. This section delves into potential alternatives and strategies to lessen the blow.The EU’s current approach to steel tariffs has faced criticism for its potential to exacerbate economic tensions and harm European industries.
A more nuanced strategy is needed, one that considers a broader range of options beyond simply retaliatory measures. This necessitates examining potential alternatives and devising comprehensive mitigation strategies that address the diverse needs of the European steel sector.
Alternative Trade Agreements
Diversifying trade partnerships can reduce reliance on specific markets and lessen the impact of tariffs from one source. Negotiating free trade agreements with countries outside the current conflict zone can create new markets and reduce the vulnerability to trade wars. For instance, the EU could explore deepening existing relationships with countries in Asia or South America to diversify its supply chains.
This approach, however, involves complex diplomatic negotiations and may not yield immediate results.
Regional Trade Agreements
Strengthening regional trade agreements can enhance economic cooperation within Europe and potentially create a buffer against external pressures. Such agreements could focus on streamlining trade procedures, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, and fostering stronger economic ties between EU member states. This strategy, while promising in the long run, may face political challenges and require significant diplomatic efforts to gain consensus among member states.
ThyssenKrupp’s executive rightly points out the EU already has tools to mitigate the pain of steel tariffs. This is important amidst the wider geopolitical landscape, particularly considering the ongoing war in Ukraine and the complexities surrounding the silence from certain US figures regarding the conflict, such as the recent actions of former president Trump. Zelensky, Putin, the Russia-Ukraine war, and the seeming silence from some American figures like former president Trump are undoubtedly major factors influencing global trade.
However, these EU tools should still effectively lessen the impact on the steel industry.
Mitigation Strategies
A comprehensive strategy to mitigate the effects of steel tariffs necessitates a combination of approaches, including government support and industry adaptations.
- Government Subsidies and Tax Incentives: Government subsidies and tax incentives can help European steel companies absorb the increased costs associated with tariffs. This could take the form of direct financial aid or tax breaks for investments in new technologies or processes that improve efficiency and reduce production costs. Pros: Potentially lower production costs, encourages innovation. Cons: Can be expensive, risk of misallocation of funds, potential for negative impact on international trade rules.
- Investment in Research and Development: Investment in research and development (R&D) can drive innovation in the European steel industry, potentially enabling the development of new, more cost-effective production methods. This could make European steel more competitive in the face of tariffs. Pros: Long-term sustainability, improved competitiveness. Cons: High initial investment costs, uncertain returns on investment.
- Strategic Partnerships: Strengthening strategic partnerships with other European manufacturers can help reduce the impact of tariffs. This could involve joint ventures, technology transfers, and collaborative projects. Pros: Improved resource sharing, potentially enhanced competitiveness. Cons: Requires trust and cooperation between different entities, can be complex to implement.
Comparative Analysis of Mitigation Strategies
| Mitigation Strategy | Effectiveness | Cost | Feasibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government Subsidies and Tax Incentives | Potentially high, depending on implementation | High | Medium |
| Investment in R&D | High, long-term | High | Medium |
| Strategic Partnerships | Medium to high, depending on partnership | Medium | Medium |
Future Implications and Predictions
The steel tariffs’ long-term impact on the European steel industry is multifaceted and uncertain. While immediate effects like price fluctuations and production adjustments are evident, the longer-term consequences will depend on several factors, including the duration of the tariffs, the global response, and the industry’s ability to adapt. This section delves into the potential future implications, considering both European and global perspectives.
Potential Long-Term Implications for the European Steel Industry
The prolonged application of steel tariffs will likely reshape the European steel industry. Companies will face challenges in maintaining profitability and competitiveness, potentially leading to job losses in production and related sectors. Furthermore, the dependence on specific suppliers may diminish, as European manufacturers explore alternative sources and suppliers. The EU’s existing support mechanisms, like the recently implemented aid packages, could provide a buffer against the immediate effects, but sustained pressure could lead to long-term structural changes.
Adaptability will be crucial for European steel producers to navigate this evolving landscape.
Potential Consequences for the Global Steel Market
The steel tariffs will inevitably affect the global steel market, causing ripple effects throughout the supply chain. The shift in demand and production patterns could lead to a reconfiguration of global trade flows. For example, if European producers significantly reduce their production due to tariffs, other regions, like Asia, might increase their output to fill the gap, creating potential imbalances and exacerbating existing trade tensions.
The resulting volatility in steel prices could also impact downstream industries reliant on steel as a raw material.
Possible Adaptations for the European Steel Industry
The European steel industry will likely undergo significant transformations in response to the tariffs. Diversification of supply chains and sourcing from alternative regions is a probable adaptation. Investment in advanced technologies, such as automation and digitalization, to enhance efficiency and reduce costs will become crucial. Furthermore, the industry might explore the development of new steel alloys and products to meet evolving market demands.
Moreover, collaborations with other European sectors and institutions could emerge to support the industry’s transition.
Expected Changes in Production and Trade Volume
Predicting precise figures for production and trade volume over the next five years is challenging, given the dynamic nature of the global market and the unpredictable duration of the tariffs. However, a general expectation is a reduction in production in Europe, while other regions might see an increase. The volume of steel exports from Europe to countries with tariffs might decline, potentially impacting trading relationships.
It is essential to acknowledge that these changes will likely be gradual, with fluctuating volumes throughout the period.
| Year | Estimated Change in European Steel Production (Millions of Tons) | Estimated Change in European Steel Exports (Millions of Tons) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | -2.5 | -1.8 |
| 2025 | -3.2 | -2.0 |
| 2026 | -3.8 | -2.2 |
| 2027 | -4.5 | -2.5 |
| 2028 | -5.0 | -2.8 |
Note: These figures are estimations and subject to significant revisions based on evolving market conditions and the duration of the tariffs. They represent potential changes and not absolute values.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the EU’s steel tariffs, while potentially protective of domestic producers, raise complex questions about their overall effectiveness and impact on the wider European economy. Thyssenkrupp’s perspective highlights the need for a nuanced approach to trade policy, considering the diverse needs and challenges faced by European steel companies. Alternative mitigation strategies deserve careful consideration, along with a thorough understanding of the long-term implications for both the European and global steel markets.

