Hyperfixating focus autism adhd neurodivergent – Hyperfixating focus, autism, ADHD, neurodivergent – this fascinating topic delves into the unique world of intense focus experienced by many neurodivergent individuals. We’ll explore the characteristics of hyperfixation, distinguishing it from typical obsessions and hobbies. We’ll also look at the neurobiological underpinnings, the impact on daily life, and practical strategies for navigating these experiences.
This exploration examines the differences in hyperfixation experiences between individuals with autism and ADHD, highlighting the varied manifestations and common triggers. We’ll uncover the positive aspects of hyperfixation, its potential for learning and creativity, and how to effectively manage its intensity. Further, we will address the social implications and sensory processing components, providing actionable insights for understanding and supporting neurodivergent individuals.
Understanding Hyperfixation
Hyperfixation is a fascinating and often misunderstood aspect of neurodivergent experiences, particularly those associated with autism and ADHD. It’s a state of intense, focused attention on a specific topic, activity, or object, often characterized by an unusual level of engagement and energy. While it can be incredibly productive, hyperfixation can also present challenges in managing daily life. Understanding its characteristics and how it interacts with other aspects of neurodiversity is key to navigating this experience effectively.Hyperfixation is distinct from typical hobbies or obsessions.
While all three involve intense interest, hyperfixation is characterized by a deeper, more all-consuming engagement. A hobby might involve periodic exploration, while a hyperfixation often leads to extended periods of focused activity, often neglecting other responsibilities or social interactions. The core difference lies in the level of absorption and the impact it has on daily life.
Characteristics of Hyperfixation
Hyperfixation is typically marked by a profound and sustained focus on a particular subject. This focus can manifest in a wide range of activities, from intricate details in a specific area of knowledge to the repetitive practice of a skill. The intensity of this focus can be remarkable, often leading to exceptional levels of performance in the area of interest.
This is a distinct difference from simply enjoying a hobby or interest, as the intensity of engagement becomes a significant part of daily life.
Duration and Intensity of Hyperfixation
The duration of hyperfixations can vary significantly, ranging from a few days to several weeks or even months. While the precise duration isn’t a defining factor, the sustained intensity of focus is. Individuals experiencing hyperfixation often find themselves immersed in their chosen topic, losing track of time and often neglecting other responsibilities. The intense focus can also lead to a significant drop in other activities, impacting daily routines and potentially causing disruptions.
Hyperfixation vs. Hobbies and Obsessions
While hyperfixations share some similarities with hobbies and obsessions, they differ significantly in their nature and impact. Hobbies are typically pursued in a balanced manner, integrated into daily life without completely overshadowing other responsibilities. Obsessions, while intense, often involve a negative or anxiety-inducing element that can be disruptive and distressing. Hyperfixation, on the other hand, can be both engaging and potentially disruptive, with the intensity and duration significantly impacting daily routines.
Neurobiological Underpinnings
The neurobiological basis of hyperfixation is still being investigated, but research suggests a connection to conditions like autism and ADHD. These conditions often involve differences in brain circuitry and neurotransmitter systems, which might contribute to the heightened focus and sustained engagement characteristic of hyperfixation. Individuals with autism and ADHD might experience hyperfixations more frequently and intensely compared to neurotypical individuals.
Types of Hyperfixations and Examples
Hyperfixations can take many forms, reflecting the vast array of human interests. Some examples include:
- Specific Areas of Knowledge: A deep dive into a particular historical period, a scientific concept, or a specific genre of literature. The benefits of this could be a profound understanding of the topic and the development of new knowledge and skills. Drawbacks might include neglecting other responsibilities, or the tendency to become overly focused on specific details and losing the broader perspective.
- Skills and Activities: Developing a new skill, like programming, music, or art. The potential benefits are enhanced skills and potentially new career paths. The drawbacks include neglecting other responsibilities and social interactions, potentially leading to isolation.
- Specific Objects or Collections: A fascination with stamps, coins, or a particular type of object. Benefits might include developing a passion for collecting and potentially acquiring valuable knowledge. The drawbacks can be financial or organizational, potentially leading to significant disruption to daily life.
Impact on Daily Routines and Social Interactions
Hyperfixations can significantly impact daily routines, leading to neglect of other responsibilities and social interactions. The intensity of the focus can cause individuals to prioritize their hyperfixation over other tasks, potentially leading to missed appointments, deadlines, or other obligations. Furthermore, the sustained focus can lead to social withdrawal, as the individual may lose interest in or become overwhelmed by social interactions, potentially leading to difficulties in maintaining relationships.
It’s important to recognize and manage these impacts to ensure a healthy balance.
Hyperfixation in Neurodivergent Individuals: Hyperfixating Focus Autism Adhd Neurodivergent
Hyperfixation, a state of intense focus and absorption in a particular subject or activity, is a common experience for neurodivergent individuals, particularly those with autism and ADHD. This intense engagement can manifest in different ways, impacting learning, development, and daily life. Understanding the nuances of hyperfixation across these conditions is crucial for supporting and encouraging positive outcomes.While hyperfixation can be a powerful tool for learning and creativity, it can also lead to challenges if not managed effectively.
Recognizing the unique characteristics and triggers associated with hyperfixation in autism and ADHD is essential for tailoring support and strategies that optimize learning and well-being.
Comparing Hyperfixation Experiences in Autism and ADHD
Hyperfixation in autism and ADHD, while sharing the core characteristic of intense focus, often manifests differently due to the unique cognitive and behavioral profiles of each condition. Individuals with autism might experience hyperfixation as a deeply immersive exploration of a specific topic, often characterized by detailed analysis and meticulous attention to detail. Conversely, individuals with ADHD might experience hyperfixation as a more volatile and shifting focus, marked by rapid transitions between interests and activities.
Manifestations of Hyperfixation in Autism
Individuals with autism often exhibit a deep, focused engagement with a specific topic. This engagement can involve extensive research, collecting related materials, and creating intricate projects or systems related to the hyperfixation. Their intense focus can also lead to repetitive behaviors, such as compulsive arranging or organizing objects associated with the topic.
Manifestations of Hyperfixation in ADHD
Individuals with ADHD might experience hyperfixation as an intense burst of energy and focus, followed by rapid shifts to new interests. This fluctuating focus can make it challenging to maintain sustained engagement with a single topic for extended periods. The hyperfixation might also manifest as impulsive behaviors related to the topic, such as excessive spending or engaging in risky activities.
Common Triggers and Patterns
Hyperfixation in neurodivergent individuals is often triggered by novelty, fascination, or a perceived gap in knowledge. A new piece of information, a captivating concept, or a topic that seems unresolved can ignite an intense focus. The patterns of hyperfixation can also be influenced by sensory experiences, environmental factors, and personal history.
- Novelty: New and unfamiliar information or concepts often spark intense focus.
- Fascination: Intriguing topics or ideas that capture attention can lead to extended periods of hyperfocus.
- Gaps in Knowledge: A sense of needing to understand a specific concept or area can trigger an intense period of learning and exploration.
- Sensory Experiences: Specific sensory experiences can be linked to the initiation and persistence of hyperfixation.
- Environmental Factors: External factors like quiet environments or reduced distractions can contribute to the intensity of hyperfixation.
Impact on Learning and Development
Hyperfixation can significantly impact learning and development in neurodivergent individuals. The intense focus associated with hyperfixation can lead to rapid learning and mastery of specific topics, resulting in deeper understanding and increased knowledge. However, it can also lead to neglecting other areas of development or learning, highlighting the importance of balance and support.
Positive Applications of Hyperfixation
Hyperfixation can be a powerful tool for personal growth and learning. By channeling this focused energy, neurodivergent individuals can achieve significant progress in areas of interest. Providing appropriate support and structure can help to redirect this intense focus into positive and productive endeavors.
- Deep Learning: Hyperfixation can facilitate rapid and in-depth learning within a specific area.
- Creative Expression: The intense focus can fuel creative endeavors, leading to unique artistic expressions.
- Problem Solving: The deep dive into a specific topic can provide unique insights and solutions.
- Skill Development: Sustained engagement can lead to rapid skill development in the area of hyperfocus.
Focus and Attention in Neurodivergence
Attention and focus are fundamental aspects of human cognition, enabling us to selectively process information and respond effectively to our environment. However, neurodivergent individuals often experience these processes differently than neurotypical individuals. This difference isn’t a deficit, but rather a variation in how the brain processes information. Understanding these variations is crucial for providing support and fostering a more inclusive environment.Neurodivergence encompasses a wide spectrum of conditions, including Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), and others.
These conditions affect the brain’s ability to regulate attention, leading to diverse challenges and strengths. Recognizing the nuances of these experiences is key to providing tailored support.
Hyperfixating focus is a common experience for those on the autism spectrum, ADHD, and other neurodivergent identities. It’s that intense, almost obsessive concentration on a particular topic. Sometimes this focus can be channeled into incredible creativity and productivity, but it can also be a challenge to manage. Luckily, tools like ChatGPT can be incredibly helpful in these situations, offering various ways to refine writing skills.
For example, check out 8 ways ChatGPT can make you a better writer to see how this AI can help with brainstorming, structuring, and polishing your work. This targeted focus, when harnessed effectively, can be a powerful asset for neurodivergent individuals.
Different Types of Attentional Challenges
Neurodivergent individuals can experience various attentional challenges. These challenges are not simply about “paying attention” but involve difficulties in regulating and directing their attentional resources. A crucial aspect is understanding the multifaceted nature of attention itself.
- Sustained Attention: Difficulty maintaining focus on a task over an extended period. This can manifest as a tendency to get easily distracted or lose interest in activities that require prolonged concentration. For example, a person with ADHD might struggle to complete a lengthy report, while someone with ASD might find it difficult to sit through a lecture.
- Selective Attention: Difficulty filtering out irrelevant stimuli. This can lead to being overwhelmed by sensory input or getting easily sidetracked by environmental factors. A person with ASD might be highly sensitive to noises or lighting, making it challenging to focus in a crowded or brightly lit environment. Conversely, someone with ADHD might struggle to ignore background chatter when attempting to complete an assignment.
- Alternating Attention: Difficulty shifting focus between different tasks or types of information. This can make it hard to juggle multiple responsibilities or switch between activities. A student with ASD might find it challenging to transition from one subject to another, while someone with ADHD might struggle to switch between a creative project and a more structured task.
- Divided Attention: Difficulty attending to multiple tasks simultaneously. This can be a significant hurdle for individuals with ADHD, making it difficult to manage various responsibilities simultaneously. For example, a person with ADHD might struggle to listen to a teacher and take notes simultaneously.
Relationship Between Hyperfixation and Other Attentional Difficulties
Hyperfixation, a focused state of intense interest and engagement, is often associated with neurodivergence. While hyperfixation can be a source of strength and creativity, it can also disrupt other aspects of attention. For instance, a hyperfixation on a particular hobby might lead to neglecting other important tasks or responsibilities.The relationship between hyperfixation and other attentional challenges is complex. Hyperfocus can be a form of intense selective attention, but it can also lead to a diminished capacity for sustained attention to other areas.
Strategies for Managing Attentional Challenges and Hyperfixation
Effective strategies for managing attentional challenges and hyperfixation involve a multifaceted approach, tailored to individual needs. Understanding the specific attentional difficulties faced by the neurodivergent individual is crucial.
- Structured Environments: Creating a structured environment can help neurodivergent individuals manage distractions and maintain focus. Clear routines, designated spaces, and visual aids can all contribute to a more predictable and manageable environment. For instance, a visual schedule can help a person with ASD understand the sequence of daily activities, minimizing uncertainty and stress.
- Sensory Accommodations: Adjusting the sensory environment can significantly impact attention and focus. Providing noise-canceling headphones, fidget toys, or regulated lighting can create a more conducive learning or work environment for some individuals.
- Break-Down Tasks: Breaking down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable steps can make them less overwhelming and easier to complete. This strategy can be particularly helpful for individuals with ADHD or ASD who might struggle with the scope of a larger project.
- Reward Systems: Implementing a reward system can help reinforce positive behaviors related to focus and attention. Positive reinforcement can motivate individuals to sustain attention and complete tasks.
Environmental Factors Influencing Focus and Attention
Environmental factors can significantly influence focus and attention in neurodivergent individuals. Understanding these influences is essential for creating supportive environments.
Hyperfixating focus is a fascinating aspect of autism, ADHD, and other neurodivergent conditions. It’s like a laser beam of intense concentration, often on a very specific subject. For example, checking out the 10 greatest sports teams in history according to AI the 10 greatest sports teams in history according to ai might become a hyperfixation, consuming hours of research and discussion.
This focused energy can be incredibly productive, driving creativity and achievement in various fields, just as it can with the fascinating detail of sports history.
- Sensory Overload: Overwhelming sensory input, such as loud noises, bright lights, or cluttered spaces, can significantly disrupt focus and attention in neurodivergent individuals. For example, a classroom with excessive noise or a chaotic workspace can make it hard for someone with ASD or ADHD to concentrate.
- Lack of Structure: A lack of structure and predictability can increase feelings of anxiety and overwhelm, making it difficult to focus. Providing clear routines and expectations can improve focus and reduce stress for individuals with ASD or ADHD.
- Social Interactions: Social interactions can be stimulating or overwhelming depending on the individual and the specific interaction. Overly stimulating social environments can be disruptive, whereas structured social settings can be beneficial.
Strategies for Managing Hyperfixation
Hyperfixation, a characteristic often associated with neurodivergent conditions like autism and ADHD, can be a powerful force. It’s a state of intense focus and engagement in a specific topic or activity. While this intense focus can be incredibly productive, it can also lead to challenges if not managed effectively. This exploration delves into strategies for navigating hyperfixation, emphasizing balance and well-being.Understanding that hyperfixation is not a problem to be “cured,” but a facet of neurodiversity, empowers us to harness its potential while mitigating potential downsides.
The key lies in developing strategies that allow us to embrace the positive aspects of this focused state while maintaining a healthy equilibrium with other responsibilities and life aspects.
Framework for Understanding and Managing Hyperfixation
Hyperfixation management is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Neurodivergent individuals experience hyperfixation differently, and a tailored framework is essential. This framework recognizes the intensity and duration of the hyperfixation, the individual’s specific interests, and the potential impact on other areas of life. A critical component is identifying personal triggers and patterns that precede or accompany hyperfixation episodes. This understanding helps predict and prepare for these periods.
Hyperfixating focus is a fascinating aspect of autism, ADHD, and other neurodivergent traits. It’s amazing how intensely focused some people can become on a particular subject, and the next pope candidates, like Cardinal Zuppi, Parolin, Tagle, Turkson, and Erdő, are certainly individuals with impressive levels of dedication and focus. This intense focus, whether on theological debate or something else entirely, is a hallmark of the neurodivergent experience.
next pope candidates zuppi parolin tagle turkson erdo It’s fascinating to consider how these individuals approach such a significant role, and how their unique perspectives could shape the future of the Catholic Church. This hyperfixation can be both a strength and a challenge, but it’s a crucial part of understanding neurodivergent minds.
Practical Strategies for Supporting Neurodivergent Individuals
Effective support involves understanding the individual’s strengths and preferences. Promoting a safe and structured environment is vital, as is acknowledging and respecting the intensity of the focus. Encouraging healthy boundaries and clear communication channels are paramount to prevent burnout or overwhelm.
Coping Mechanisms for Managing Hyperfixation
| Coping Mechanism | Description | Example | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Modifications | Creating a dedicated workspace or designated “hyperfocus zone” can help contain the intensity of focus. | A quiet room with minimal distractions, or headphones to block out external noise. | Reduces distractions and allows for uninterrupted engagement with the hyperfixation. |
| Time Management Techniques | Breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable chunks, with scheduled breaks, can help prevent burnout and maintain balance. | Setting a timer for focused work sessions followed by short breaks, using a planner to schedule hyperfixation time. | Maintains productivity while preventing exhaustion and promoting overall well-being. |
| Social Support Systems | Enlisting support from family, friends, or therapists can provide understanding, encouragement, and accountability. | Discussing the hyperfixation with a trusted friend or family member, or seeking guidance from a therapist specializing in neurodiversity. | Provides emotional support, reduces isolation, and offers perspectives outside of the hyperfixation’s intensity. |
Setting Healthy Boundaries
Clearly defined boundaries, both internal and external, are crucial. Understanding the limits of engagement and communicating those limits to others is vital for preventing over-immersion in the hyperfixation. This includes setting time constraints for the hyperfixation activity and acknowledging the need for breaks and social interaction.
Balancing Hyperfixation with Other Tasks
Finding a balance between the intense focus of hyperfixation and other essential tasks and responsibilities requires careful planning and prioritization. Strategies like using a visual schedule, breaking down large tasks into smaller ones, or scheduling specific time blocks for different activities can aid in this process. This approach allows the individual to engage with their hyperfixation while also fulfilling their other obligations.
A crucial component is recognizing that hyperfixation can be a productive force.
Hyperfixation and Creativity

Hyperfixation, a characteristic often associated with neurodivergent individuals, can be a powerful catalyst for creativity. It’s a focused state of intense interest and engagement in a particular subject or activity, often accompanied by an immersive and almost obsessive level of attention. This deep dive into a topic can unlock innovative thinking and problem-solving abilities in unexpected ways. The passion and dedication fueled by hyperfixation can lead to breakthroughs and significant contributions in various fields.This intense focus, while sometimes challenging to manage, can be a remarkable asset in fostering creativity.
The sustained concentration allows for deep exploration, detailed analysis, and the synthesis of ideas in a way that might not be possible with more superficial engagement. This can manifest as original artistic expression, groundbreaking scientific discoveries, or ingenious solutions to complex problems. By understanding and leveraging the unique characteristics of hyperfixation, neurodivergent individuals can harness their intense focus for creative endeavors.
The Fueling Effect of Hyperfixation on Innovative Thinking
Hyperfixation acts as a powerful engine for innovative thinking. The sustained engagement with a specific topic allows for the development of deep expertise and a nuanced understanding of the subject matter. This profound knowledge base provides a rich foundation for creative problem-solving. The ability to connect seemingly disparate concepts and ideas, a hallmark of innovation, is often facilitated by the intense focus of hyperfixation.
Examples of Successful Individuals with Neurodivergence and Hyperfixation, Hyperfixating focus autism adhd neurodivergent
Numerous successful individuals with neurodivergence have used their hyperfixations to achieve great things. For example, Albert Einstein, often cited as a prime example of a highly creative individual, displayed a notable focus on a limited range of ideas. Similarly, many artists, musicians, and inventors have demonstrated the powerful connection between hyperfixation and artistic expression. In the realm of technology, figures like Steve Jobs, known for his relentless focus on product design and user experience, also exhibited characteristics of hyperfixation.
Harnessing Hyperfixation to Overcome Obstacles and Achieve Goals
Hyperfixation can be a valuable tool for overcoming obstacles and achieving goals. The intense focus allows for sustained effort and dedication, often surpassing the limitations of traditional methods. The immersive nature of hyperfixation can provide the motivation and persistence needed to tackle complex challenges and persevere through setbacks. This ability to overcome challenges is often tied to a passion and dedication to the subject matter, fostering resilience in the face of adversity.
Leveraging Hyperfixation to Support Learning and Skill Development
Hyperfixation can be a powerful ally in the learning process. The deep engagement with a specific topic can lead to accelerated learning and skill development. The intense focus allows for thorough understanding and mastery of the subject matter. The dedication and persistence inherent in hyperfixation can lead to significant improvements in learning and skill development. This intense focus can be harnessed to learn new languages, master musical instruments, or delve into complex scientific theories.
This deep engagement is a pathway to mastery.
Social Implications of Hyperfixation
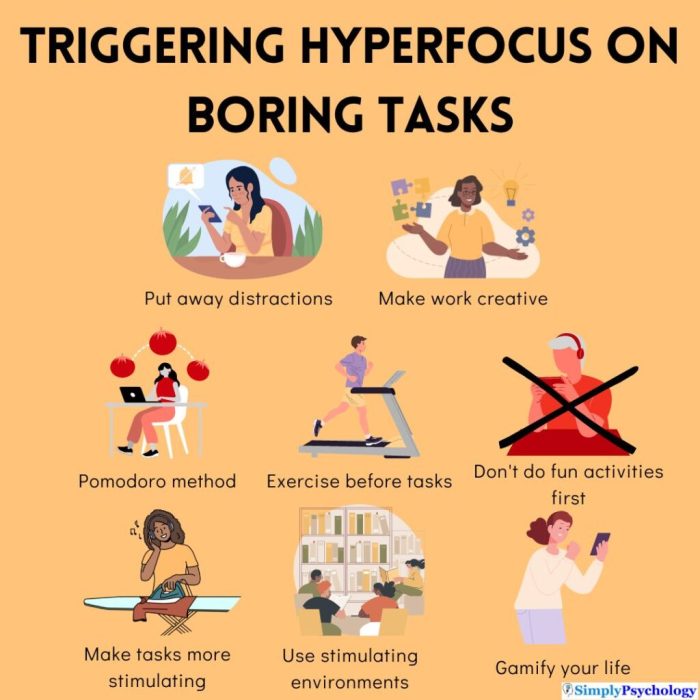
Hyperfixation, a common experience for neurodivergent individuals, can significantly impact social interactions. While often viewed as a solitary pursuit, the intense focus associated with hyperfixation can create challenges in navigating the complexities of social environments. Understanding these implications is crucial for fostering empathy and creating supportive social networks.Hyperfixation, characterized by an all-consuming interest, can lead to a disconnect from the immediate social context.
This intense focus can manifest in various ways, from neglecting social cues to becoming overly absorbed in conversations related to the hyperfixation topic, potentially leaving others feeling excluded or unheard. Recognizing these patterns can pave the way for more inclusive and meaningful social interactions.
Social Challenges Associated with Hyperfixation
Hyperfixation can present various social challenges. Neurodivergent individuals may struggle to maintain appropriate social boundaries, find common ground in conversations, or adapt to shifting social situations. This is because the intense focus on the hyperfixation topic can overshadow other social considerations. Their responses might seem inappropriate or disengaged to others unfamiliar with hyperfixation.
Impact on Social Interactions
Hyperfixation can significantly impact social interactions in numerous ways. For example, an individual hyperfixated on trains might dominate conversations with detailed descriptions of specific train routes, schedules, and histories, potentially leaving others feeling overwhelmed or uninterested. Similarly, a person hyperfixated on a specific video game might be overly enthusiastic about discussing strategies, characters, or lore, leading to social awkwardness or a perceived lack of interest in other topics.
These examples highlight how hyperfixation can create social barriers, even when the individual has good intentions.
Strategies for Fostering Understanding and Acceptance
Creating a supportive social environment for neurodivergent individuals experiencing hyperfixation involves actively fostering understanding and acceptance. Open communication, empathy, and patience are essential components. Explicitly explaining the experience of hyperfixation to others can help them understand the underlying motivation and the intensity of the focus.
Importance of Open Communication and Empathy
Open communication and empathy are vital when interacting with neurodivergent individuals experiencing hyperfixation. Instead of dismissing their enthusiasm or perceived “off-topic” discussions, empathetic individuals can actively listen and engage with the hyperfixation topic, even if it doesn’t align with their own interests. This demonstrates respect and fosters a sense of connection.
Strategies for Building Supportive Social Networks
Building supportive social networks for neurodivergent individuals with hyperfixation involves recognizing the unique needs and strengths associated with this experience. Creating a safe space where these individuals can express their interests without judgment or ridicule is crucial. This includes fostering environments where shared interests are encouraged and valued. Support groups, online communities, or dedicated social events can serve as valuable platforms for connection and support.
Hyperfixation and Sensory Processing
Hyperfixation, a state of intense focus and absorption, is a common experience for neurodivergent individuals. However, this intense focus can be intricately intertwined with sensory processing differences. Understanding how sensory experiences interact with hyperfixation is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage and support these individuals.Sensory processing differences are often significant factors that contribute to, trigger, and influence hyperfixation episodes.
The unique way neurodivergent individuals perceive and react to sensory information can create a powerful interplay with their intense focus. This interplay can make hyperfixation experiences both rewarding and challenging.
The Relationship Between Hyperfixation and Sensory Processing
Neurodivergent individuals frequently experience sensory sensitivities, either heightened or muted responses to stimuli. These sensitivities can play a significant role in the development and intensity of hyperfixation. For example, a person might hyperfocus on a specific topic because the sensory input associated with it—a particular sound, texture, or visual pattern—is particularly calming or engaging. Conversely, overwhelming sensory input can disrupt or even derail a hyperfixation, causing the focus to shift or break altogether.
How Sensory Sensitivities Trigger or Influence Hyperfixation
Sensory sensitivities can act as both catalysts and constraints for hyperfixation. A calming sensory experience can trigger and sustain hyperfixation, whereas an overwhelming one can disrupt it. For instance, a person with a strong preference for quiet might hyperfocus on a hobby that involves minimal background noise, while another might be overwhelmed by a crowded environment during a hyperfixation.
The sensory environment is a powerful influencer of the hyperfixation experience.
Examples of How Sensory Environments Impact Hyperfixation Experiences
Specific sensory environments can significantly impact the nature and duration of a hyperfixation. A brightly lit space might be stimulating and distracting, hindering a hyperfixation on a detailed project. Conversely, a dimly lit space with soft music might be conducive to sustained hyperfocus. The sensory environment plays a critical role in the quality and intensity of a hyperfixation experience.
Sensory Regulation in Managing Hyperfixation
Recognizing the impact of sensory processing on hyperfixation is vital for effective management. Strategies for sensory regulation can help maintain a balanced environment, supporting and guiding the individual during a hyperfixation episode. This allows for greater control over the intensity and duration of the focus.
Sensory Strategies for Managing Hyperfixation
Sensory regulation is key to managing hyperfixation effectively. Different strategies can be employed to create an optimal environment, minimizing distractions and maximizing focus.
| Sensory Strategy | Description | Example | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Regulation | Controlling visual stimuli through filters, reducing clutter, or using specific lighting. | Using a visual timer, minimizing background distractions, using noise-canceling headphones. | Improved focus and reduced distractions. |
| Auditory Regulation | Managing auditory input by using noise-canceling headphones, white noise, or creating a quiet space. | Listening to calming music, using a white noise machine, or working in a soundproof room. | Reduced sensory overload and increased concentration. |
| Tactile Regulation | Providing calming or engaging tactile experiences, like fidget toys or weighted blankets. | Using a weighted lap pad, playing with clay, or wearing textured clothing. | Reduced anxiety and improved focus. |
| Movement Regulation | Incorporating movement breaks or activities to manage energy and sensory input. | Taking a walk, stretching, or doing light exercise. | Improved focus and reduced restlessness. |
Last Point
In conclusion, hyperfixation in neurodivergent individuals presents a complex interplay of intense focus, unique challenges, and considerable potential. Understanding the neurobiological underpinnings, diverse manifestations, and practical strategies for management is crucial for fostering inclusivity and supporting the remarkable talents of these individuals. This exploration underscores the importance of empathy, open communication, and tailored support systems.

