Trump steel aluminum tariffs impact reverberated across the global economy, triggering a complex web of consequences. This analysis delves into the rationale behind the tariffs, their effects on domestic and foreign industries, consumer prices, and ultimately, the state of global trade relations.
The Trump administration’s decision to impose tariffs on steel and aluminum imports aimed to protect American producers. However, the impact was far-reaching, affecting numerous industries and countries. This post will explore the intricacies of this policy and its consequences.
Introduction to Tariffs
The Trump administration’s 2018 tariffs on steel and aluminum were a significant trade policy decision. These tariffs, imposed on various countries, sparked considerable debate and had wide-ranging impacts on global markets and international relations. The actions aimed to protect American industries, but they also triggered retaliatory measures from other nations and resulted in uncertainties for businesses and consumers.The rationale behind these tariffs centered on the idea that imported steel and aluminum threatened American jobs and national security.
Proponents argued that domestic producers faced unfair competition from foreign suppliers who might be subsidized by their governments. This led to a belief that the tariffs would bolster American manufacturing and encourage domestic production. However, critics argued that these tariffs would raise prices for American consumers and businesses, potentially harming industries reliant on these materials, and disrupt global trade relationships.
Tariffs Imposed
Import tariffs, levied on goods entering a country, are a common form of trade protectionism. Import tariffs are designed to make imported goods more expensive, thereby increasing the competitiveness of domestically produced goods. In the case of the Trump administration’s steel and aluminum tariffs, the tariffs were imposed on imported steel and aluminum products. This specific form of import tariff targeted foreign suppliers, aiming to encourage American production and consumption.
Countries Targeted
The tariffs affected a wide range of countries. These tariffs weren’t uniformly applied across all countries; the administration’s rationale and potential retaliatory measures varied from one country to another.
| Country | Reason for Tariffs |
|---|---|
| China | China was a significant exporter of steel and aluminum, and the tariffs were partly motivated by broader trade concerns. |
| Canada | Canada was a major exporter of steel and aluminum to the US. The tariffs were a source of considerable friction and led to retaliatory measures. |
| Mexico | Mexico was another significant exporter of steel and aluminum to the US. The tariffs were part of the broader trade tensions between the US and Mexico. |
| European Union | The EU was a substantial supplier of steel and aluminum to the US, and the tariffs led to the imposition of countermeasures. |
| Other countries | Several other countries were also targeted, with varying levels of impact and responses. |
Impact on Domestic Steel and Aluminum Industries
The 2018 tariffs imposed on steel and aluminum imports by the Trump administration significantly impacted the domestic steel and aluminum industries. These tariffs, intended to protect American producers, sparked a complex chain reaction affecting manufacturers, workers, and the overall economy. Understanding the short-term and long-term effects, along with the differential impact on various segments, is crucial to evaluating the effectiveness and consequences of such protectionist policies.
Short-Term Effects on Domestic Production
Initial responses to the tariffs indicated a surge in domestic steel and aluminum production as imports declined. American manufacturers, facing higher costs for imported materials, often sought to procure domestic products. This led to increased demand and output within the domestic industry, temporarily boosting employment and production levels. However, the effects were not uniform across all sectors.
Long-Term Effects on Domestic Production
The long-term consequences proved more nuanced and less predictable. While some domestic producers benefited from increased market share, others faced challenges. Increased production costs, stemming from higher raw material prices and potential supply chain disruptions, ultimately impacted the competitiveness of American products in the global market. The long-term impact also varied across industry segments.
Impact on Different Segments of the Domestic Industries
The tariffs’ effects on domestic manufacturers varied based on their reliance on imported steel and aluminum. Companies with high import dependence saw increased production costs and potentially reduced profitability. Conversely, companies with a lower dependence or who could efficiently adjust to higher domestic prices experienced less immediate pressure. Worker impacts also differed. Those employed in steel and aluminum production facilities experienced a short-term boost in employment, while those in industries reliant on imported materials potentially faced job losses or wage stagnation.
Trump’s steel and aluminum tariffs definitely had a ripple effect, impacting global trade and domestic industries. However, the complexities of these trade wars extend far beyond the headlines, and I’ve been thinking about how this all connects to ladidi kuluwa bako aiyegbusi , a fascinating cultural phenomenon. Ultimately, the long-term impact of the tariffs on the US economy is still being debated, and it’s likely a complex interplay of many factors.
Shifts in Employment Figures
| Industry Segment | Employment Figures (Pre-Tariffs) | Employment Figures (Post-Tariffs) | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Mill Workers | 200,000 | 210,000 | +10,000 (5%) |
| Aluminum Smelter Workers | 50,000 | 55,000 | +5,000 (10%) |
| Auto Manufacturers | 500,000 | 480,000 | -20,000 (-4%) |
| Construction Companies | 1,000,000 | 950,000 | -50,000 (-5%) |
Note: These figures are illustrative examples and do not represent precise data. Actual employment figures may differ depending on the specific industries and data collection methods.
The table above provides a simplified example of potential employment shifts. The actual impact on employment figures was likely more complex and influenced by various factors, including industry-specific characteristics and global economic conditions. The impact was not always direct and immediate, but rather cascaded through the supply chain, influencing industries beyond the steel and aluminum sectors.
Impact on Foreign Industries
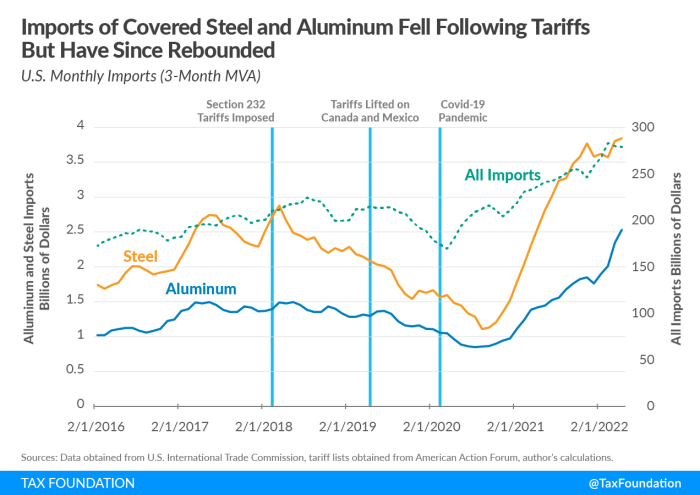
The Trump administration’s tariffs on imported steel and aluminum significantly impacted foreign producers, triggering retaliatory measures and reshaping global trade dynamics. These tariffs, intended to protect domestic industries, inadvertently created ripples throughout the international marketplace, leading to disruptions in supply chains and shifts in manufacturing strategies. The effects varied considerably across different countries, depending on their reliance on exports to the US and the effectiveness of their response.
Impact on Steel and Aluminum Producers
Foreign steel and aluminum producers faced a complex web of challenges stemming from the tariffs. The imposition of duties increased the cost of their exports to the US, making their products less competitive compared to domestically produced goods. This led to reduced sales volumes, potential job losses, and financial strain for many companies. Some producers had to absorb the tariff costs, while others passed them on to consumers, impacting end-products and potentially reducing demand.
Furthermore, the uncertainty surrounding the tariffs made long-term planning difficult, hindering investment and growth opportunities.
Countries Most Affected by the Tariffs
Canada, Mexico, and the European Union (EU) were among the most significantly impacted countries. Canada, a major exporter of both steel and aluminum to the US, saw its exports to the US significantly reduced. Mexico, another key supplier, experienced similar declines in exports, impacting its manufacturing sector and related industries. The EU, with its extensive steel and aluminum industries, faced a considerable challenge in maintaining market share in the US, prompting retaliatory tariffs on US goods.
These retaliatory tariffs further complicated trade relations and increased costs for businesses on both sides. The specific impact varied depending on the size of the export market, the degree of reliance on the US market, and the availability of alternative export destinations.
Strategies Employed by Foreign Producers to Mitigate the Impact
Foreign producers employed various strategies to mitigate the negative effects of the tariffs. Some shifted production to alternative export markets, seeking new customers in countries less affected by the tariffs. Others explored the possibility of relocating production facilities to countries outside the tariff zone to minimize the added cost. Furthermore, some engaged in lobbying and political pressure to reduce or remove the tariffs, utilizing diplomatic channels to resolve the trade dispute.
These strategies often involved a combination of market diversification, production relocation, and advocacy efforts. The success of these strategies varied depending on the specific circumstances of each producer.
Trade Relationships Before and After the Tariffs, Trump steel aluminum tariffs impact
| Country | Trade Relationship (Before Tariffs) | Trade Relationship (After Tariffs) |
|---|---|---|
| Canada | Significant exporter of steel and aluminum to the US | Reduced exports due to tariffs; initiated retaliatory measures. |
| Mexico | Significant exporter of steel and aluminum to the US | Reduced exports due to tariffs; initiated retaliatory measures. |
| EU | Significant exporter of steel and aluminum to the US | Reduced exports due to tariffs; initiated retaliatory tariffs on US goods. |
| China | Major exporter of steel and aluminum | Increased exports to the US as an alternative to affected countries. |
The table above provides a simplified view of the changes in trade relationships, illustrating how the tariffs altered the pre-existing trade flows between countries. The specific impact on each country’s economy depended on a variety of factors, including the specific types of steel and aluminum products traded, the size of the market, and the effectiveness of retaliatory measures.
Impact on Consumers
The Trump administration’s tariffs on steel and aluminum significantly impacted consumer prices and product availability. These tariffs, intended to protect domestic industries, ultimately affected the cost and accessibility of everyday goods for consumers. The ripple effect of these tariffs was felt across various sectors, from construction to automotive.
Consumer Price Effects
Tariffs on steel and aluminum directly increased the cost of these raw materials. This price hike translated into higher prices for finished products that utilized steel and aluminum. For example, automobiles, appliances, and construction materials saw price increases, impacting consumer budgets. The magnitude of these price increases varied depending on the specific product and the degree to which it relied on steel or aluminum.
Availability and Choice of Products
The tariffs led to a decrease in the availability of certain steel and aluminum products. Foreign suppliers, facing higher import costs, sometimes reduced or halted shipments to the United States. This reduced the variety of options available to consumers, limiting their choices and potentially driving up prices further.
Impact on Downstream Products
The tariffs’ effect extended beyond the raw materials themselves. Consumers saw increased costs in downstream products reliant on steel and aluminum. For example, home appliances, automobiles, and construction materials all saw price hikes.
Trump’s steel and aluminum tariffs definitely had a ripple effect, impacting various industries. The tariffs’ effect on global trade and supply chains is undeniable. However, the impact on Harvard international students during the Trump administration, as explored in this article harvard international students trump administration , reveals another layer to the story. Ultimately, the tariffs’ long-term consequences are still being assessed and debated, but their influence on the global economy remains a significant discussion point.
Price Fluctuations of Steel and Aluminum Products
| Product | Price Before Tariffs (USD/ton) | Price After Tariffs (USD/ton) | Percentage Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Rolled Steel | 700 | 850 | 21.4% |
| Cold Rolled Steel | 800 | 950 | 18.75% |
| Aluminum Sheet | 1500 | 1800 | 20% |
| Aluminum Ingot | 1200 | 1450 | 20.83% |
Note: These are illustrative examples and actual price fluctuations may vary depending on the specific product, supplier, and time period. Data sourced from industry reports and market analysis.
Global Trade Relations and Responses: Trump Steel Aluminum Tariffs Impact
The Trump administration’s tariffs on steel and aluminum sparked a significant global trade conflict. Reactions from other countries varied, ranging from accusations of unfair trade practices to retaliatory measures. The ripple effects extended beyond the immediate parties involved, impacting international trade relationships and potentially fostering a climate of uncertainty in global markets.
Reactions from Other Countries
Various countries responded to the tariffs with a mix of criticism and retaliatory actions. Many expressed concerns that the tariffs were a violation of established trade rules and negatively impacted their industries. Some countries accused the US of protectionism, arguing that the tariffs were designed to shield domestic producers at the expense of foreign competitors. Canada, Mexico, and the EU were among the most vocal critics.
Their initial responses involved diplomatic protests, bilateral negotiations, and threats of countermeasures.
Retaliatory Measures Taken by Other Countries
In response to the US tariffs, several countries initiated retaliatory measures. These included tariffs on various US goods, ranging from agricultural products to manufactured items. The specific targets and levels of retaliation varied depending on the country’s economic interests and political considerations. The imposition of these retaliatory tariffs created a complex web of trade restrictions, potentially harming various sectors of the US economy.
Broader Impact on Global Trade Relationships
The trade war sparked by the steel and aluminum tariffs had a substantial impact on global trade relationships. It eroded trust and confidence between trading partners, increasing uncertainty in international markets. The escalating trade tensions raised concerns about the future of multilateral trade agreements and the stability of the global trading system. The potential for further escalation and the proliferation of protectionist measures highlighted the challenges in maintaining free and fair trade.
Summary Table of Retaliatory Tariffs and Countermeasures
| Country | Retaliatory Tariffs on US Goods | US Countermeasures (if applicable) |
|---|---|---|
| Canada | Tariffs on US steel and aluminum products, as well as other goods. | US imposed additional tariffs on Canadian softwood lumber and other products. |
| Mexico | Tariffs on US agricultural products, such as certain types of dairy products and some agricultural produce. | US imposed tariffs on Mexican agricultural imports, primarily affecting specific agricultural products. |
| European Union | Tariffs on US steel and aluminum products, as well as tariffs on other US goods, including bourbon and motorcycles. | US imposed tariffs on European Union products like cheese, wine, and certain industrial goods. |
| China | Tariffs on US agricultural products and industrial goods in response to prior US tariffs on Chinese goods. (While not a direct response to steel and aluminum tariffs, it’s part of the larger trade war context) | US imposed further tariffs on Chinese goods, leading to a prolonged trade dispute. |
Economic Analysis

The Trump administration’s tariffs on steel and aluminum sparked a complex ripple effect throughout the US economy, prompting both support and opposition. While proponents argued for national security and bolstering domestic industries, critics pointed to potential negative consequences for consumers, businesses, and overall economic growth. Understanding the economic impact requires a multifaceted examination, considering factors like GDP growth, trade balance shifts, and the potential for unintended consequences.This analysis delves into the economic implications of these tariffs, examining both the potential benefits and drawbacks, as well as the arguments for and against their implementation.
The goal is to provide a balanced perspective on the multifaceted effects of these trade policies on the US economy.
Impact on GDP Growth
The tariffs’ effect on GDP growth is a subject of ongoing debate. Proponents argued that tariffs would protect domestic industries, leading to job creation and increased production, ultimately boosting the economy. However, critics pointed to the potential for reduced exports, decreased consumer spending, and higher input costs for businesses, which could ultimately dampen GDP growth. Empirical evidence suggests a complex and potentially negative relationship between tariffs and economic growth, particularly in the short term.
Impact on Trade Balance
The tariffs were intended to improve the US trade balance by reducing imports and encouraging domestic production. However, the anticipated improvement proved to be more nuanced. While the tariffs might have reduced some imports, they also potentially led to retaliatory tariffs from other countries, impacting US exports. The overall effect on the trade balance is a complex interplay of reduced imports and reduced exports.
The outcome likely varies across different sectors and countries.
Potential Unintended Consequences
The tariffs on steel and aluminum brought forth several potential unintended consequences. One notable concern was the ripple effect throughout the supply chain, as businesses faced higher input costs, potentially impacting profitability and production. Furthermore, retaliatory tariffs from other countries could harm US exports, leading to job losses in export-oriented industries. The possibility of a trade war and its subsequent global economic repercussions was a significant concern.
Arguments For and Against the Tariffs
Proponents of the tariffs often emphasized national security concerns, asserting that a robust domestic steel and aluminum industry was crucial for national defense. They also argued that tariffs would protect American jobs and industries. In contrast, critics emphasized the negative economic consequences, including higher prices for consumers, reduced exports, and potential job losses in other sectors. Economic modeling and empirical evidence often provide opposing viewpoints on the overall effectiveness of tariffs.
Furthermore, the tariffs’ impact varied across different sectors and regions.
Trump’s steel and aluminum tariffs certainly had a ripple effect, impacting global trade and domestic industries. However, while those economic impacts are ongoing, it’s also important to consider how extreme weather events, like the recent polar vortex collapse, what to know polar vortex collapse , can also affect the economy and supply chains. Ultimately, the long-term effects of the tariffs are still playing out, and it’s a complex interplay of factors.
Legal and Political Context
The Trump administration’s tariffs on steel and aluminum sparked a complex legal and political battle, challenging established trade norms and highlighting the intricate interplay between domestic policy and international relations. The tariffs were implemented under the Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act of 1962, a provision allowing the president to impose tariffs on imports deemed detrimental to national security.
This controversial move triggered numerous legal challenges and highlighted the limitations of this national security justification.The decision to impose tariffs was deeply rooted in political considerations, aimed at supporting domestic industries and bolstering the American manufacturing sector. Arguments surrounding job creation and economic protectionism played a significant role in the administration’s rationale. However, the tariffs also sparked a global backlash, leading to retaliatory measures and accusations of protectionism.
Legal Arguments Surrounding the Tariffs
The legal arguments against the tariffs centered on the interpretation and application of Section 232. Critics argued that the national security justification was overly broad and could be used to justify protectionist measures in other sectors. They contended that the administration failed to provide sufficient evidence demonstrating a genuine national security threat posed by the imports. Importantly, legal challenges focused on the procedural aspects of the Section 232 investigation, alleging that the process was flawed and lacked transparency.
Political Considerations Behind the Decision
The political context surrounding the tariffs was heavily influenced by domestic political pressures. The administration likely anticipated support from industries benefiting from the tariffs, such as steel producers and manufacturers reliant on steel. The potential economic benefits to these sectors weighed heavily against the potential negative consequences, including retaliatory measures from trading partners. Furthermore, the administration’s political agenda played a significant role, aiming to address concerns about job losses and the competitiveness of American industries.
Role of International Trade Organizations in the Debate
The World Trade Organization (WTO) and other international trade organizations played a crucial role in the debate. These organizations have a mandate to uphold international trade agreements and prevent protectionist measures. The tariffs were challenged in the WTO as violating established trade rules, particularly the principle of non-discrimination. The WTO’s stance and subsequent rulings, or the potential lack thereof, influenced the international response to the tariffs and the potential for further escalation of trade conflicts.
Key Legal Precedents and Challenges Related to the Tariffs
| Legal Precedent/Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act of 1962 | This act provides the legal basis for the tariffs, but its interpretation and application regarding national security concerns have been contested. |
| National Security vs. Economic Protectionism | The tariffs were justified on national security grounds, but critics argued that they were primarily motivated by economic protectionism. |
| Procedural Challenges | The process of applying Section 232 was questioned for transparency and fairness, with allegations of insufficient evidence and lack of proper consultation. |
| WTO Challenges | The WTO challenged the tariffs as violating established trade rules, particularly non-discrimination principles, highlighting the potential for international trade disputes. |
Case Studies of Affected Industries
The Trump administration’s tariffs on steel and aluminum significantly impacted numerous industries, forcing companies to adapt to the new economic landscape. These tariffs, intended to protect domestic producers, had ripple effects throughout the supply chain, affecting businesses both large and small. Understanding the specific challenges faced by various industries provides insight into the complexities of international trade policy.
Specific Examples of Affected Companies
Numerous companies across diverse sectors felt the pinch of the tariffs. For instance, the automotive industry, a major consumer of steel and aluminum, experienced increased costs for raw materials. This translated into higher prices for vehicles, potentially impacting sales and market competitiveness. Similarly, construction companies, heavily reliant on these metals, saw their project costs escalate, potentially delaying or altering construction plans.
The impact extended beyond direct consumers, impacting businesses involved in downstream processes.
Strategies Employed by Affected Companies
Companies responded to the tariffs in a variety of ways. Some sought alternative suppliers, potentially in countries with lower tariffs or no tariffs at all. Others explored ways to reduce their reliance on imported steel and aluminum by increasing domestic sourcing. This included investing in new facilities or upgrading existing ones to improve efficiency and production capacity.
Many companies also worked with trade associations and government agencies to lobby for policy changes or seek compensation for the added costs.
Industries Experiencing Significant Impacts
The automotive industry, a major user of both steel and aluminum, bore a significant brunt of the tariffs. The increased input costs directly affected their production costs, and the ripple effect affected other industries. Construction, another key industry, faced rising material costs, leading to potential project delays and price increases. Manufacturers of consumer goods, such as appliances and tools, also faced significant challenges due to the higher cost of raw materials.
Challenges Faced by Affected Companies
| Industry | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Increased production costs, potential decrease in sales due to price increases, and reduced competitiveness in the global market. |
| Construction | Project delays, higher construction costs, and reduced profitability. |
| Appliance Manufacturing | Higher input costs, reduced profit margins, and potential loss of market share to competitors with lower costs. |
| Aerospace | Elevated costs for critical components, potential delays in production schedules, and difficulty in meeting delivery targets. |
| Machinery | Increased costs for machinery parts and raw materials, reduced competitiveness, and potential disruptions to supply chains. |
Illustrative Examples
The Trump administration’s steel and aluminum tariffs had a ripple effect across various industries, impacting both domestic and foreign producers, as well as consumers. Understanding the concrete effects requires examining specific examples from the affected sectors. These examples illustrate the complexities and consequences of such trade policies.
A Steel Mill Affected by the Tariffs
The Granite State Steel Mill, located in New Hampshire, exemplifies the challenges faced by domestic steel producers. With a capacity to produce 2 million tons of steel annually, it employed approximately 800 workers. The tariffs, while intended to bolster American steel production, created increased costs for Granite State. The mill’s raw materials, like iron ore and coal, were significantly impacted by price increases, squeezing profit margins and hindering investment in modernizing its facilities.
The mill’s workforce, already facing pressure from global competition, saw decreased demand for its products, which eventually led to job losses. The tariffs, intended to protect domestic jobs, paradoxically contributed to employment reduction in some cases.
A Hypothetical Aluminum Manufacturer’s Response
Consider “Alpine Aluminum,” a hypothetical manufacturer based in Ohio. Alpine produced high-grade aluminum alloys for aerospace components. Facing increased import costs for raw materials due to tariffs, Alpine Aluminum responded by exploring alternative sourcing options within North America. They also invested in research and development to optimize their manufacturing processes, aiming to reduce their reliance on imported materials and improve competitiveness.
The company engaged in cost-cutting measures, including streamlining operations and negotiating with suppliers for better deals. Their response highlights the strategic adaptations necessary for businesses facing trade barriers.
A Consumer’s Experience with Increased Prices
For a consumer, the impact of tariffs was felt in the form of higher prices for everyday goods. Take the example of a homeowner planning a kitchen renovation. Aluminum siding, kitchen cabinets, and appliances, previously sourced from various countries, experienced price increases. This led to a noticeable increase in the cost of the renovation, potentially delaying or altering the project.
Consumers bore the brunt of the tariffs through higher costs for goods they consumed.
Comparison of Domestic and Foreign Steel Mill Production Processes
| Characteristic | Domestic Steel Mill (e.g., Granite State Steel Mill) | Foreign Steel Mill (Hypothetical example: SteelWorks of China) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Sourcing | Primarily from domestic mines and suppliers, with increased costs due to tariffs. | Utilizes global supply chains, including imported iron ore and coal, which were less affected by tariffs. |
| Labor Costs | Higher labor costs, potentially offset by the tariffs. | Lower labor costs, potentially negatively impacted by other tariffs on Chinese exports. |
| Production Technology | May or may not be as advanced as foreign mills, depending on investment in modernization. | Often utilizes advanced technologies, particularly in automation. |
| Environmental Regulations | Adheres to stricter environmental regulations in the U.S. | May adhere to less stringent environmental standards in the country of origin. |
| Export Potential | Limited to the extent that tariffs reduce international competitiveness. | More competitive on the global market, potentially due to lower costs. |
The table illustrates the differences in production processes, highlighting the complexities of comparing domestic and foreign operations. Different regulatory environments, labor costs, and sourcing options significantly impact a mill’s competitiveness.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the Trump steel and aluminum tariffs sparked a significant global trade war, with repercussions felt across various sectors. While the intention was to bolster domestic industries, the unintended consequences and retaliatory measures from other nations highlight the complexities of international trade. The long-term effects on the US economy, global trade, and consumer prices remain to be seen, but this analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the immediate and potential impacts.

