How China is boosting renewable energy goals is a fascinating story of rapid progress and ambitious targets. China’s government is aggressively pursuing renewable energy, with a mix of policies, investments, and technological advancements driving this growth. This exploration dives into the key strategies behind China’s impressive renewable energy journey.
From substantial government incentives and funding to cutting-edge technological breakthroughs, China is leaving a mark on the global renewable energy landscape. This detailed look at the various facets of China’s renewable energy push reveals a complex picture of policy implementation, industry collaboration, and societal impact.
Government Policies and Incentives
China’s rapid expansion in renewable energy is deeply intertwined with a robust and evolving set of government policies. These policies have acted as a catalyst, driving significant investment and technological advancements in the sector. From massive solar farms to wind power projects across vast landscapes, the government’s proactive approach has played a pivotal role in shaping China’s energy landscape.These policies are not static; they adapt to changing global energy dynamics and technological advancements.
The government’s commitment to achieving its renewable energy targets is evident in the consistent evolution of these policies, creating a supportive environment for both domestic and international investors.
Key Government Policies, How china is boosting renewable energy goals
China’s government has implemented a diverse range of policies to promote renewable energy. These policies span financial incentives, regulatory frameworks, and technological advancements. Understanding these policies is crucial to appreciating the scale and pace of China’s renewable energy transition.
- Feed-in Tariffs (FITs) and Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS): FITs guarantee a minimum price for renewable energy, making it attractive for developers. RPS mandates a certain percentage of electricity from renewable sources, ensuring market demand. These policies are designed to stimulate investment and encourage the integration of renewable energy into the grid.
- Financial Incentives and Subsidies: China offers substantial subsidies and tax breaks for renewable energy projects. These incentives range from direct financial support to preferential lending rates. The aim is to lower the initial investment costs and make renewable energy more competitive compared to fossil fuels.
- Renewable Energy Development Plans: Long-term national plans Artikel targets for renewable energy generation, encouraging long-term investments and fostering industry growth. These plans provide a roadmap for achieving specific goals and create a predictable environment for businesses.
- Grid Modernization and Infrastructure Development: China is investing heavily in grid modernization and infrastructure to accommodate the increasing share of renewable energy. This includes developing smart grids, transmission lines, and energy storage solutions to ensure reliable and efficient integration of renewable energy sources.
Financial Incentives and Subsidies
Financial incentives are a critical component of China’s renewable energy policies. They directly impact project feasibility and attract private sector participation.
- Tax Credits and Deductions: Companies and individuals involved in renewable energy projects often receive tax credits and deductions, reducing their financial burden and encouraging investment.
- Grants and Subsidies: Direct financial support, in the form of grants and subsidies, is provided to projects. These funds help cover initial development costs, making renewable energy more affordable.
- Preferential Lending Rates: Banks often offer preferential lending rates to renewable energy projects, reducing the cost of capital and stimulating investment.
Comparison with Other Major Economies
China’s policies compare favorably with those of other major economies, particularly in terms of scale and ambition. However, specific approaches and implementation vary.
- Scale of Incentives: China’s financial incentives are often substantial, potentially surpassing those in other economies. This strong support is a key driver of rapid growth.
- Policy Focus: China’s policies tend to be more focused on rapid deployment, while some other economies prioritize specific technological advancements or environmental considerations.
- Regulatory Environment: China’s regulatory environment for renewable energy is evolving, creating a dynamic and potentially uncertain context for long-term planning.
Evolution of Key Policies
The table below highlights the evolution of key policies related to renewable energy in China.
| Year | Policy Name | Main Features |
|---|---|---|
| 2005 | National Renewable Energy Development Plan | Artikeld initial targets and policies for renewable energy development. |
| 2010 | Renewable Energy Law | Established a legal framework for renewable energy development. |
| 2013 | Revised Renewable Energy Development Plan | Increased targets and Artikeld specific support mechanisms. |
| 2018 | New Energy Development Plan | Emphasized smart grids and infrastructure improvements. |
Investment and Funding
China’s ambitious renewable energy goals are being fueled by substantial investment and funding. Government policies, while crucial, are only one piece of the puzzle. Private sector involvement, both domestic and international, plays a vital role in driving project development and technology advancements. This section delves into the major players, funding sources, and investment strategies within this dynamic sector.
Major Investors in China’s Renewable Energy Sector
A diverse range of investors are contributing to China’s renewable energy expansion. State-owned enterprises (SOEs) like China Three Gorges Corporation and State Grid Corporation of China are heavily involved, leveraging their vast resources and established infrastructure. Private companies, such as some of the largest energy conglomerates in China, are also actively seeking opportunities in this growing market, driven by both profit motives and nationalistic goals.
International investors are increasingly participating, drawn by the significant market potential and supportive government policies.
Sources of Funding for Large-Scale Renewable Energy Projects
Funding for large-scale renewable energy projects comes from a variety of sources. Government subsidies and tax incentives, a key component of the Chinese approach, provide crucial support. Furthermore, public-private partnerships (PPPs) are prevalent, combining government funding with private sector capital. Project financing, utilizing bonds and other debt instruments, is another crucial method for securing capital for large-scale projects.
Venture capital and private equity firms are also active, particularly in emerging technologies like offshore wind and green hydrogen.
Investment Strategies of Chinese Companies
Chinese companies often employ a strategy of vertical integration, aiming to control the entire value chain from resource acquisition to power generation and distribution. This approach is often contrasted with international counterparts, which frequently prioritize specific segments of the value chain. Chinese companies are also more heavily influenced by government directives and long-term national goals, while international firms often have more flexibility in adapting their strategies to market conditions.
Top 5 Renewable Energy Investment Projects in China
| Project | Funding (USD Billion) | Location | Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xingan Wind Farm | ~2.5 | Inner Mongolia | Onshore wind |
| Huanghe Hydropower Project | ~3.8 | Gansu Province | Hydropower |
| Yangtze River Solar Farm | ~1.2 | Jiangsu Province | Solar PV |
| Tianjin Offshore Wind Farm | ~2.0 | Bohai Sea | Offshore wind |
| Lhasa Geothermal Power Plant | ~0.8 | Tibet Autonomous Region | Geothermal |
Note: Figures are approximate and based on publicly available information. Specific funding amounts may vary depending on the source. These projects demonstrate the diverse range of renewable energy technologies being pursued in China, reflecting the country’s commitment to a low-carbon future.
Technological Advancements
China’s commitment to renewable energy isn’t just about policy and investment; it’s deeply intertwined with groundbreaking technological advancements. These innovations are driving down costs, increasing efficiency, and positioning China as a global leader in renewable energy technology. From solar panel manufacturing to wind turbine design, Chinese ingenuity is transforming the landscape of sustainable energy.
Latest Breakthroughs in Solar Technology
China has significantly advanced in photovoltaic (PV) technology. Improvements in silicon-based solar cells have led to higher efficiency rates, enabling greater energy generation from a smaller area. Perovskite solar cells, a relatively new technology, are showing promising results in China, with ongoing research focusing on cost reduction and scalability. These advancements are crucial in reducing the overall cost of solar power, making it more competitive with traditional energy sources.
Advances in Wind Turbine Technology
Significant progress has been made in wind turbine design and manufacturing. Larger rotor diameters and advanced blade materials are allowing turbines to capture more wind energy. Improved gearboxes and generator technologies are enhancing efficiency and reducing maintenance costs. These innovations are leading to more powerful and cost-effective wind farms, bolstering China’s wind energy sector.
Research and Development in Renewable Energy
China’s commitment to research and development (R&D) in renewable energy is substantial. Government funding, coupled with industry investment, is driving innovation across the sector. National labs and universities are collaborating with private companies, fostering a dynamic ecosystem for technological advancement. This collaborative approach accelerates the development and deployment of new technologies, positioning China at the forefront of renewable energy innovation.
Comparison of Key Technological Advancements
| Technological Advancement | China | Other Countries (e.g., US, Europe) |
|---|---|---|
| Photovoltaic Efficiency | Significant improvements in silicon-based solar cells; exploring perovskite cells | Focus on efficiency and cost reduction, but China appears to be leading in certain areas |
| Wind Turbine Size and Efficiency | Larger rotor diameters and advanced blade materials; improved gearboxes | Ongoing development in turbine design, but China has shown rapid advancements in scale and efficiency |
| Energy Storage Technologies | Development of advanced battery technologies for grid integration; exploring pumped hydro storage | Continued innovation in battery technology; investments in various energy storage solutions |
| Smart Grid Technologies | Integration of smart grid technologies into renewable energy systems | Significant investments in smart grid infrastructure and integration with renewables |
The table above provides a comparative overview of key technological advancements. It highlights China’s proactive approach to innovation and its global competitiveness in the renewable energy sector. Further research and collaboration across nations are essential to accelerate the transition to sustainable energy.
Infrastructure Development
China’s ambitious renewable energy goals necessitate a robust infrastructure foundation. This involves the creation of a sophisticated network of transmission lines and storage facilities to effectively integrate intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind into the national grid. The sheer scale of this undertaking demands meticulous planning and execution, a testament to China’s engineering prowess and commitment to sustainable energy.The development of this infrastructure is crucial for ensuring the reliable and consistent supply of renewable energy, thereby supporting economic growth and environmental sustainability.
A robust grid is the cornerstone of a functional renewable energy system.
Transmission Line Expansion
China is aggressively expanding its high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission lines. These lines are essential for transporting electricity over long distances from renewable energy generation hubs to consumption centers. HVDC technology significantly reduces transmission losses compared to alternating current (AC) lines, increasing the overall efficiency of the energy network. This strategic investment underscores the country’s determination to facilitate the seamless flow of renewable energy across the vast expanse of its territory.
Storage Facility Development
The intermittent nature of solar and wind power necessitates energy storage solutions. China is actively investing in various storage technologies, including pumped hydro storage, battery storage, and compressed air energy storage. These technologies play a vital role in smoothing out the fluctuations in renewable energy production, ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply. The development of large-scale storage facilities is a key element in the country’s strategy for a stable and sustainable energy system.
Grid Integration Challenges and Solutions
Integrating renewable energy sources into the existing power grid presents unique challenges. Intermittency is a primary concern, requiring sophisticated grid management strategies. One solution is the development of smart grids, which use advanced technologies to optimize energy flow and distribution. Another solution is incorporating flexible generation resources, such as natural gas plants, to compensate for fluctuations in renewable energy production.
Smart Grid Optimization
Smart grids leverage advanced technologies like sensors, communication networks, and data analytics to optimize energy distribution. They enable real-time monitoring of energy flow, enabling grid operators to respond swiftly to fluctuations in renewable energy generation. This intelligence allows for proactive adjustments to ensure grid stability and reliability. The incorporation of smart grid technology enhances the overall efficiency of the energy system and promotes grid resilience.
Key Infrastructure Projects and Projected Impact
| Project Name | Description | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Xianghe-Beijing HVDC Project | High-voltage direct current transmission line connecting a renewable energy hub in Xianghe to Beijing. | Enhanced energy reliability in Beijing and surrounding areas, enabling more renewable energy integration. |
| Three Gorges Dam Upgrade | Modernization and expansion of the dam’s infrastructure to facilitate pumped hydro storage for greater renewable energy support. | Significant increase in energy storage capacity, promoting grid stability and reliability during peak demands. |
| National Smart Grid Demonstration Project | Development of pilot smart grids in various regions to test and refine technologies for integrating renewable energy. | Improved grid management, optimization of energy distribution, and creation of a blueprint for national smart grid implementation. |
Public Awareness and Acceptance
China’s ambitious renewable energy goals are inextricably linked to public awareness and acceptance. A well-informed and supportive populace is crucial for successful policy implementation and broad societal adoption of these technologies. Without widespread understanding of the benefits and practical applications of renewables, achieving these targets faces significant obstacles.Public understanding of renewable energy in China is multifaceted. Early adopters and those in regions heavily impacted by air pollution or experiencing energy shortages are often more receptive to renewable energy initiatives.
However, public awareness and acceptance remain unevenly distributed across different demographics and geographic locations. Government efforts are focused on bridging this gap and ensuring that the benefits of renewable energy are accessible and understandable to all citizens.
Government Efforts to Educate the Public
The Chinese government actively promotes renewable energy through various channels. Educational campaigns often target schools, communities, and online platforms. These campaigns frequently highlight the environmental and economic advantages of renewable energy sources, emphasizing energy independence and improved air quality. Government-funded initiatives also showcase success stories of renewable energy projects and the tangible benefits they provide to local communities.
Public Opinion and Policy Influence
Public opinion plays a critical role in shaping renewable energy policies. Surveys and feedback mechanisms, although not always comprehensive, offer valuable insights into public sentiment and priorities. Government officials utilize this data to refine policies and address concerns, ensuring that initiatives align with public expectations and needs. Active public participation in discussions and forums can influence the direction and implementation of renewable energy projects.
By incorporating public feedback, the government can ensure that renewable energy initiatives resonate with the broader population and gain broader acceptance.
Public Awareness Campaigns and Their Impact
| Campaign | Focus | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| National Renewable Energy Awareness Week | Highlighting environmental benefits, showcasing successful projects, and emphasizing economic opportunities. | Increased public interest in renewable energy, particularly among younger demographics. Initial data shows a notable increase in online searches related to renewable energy topics during and after the campaign. |
| Community-based workshops and presentations | Providing practical information on solar energy installation, wind turbine operation, and energy efficiency. | Enhanced local knowledge and interest. Follow-up surveys suggest increased willingness among residents to adopt energy-efficient appliances and solar panels in their homes. |
| Online educational platforms and social media campaigns | Using multimedia content to disseminate information about renewable energy technologies and their societal impact. | Reached a broader audience, particularly younger generations. The campaigns have been successful in engaging online communities and promoting conversations about renewable energy. Social media engagement metrics suggest significant interest. |
Energy Mix and Transition: How China Is Boosting Renewable Energy Goals
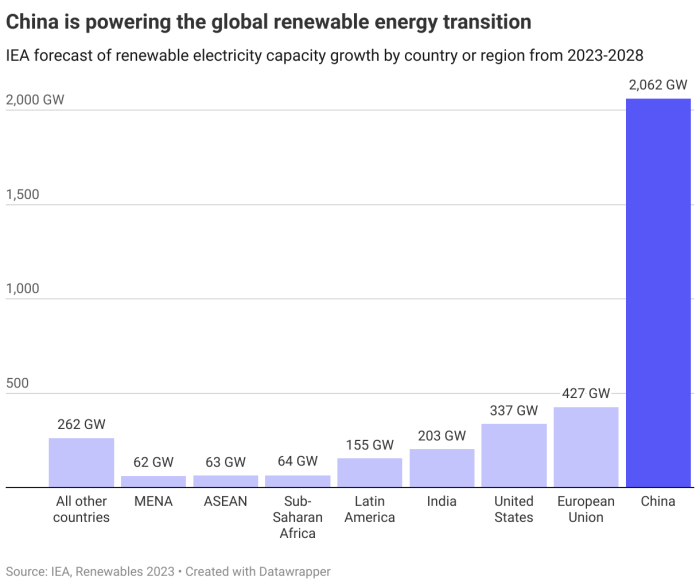
China’s ambitious renewable energy targets are deeply intertwined with its overall energy mix and the phased retirement of fossil fuels. The country’s current reliance on coal for electricity generation presents a significant challenge, but the government is actively working to shift the balance towards cleaner sources. This transition is crucial not only for environmental sustainability but also for energy security and long-term economic stability.China’s energy mix is currently dominated by fossil fuels, particularly coal.
The nation’s significant industrialization and population growth have historically driven a heavy reliance on coal-fired power plants. This reliance, while providing energy security in the short term, has also led to severe environmental consequences, including air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The shift towards renewable energy is a strategic imperative to address these challenges.
Renewable Energy’s Role in China’s Energy Mix
China’s renewable energy sources, including hydro, wind, solar, and biomass, are increasingly playing a critical role in diversifying the nation’s energy mix. The substantial investment in these sectors has led to noticeable growth in their contribution to the overall energy supply. This diversification aims to reduce reliance on volatile fossil fuel markets and enhance energy independence.
Comparison of Renewable and Fossil Fuel Reliance
The shift towards renewable energy is evident when comparing China’s current fossil fuel reliance to its growing renewable energy capacity. While coal remains the dominant energy source, the increasing deployment of wind, solar, and hydro power plants signals a deliberate move away from fossil fuels. The government’s ambitious targets aim to significantly reduce the country’s dependence on coal and other fossil fuels, thereby mitigating the environmental impact of energy production.
Government Plan for Phasing Out Fossil Fuels
The Chinese government has Artikeld a clear plan for phasing out fossil fuels in favor of renewables. This plan involves gradually reducing the share of coal in the energy mix, promoting the development of renewable energy technologies, and investing in supporting infrastructure. The phased retirement of coal-fired power plants is a key component of this strategy, coupled with policies incentivizing the development and adoption of cleaner alternatives.
Achieving Renewable Energy Targets
China’s ambitious renewable energy targets are being pursued through various strategies. These strategies include:
- Policy Support: Government policies and incentives, such as tax breaks and subsidies, are actively encouraging investment and growth in the renewable energy sector. This supportive environment creates a favorable landscape for companies to develop and deploy renewable energy technologies.
- Investment and Funding: Significant investment from both the public and private sectors is fueling the development and deployment of renewable energy projects. This substantial funding is critical to achieving the ambitious targets and ensuring a steady transition.
- Technological Advancements: China is actively pursuing advancements in renewable energy technologies, particularly in areas like solar and wind power. These innovations are improving efficiency and lowering costs, making renewable energy more competitive with fossil fuels.
- Infrastructure Development: The construction of transmission lines and storage facilities is crucial for integrating renewable energy into the national grid. This development ensures reliable and consistent access to clean energy sources, facilitating the smooth transition.
- Public Awareness and Acceptance: Efforts to raise public awareness about the benefits of renewable energy are fostering greater public acceptance of the shift. This public understanding and support are crucial for achieving the government’s targets.
Examples of Successful Renewable Energy Projects
China has already undertaken numerous successful renewable energy projects. These projects showcase the country’s commitment to transitioning to a cleaner energy future. The construction of large-scale solar and wind farms, coupled with advancements in energy storage technologies, demonstrate the significant strides made in this area.
International Collaboration
China’s renewable energy ambitions extend beyond its borders, actively fostering international collaborations to accelerate technological advancements and knowledge sharing. This approach recognizes the global nature of the energy transition and leverages the expertise and resources of other nations. The collaborative spirit fosters innovation and accelerates the deployment of renewable energy solutions worldwide.
China’s impressive strides in renewable energy are truly remarkable. They’re making significant investments and pushing the boundaries of solar and wind power. While that’s happening, it’s interesting to see the political landscape, like the discussion around does Trump plan to annex Canada? Marco Rubio’s 51st state comments , which, frankly, distracts from the real progress being made in clean energy.
China’s focus on sustainable solutions is a positive global development.
China’s International Partnerships
China engages in numerous partnerships with other countries, recognizing the benefits of knowledge exchange and joint projects. These partnerships are not just limited to governments; they often involve collaborations with research institutions, businesses, and NGOs, demonstrating a comprehensive approach to international cooperation. This multifaceted approach allows for the transfer of advanced technologies, best practices, and financial resources, fostering mutual benefit and accelerating progress in the renewable energy sector.
Exchange of Knowledge and Technologies
The exchange of knowledge and technologies is a crucial aspect of China’s international collaborations. China actively seeks to learn from other countries’ experiences and expertise, while also sharing its own advancements in renewable energy technologies. This exchange benefits both sides, promoting the rapid development and deployment of innovative renewable energy solutions. This includes sharing research findings, technological blueprints, and training programs.
Collaboration with International Organizations
China actively collaborates with international organizations on renewable energy projects. These partnerships leverage the global platform and resources of organizations like the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), and others. This collaboration facilitates the sharing of best practices, the development of global standards, and the mobilization of financial resources for renewable energy projects.
These partnerships facilitate joint research, capacity building programs, and the establishment of common goals and standards.
Key International Collaborations
| Partner Country/Organization | Project Details |
|---|---|
| Germany | Joint research and development on advanced photovoltaic technologies, including perovskite solar cells, and energy storage solutions. This collaboration involves several research institutions and companies on both sides. |
| United States | Collaboration on offshore wind energy technologies, focusing on turbine design, installation techniques, and grid integration strategies. Specific projects include joint studies and pilot programs in the respective countries. |
| European Union | Developing standardized protocols and methodologies for assessing the environmental impact of renewable energy projects, sharing best practices in environmental impact assessments. This includes training programs for Chinese environmental assessment experts. |
| International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) | Active participation in IRENA initiatives, including the development of regional renewable energy strategies, supporting capacity building programs for developing countries, and contributing to the global dissemination of renewable energy knowledge. |
Case Studies of Success
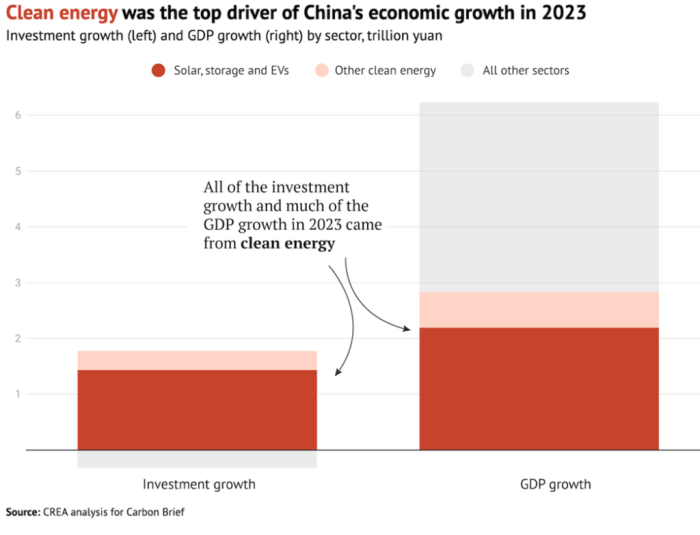
China’s robust renewable energy push isn’t just about policy and investment; it’s about tangible results. Real-world projects showcase the effectiveness of China’s strategies and highlight the crucial elements driving this transition. These successful initiatives offer valuable lessons for other nations seeking to embrace sustainable energy.
The Three Gorges Dam Solar Integration
The Three Gorges Dam, a massive hydroelectric power station, has begun integrating solar power into its operations. This innovative approach leverages the dam’s existing infrastructure and grid connections to seamlessly incorporate solar energy. The project demonstrates a strategic use of existing infrastructure to diversify the energy mix and enhance grid stability.
- Enhanced Grid Reliability: The integration of solar power into the grid helps to balance fluctuations in energy supply, providing a more reliable and stable energy source.
- Reduced Reliance on Fossil Fuels: By increasing the share of renewable energy, the project helps reduce the overall dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to cleaner energy generation.
- Economic Benefits: The project has spurred the growth of the local solar industry, creating jobs and opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- Community Engagement: The integration project fostered collaboration between the government, local communities, and energy companies, enhancing public acceptance of renewable energy sources.
The Xinjiang Wind Power Project
The Xinjiang wind power project stands as a testament to China’s vast renewable energy potential. The project showcases the effectiveness of large-scale wind farm development, demonstrating the significant role of government support in infrastructure creation and the long-term economic viability of renewable energy sources.
China’s impressive strides in renewable energy are truly remarkable. From massive solar farms to groundbreaking wind turbine technology, they’re clearly demonstrating a commitment to a cleaner future. However, the global geopolitical landscape is complex, and events like the ongoing Gaza-Israel military plan, as detailed in this article gaza israel military plan netanyahu , highlight the stark contrast between these advancements and the urgent need for peaceful resolutions.
Despite these challenges, China’s focus on renewable energy remains a vital step towards a sustainable future.
- Technological Advancement: The project leveraged cutting-edge wind turbine technology, driving innovation and improving energy generation efficiency.
- Significant Job Creation: The project attracted significant investment and resulted in substantial job creation, fostering economic growth in the region.
- Environmental Impact Reduction: The transition from fossil fuels to wind power significantly reduced the environmental footprint of energy production in the region.
- Infrastructure Development: The project required extensive infrastructure development, including grid upgrades and transmission lines, illustrating the long-term investment needed for renewable energy projects.
The Inner Mongolia Photovoltaic Park
The Inner Mongolia photovoltaic park is a prime example of large-scale solar energy development. The project showcases the effectiveness of economies of scale in solar power generation.
- Economies of Scale: The sheer size of the park facilitated cost reductions and improved efficiency in solar energy production.
- Government Support: The project demonstrates the significance of government incentives and policies in encouraging renewable energy investments and reducing barriers to entry.
- Energy Security: The large-scale solar project significantly contributes to China’s energy security, reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels.
- Land Use Efficiency: The project effectively utilizes vast land areas, minimizing the environmental impact on surrounding ecosystems.
“The success of these projects hinges on a confluence of factors: strong government support, robust investment, technological innovation, and a focus on building the necessary infrastructure.”
China’s impressive strides in renewable energy are truly remarkable. They’re aggressively pursuing ambitious goals, from massive solar farms to wind power expansions. However, it’s worth considering the broader global context, like the ongoing legal debate surrounding potential deportations of US citizens, as sparked by recent Trump comments can a u s citizen be deported trumps comments spark legal debate.
These issues, while different, highlight the complex interplay between national policies and global issues. Ultimately, China’s dedication to renewable energy is still a positive development for the planet.
Challenges and Obstacles
China’s ambitious renewable energy goals face significant hurdles, requiring careful consideration and proactive solutions to ensure a successful transition. The country’s rapid industrialization and energy demands present complex trade-offs between economic growth and environmental sustainability. Overcoming these challenges necessitates a multifaceted approach encompassing technological advancements, policy refinements, and public engagement.
Geographic and Infrastructure Limitations
China’s vast and diverse geography presents significant obstacles to renewable energy deployment. Uneven distribution of resources, such as solar irradiance and wind potential, necessitates tailored strategies for different regions. Existing infrastructure, particularly in remote areas, may be inadequate for the transmission and distribution of renewable energy. Building new transmission lines and upgrading existing ones is crucial to ensure grid stability and efficient energy delivery.
Furthermore, the uneven distribution of renewable resources across the country requires targeted investments in specific regions to maximize their potential.
Intermittency of Renewable Sources
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are inherently intermittent. This fluctuation in power generation poses a challenge to grid stability and necessitates robust energy storage solutions. Integrating large-scale renewable energy into the existing grid requires sophisticated forecasting and control systems to manage the variability of supply. Strategies for energy storage, such as pumped hydro storage, battery storage, and hydrogen production, are crucial for overcoming this challenge and ensuring a reliable energy supply.
Financial and Economic Barriers
While significant investments have been made, the financial resources required for large-scale renewable energy projects are substantial. High upfront costs and concerns about return on investment can deter private sector participation. Government subsidies and incentives can help mitigate these costs and encourage private investment. Developing innovative financing mechanisms, such as green bonds and project financing, is essential to attract capital and accelerate the transition to renewables.
Policy and Regulatory Uncertainty
Inconsistencies or changes in government policies and regulations can create uncertainty for investors and hinder the development of renewable energy projects. Long-term policy stability is essential for attracting and retaining investment. Clearer regulatory frameworks and predictable policy environments are critical for creating a favorable investment climate and ensuring the sustainability of renewable energy projects.
Public Awareness and Acceptance
While public awareness of renewable energy is growing, concerns about job displacement and local impacts of projects can hinder acceptance. Addressing these concerns through transparent communication, community engagement, and workforce retraining programs is essential. Building public trust and fostering a sense of shared responsibility are vital for achieving widespread support for renewable energy initiatives.
Table: Challenges and Proposed Solutions
| Challenge | Proposed Solution |
|---|---|
| Geographic and Infrastructure Limitations | Targeted investments in specific regions, building new transmission lines, upgrading existing infrastructure. |
| Intermittency of Renewable Sources | Development and implementation of energy storage solutions (e.g., pumped hydro, batteries), sophisticated forecasting and control systems. |
| Financial and Economic Barriers | Government subsidies and incentives, innovative financing mechanisms (e.g., green bonds, project financing), promoting private sector participation. |
| Policy and Regulatory Uncertainty | Long-term policy stability, clear regulatory frameworks, predictable policy environments. |
| Public Awareness and Acceptance | Transparent communication, community engagement, workforce retraining programs. |
Future Outlook
China’s ambitious renewable energy targets are poised for significant growth in the coming decade. The nation’s commitment to a cleaner energy future is driving substantial investment, technological advancements, and infrastructure development. This commitment reflects a strategic move to diversify energy sources, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and mitigate the impacts of climate change. The projected trajectory suggests a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector, presenting both opportunities and challenges.
Projected Growth of Renewable Energy
China’s renewable energy sector is expected to experience substantial growth over the next decade. Government policies, supportive incentives, and increasing public awareness are fueling this expansion. Factors such as declining costs of renewable energy technologies, rising energy demands, and the need to achieve emission reduction goals are all contributing to this growth. The increasing integration of renewable energy sources into the national grid will be crucial in this expansion.
Potential Impact on the Chinese Economy and Society
The growth of renewable energy will have a multifaceted impact on the Chinese economy and society. Job creation in the renewable energy sector will be a key outcome. The development of new technologies and industries will stimulate innovation and economic growth. Improved air quality and reduced reliance on imported fossil fuels will contribute to a healthier environment and a more secure energy supply.
Predictions for Sector Future Development
Several key predictions regarding the sector’s future development can be made. Firstly, solar and wind power generation are expected to significantly increase, further enhancing the energy mix. Secondly, energy storage technologies will play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and stability of the grid as renewable energy sources become more prominent. Thirdly, smart grids and digital technologies will optimize the management and distribution of renewable energy.
These advancements will also lead to greater energy efficiency and grid resilience.
Expected Changes in the Sector
The expected changes in the sector can be visualized in a bar graph depicting the projected growth of different renewable energy sources (solar, wind, hydro) from 2024 to 2034. The graph would show a steady and substantial increase in the contribution of renewable energy to the total energy mix. The y-axis would represent the percentage of total energy generation, while the x-axis would represent the years.
A noticeable upward trend in all three renewable energy sources would be observed, highlighting the significant growth trajectory. The graph would also illustrate the anticipated transition from a primarily fossil fuel-based energy system to a more diversified and sustainable energy mix.
Closing Summary
China’s dedication to renewable energy is a significant global development. This journey is not without challenges, but the nation’s commitment to ambitious goals and innovative approaches offers valuable lessons for other countries striving for a sustainable future. The combination of government support, technological prowess, and substantial investment positions China as a key player in the global transition to renewable energy.
The future outlook is bright, and China’s influence on the renewable energy sector will undoubtedly continue to grow.

