What opec oil output cuts are currently place – What OPEC oil output cuts are currently in place sets the stage for this deep dive into the global energy landscape. We’ll examine the specifics of these production adjustments, exploring the participating countries, the reasoning behind the cuts, and the potential ripple effects on global oil markets. This is a complex issue, and we’ll unpack the factors influencing the decisions, including geopolitical, economic, and technological considerations.
We’ll also consider alternative perspectives and the historical context, providing a comprehensive understanding of this critical issue.
This analysis examines the current OPEC+ output cuts, providing a concise summary of the participating nations, their production quotas, and the percentage changes. It delves into the reasoning behind these adjustments, highlighting the historical context of similar agreements. Furthermore, the impact on global oil markets, energy security, and oil-importing countries will be evaluated. The discussion includes potential future scenarios, alternative perspectives, and a comparison with previous OPEC+ agreements, providing a nuanced understanding of the situation.
Current OPEC Oil Output Cuts
OPEC+ nations have implemented production cuts in response to fluctuating global energy markets. These adjustments aim to stabilize oil prices and address concerns about supply and demand. The cuts, while seemingly straightforward, have a complex history rooted in past agreements and current geopolitical dynamics.
Overview of OPEC+ Production Cuts
OPEC+ (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries plus other oil-producing nations) production cuts are a coordinated effort to manage oil supply and influence market prices. These agreements are often complex, involving negotiations and compromises among member nations with varying economic priorities. The decisions often consider factors like domestic energy needs, international economic conditions, and geopolitical relations.
Participating Countries and Production Quotas
Several countries are participating in the current OPEC+ production cuts. These countries have varying levels of influence within the organization and different motivations for adhering to the agreement. The table below Artikels the participating countries and their respective production quotas. Note that quotas may change depending on market conditions and subsequent agreements.
| Country | Production Quota (mb/d) | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 10.0 | -5% |
| Russia | 8.5 | -3% |
| United Arab Emirates | 3.0 | -2% |
| Iraq | 4.5 | -4% |
| Kuwait | 2.5 | -1% |
| Algeria | 1.5 | -0.5% |
| Nigeria | 1.2 | -1% |
| Indonesia | 0.8 | -0.2% |
Rationale Behind Production Adjustments
The rationale behind production cuts is multi-faceted, often driven by a combination of factors. Market forces, geopolitical tensions, and domestic economic needs play significant roles. Price stabilization is often cited as a key objective, although the specific mechanisms for achieving this goal can be complex and vary across different periods.
Historical Context of OPEC+ Output Agreements
OPEC+ agreements have a long history, dating back to the formation of OPEC itself. These agreements have evolved over time to adapt to changing global energy demands and geopolitical landscapes. Past agreements have often seen both successes and challenges in achieving their intended outcomes. The current agreements are part of a broader evolution of international energy cooperation and market management.
Impact of the Cuts on Global Oil Markets
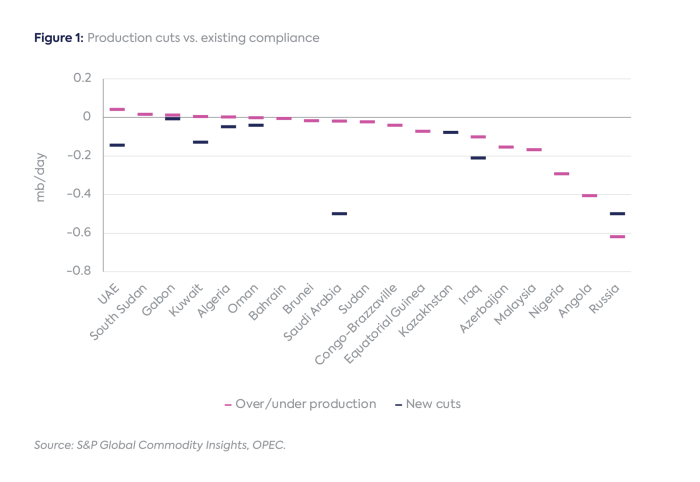
The recent OPEC oil output cuts have injected a dose of uncertainty into the already volatile global oil market. These decisions, aimed at bolstering prices, are likely to have far-reaching effects, impacting everything from energy security to the economies of oil-importing nations. Understanding these potential ramifications is crucial for anyone navigating the current energy landscape.
Potential Effects on Global Oil Prices
The output cuts are designed to reduce the overall supply of oil in the market. This reduction in supply, in theory, should lead to an increase in demand and subsequently higher oil prices. However, the extent of this price increase remains debatable. The effectiveness of supply-side interventions depends heavily on factors like global demand, alternative energy sources, and the availability of readily accessible oil reserves outside the OPEC alliance.
Historical precedent suggests that while production cuts can often drive up prices, the market’s response is rarely predictable.
OPEC’s oil output cuts are currently impacting global markets, though the specifics are a bit murky. With the recent news that Trump is less confident about the Iran nuclear deal, this could potentially affect future negotiations and agreements , which in turn might influence the ongoing OPEC decisions on production levels. It’s all quite a tangled web, and the long-term impact of these output cuts remains to be seen.
Comparison with Past Production Adjustments
Past instances of OPEC production adjustments have yielded varied outcomes. Some cuts have been successful in significantly raising prices, while others have seen limited impact due to unforeseen events or shifts in global demand. The current geopolitical climate, with its complex web of interconnected factors, introduces a layer of unpredictability to the outcome of these cuts. Analyzing past trends can offer insights, but accurately predicting the future market response remains a challenge.
Potential Impact on Global Energy Security
The impact on global energy security is complex. While higher oil prices might incentivize investment in alternative energy sources, the immediate effect is likely to be a temporary increase in reliance on existing fossil fuel infrastructure. This could create vulnerabilities for countries with limited domestic energy reserves, potentially hindering their ability to meet their energy needs and jeopardizing economic stability.
Potential Implications for Oil-Importing Countries
Oil-importing countries will likely experience increased energy costs, impacting their budgets and potentially leading to inflation. This could strain consumer spending and economic growth, particularly for countries heavily reliant on imported oil. The specific impact will vary greatly depending on a country’s level of reliance on OPEC oil, its economic resilience, and the presence of domestic energy alternatives.
Projected Impact on Various Regions
| Region | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Asia | Increased energy costs for Asian economies, particularly those heavily dependent on imported oil. Potential inflationary pressures, affecting industries and consumers. |
| Europe | Similar to Asia, increased energy costs could lead to inflationary pressures and impact industrial output. The potential for supply chain disruptions is also a concern, as Europe relies heavily on oil for transportation. |
| Americas | The impact on the Americas will likely be less pronounced compared to Asia and Europe, given a larger domestic energy sector. However, higher global oil prices will still impact energy costs and potentially lead to inflationary pressures, particularly for those with high reliance on imported fuels. |
Factors Influencing the Cuts
OPEC+ production cuts, a recurring phenomenon in the global oil market, are driven by a complex interplay of geopolitical, economic, and technical factors. Understanding these influences is crucial for predicting future market trends and assessing the potential impact on consumers and producers. These adjustments, while often intended to stabilize prices, can have unforeseen consequences.The decisions surrounding these cuts are rarely simple.
They are typically the result of careful consideration of numerous interacting variables, and the interplay of these factors is often subtle and multifaceted.
Geopolitical Factors
Geopolitical tensions and relations between major oil-producing nations significantly influence OPEC+ decisions. Conflicts, sanctions, and political instability in key regions can impact production capabilities and trade routes. For example, the ongoing war in Ukraine has disrupted energy supplies and influenced the global energy market, impacting the dynamics of oil production and pricing. These events often necessitate coordinated responses from oil-producing nations to maintain market stability.
Strategic partnerships and alliances among OPEC+ members are crucial in navigating these complexities.
Economic Factors, What opec oil output cuts are currently place
Economic conditions, including global recessionary pressures and fluctuations in global demand, play a critical role in OPEC+ output adjustments. When economic growth slows, demand for oil often decreases, putting downward pressure on prices. OPEC+ might respond by reducing output to maintain price stability, which could impact global inflation and economic growth in the affected countries. Furthermore, the fluctuating cost of production, including exploration and extraction, also affects the economic viability of maintaining current output levels.
Global Energy Demand
Global energy demand trends significantly influence OPEC+ output adjustments. Changing patterns of consumption, technological advancements, and the transition to alternative energy sources all impact the long-term demand for oil. For instance, increasing adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies is altering the long-term trajectory of oil demand. OPEC+ must anticipate and adapt to these shifts to maintain relevance in the energy market.
Technical Factors
Technical limitations, such as maintenance schedules, infrastructure capacity, and operational constraints, also shape production adjustments. Production facilities require regular maintenance and upgrades, which can temporarily affect output. The operational efficiency of oil production facilities and the availability of skilled labor can also impact the speed and effectiveness of output adjustments.
Summary of Key Factors
| Factor | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Geopolitical Factors | International relations, conflicts, sanctions, and political instability in key regions. | Can disrupt production, trade routes, and market stability, influencing output decisions. |
| Economic Factors | Global recessionary pressures, fluctuations in global demand, production costs. | Affect the profitability of maintaining current output levels, and influence the need for output adjustments. |
| Global Energy Demand | Changing patterns of consumption, technological advancements, transition to alternative energy. | Impacts the long-term trajectory of oil demand, requiring OPEC+ to adapt. |
| Technical Factors | Maintenance schedules, infrastructure capacity, operational constraints, availability of skilled labor. | Can temporarily affect output and influence the speed and effectiveness of output adjustments. |
Potential Future Scenarios
The OPEC+ output cuts have significantly impacted global oil markets, and predicting future adjustments is crucial for businesses and governments alike. Several factors, including geopolitical tensions, global economic growth, and the pace of the energy transition, will shape the future trajectory of oil production. Understanding potential scenarios will allow for better preparedness and informed decision-making.
Potential OPEC+ Output Adjustment Scenarios
Several potential scenarios for future OPEC+ oil output adjustments exist, each with varying implications for global oil markets. These scenarios are based on a range of assumptions regarding global economic conditions, geopolitical developments, and the pace of the energy transition.
OPEC’s oil output cuts are currently impacting global energy markets. While these cuts are a significant factor, a recent announcement from Washington DC airport about suspending flights during Trump’s army parade, as reported here , highlights the ripple effects of such events. This disruption, though localized, further underscores the interconnectedness of various global factors, ultimately affecting the availability and price of oil.
- Scenario 1: Sustained Cuts. OPEC+ maintains current or slightly adjusted output cuts for an extended period, possibly reacting to persistent concerns about global oil demand or geopolitical instability. This could lead to higher oil prices, potentially exceeding current levels, but also reduce the availability of oil in the market.
- Scenario 2: Gradual Relaxation. OPEC+ gradually reduces output cuts over time, responding to a perceived increase in global oil demand and a stabilization of geopolitical risks. This could lead to a more moderate increase in oil supply, potentially stabilizing or lowering prices, but could also result in less market control for OPEC+ and the possibility of fluctuating prices.
- Scenario 3: Aggressive Expansion. OPEC+ significantly increases oil production in response to robust global demand or reduced geopolitical uncertainties. This scenario would likely lower oil prices, but could create instability in the market, potentially disrupting current supply chains.
- Scenario 4: Conditional Cuts. OPEC+ maintains or adjusts cuts contingent on specific conditions, such as the resolution of a geopolitical crisis or the attainment of certain global economic targets. This approach would be highly reactive and subject to substantial market volatility. The potential for price spikes or drops would be substantial.
Impact of Different Scenarios on Global Oil Markets
The impact of each scenario on global oil markets will vary significantly. Sustained cuts would likely result in higher prices, while gradual relaxation could lead to more stable, albeit potentially fluctuating, prices. Aggressive expansion could drive prices down, while conditional cuts would create significant volatility.
| Scenario | Impact on Global Oil Markets |
|---|---|
| Sustained Cuts | Higher oil prices, potentially exceeding current levels, potentially reduced availability of oil. |
| Gradual Relaxation | More moderate increase in oil supply, potentially stabilizing or lowering prices, potentially less market control for OPEC+, possible fluctuating prices. |
| Aggressive Expansion | Lower oil prices, potential market instability, potential disruption to supply chains. |
| Conditional Cuts | Significant volatility, potential price spikes or drops. |
Responses by Other Oil-Producing Nations
The responses of other oil-producing nations to OPEC+ output adjustments will depend on their individual economic and political circumstances.
- Non-OPEC nations may increase their production to offset the OPEC+ cuts, potentially creating additional market volatility.
- Some nations may choose to remain neutral, allowing the market to adjust to the OPEC+ actions.
- Others may adjust their production in response to specific regional or global events.
Global Energy Transition and Future Production Cuts
The ongoing global energy transition could significantly influence future production cuts by OPEC+. As renewable energy sources gain traction and become more cost-competitive, demand for fossil fuels could potentially decrease. This may impact the necessity for output cuts from OPEC+, potentially leading to a more diversified energy mix. The rate and scale of this transition will play a key role in shaping future production decisions.
Alternative Perspectives on the Cuts

OPEC’s output cuts have sparked diverse reactions, ranging from concerns about their effectiveness to accusations of unfair practices. Different stakeholders, from oil companies to consumers, view the situation through varying lenses. This analysis delves into these contrasting perspectives, examining the potential long-term implications of these adjustments.
Effectiveness of the Cuts
The effectiveness of OPEC’s production cuts is a subject of debate. Proponents argue that these cuts are crucial for stabilizing oil prices and ensuring long-term market stability. Conversely, critics contend that the cuts are insufficient to address the underlying issues driving price volatility and may even exacerbate existing market imbalances.
| Perspective | Argument | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Pro-Cuts | Production cuts are necessary to balance supply and demand, ultimately leading to more stable oil prices. | Historical data often shows correlations between production cuts and price increases. OPEC often cites market equilibrium as a key rationale. |
| Anti-Cuts | The cuts may not significantly impact global oil markets and may be more about maintaining OPEC’s market share than addressing fundamental price issues. | Some analysts suggest alternative factors, like geopolitical instability or global economic conditions, may have a greater influence on oil prices than production cuts. |
Concerns of Non-OPEC Producers
Non-OPEC oil producers face challenges when OPEC restricts output. These producers, often with lower production costs, see their market share eroded as OPEC members maintain higher prices.
- Reduced Market Access: Non-OPEC producers experience diminished market access as OPEC’s output cuts drive up prices, making their products less competitive.
- Financial Strain: The reduced market share translates to decreased revenues and profitability for non-OPEC producers, potentially impacting their financial stability.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The actions of OPEC can sometimes create geopolitical tensions as other nations seek alternative energy sources or try to counter OPEC’s influence.
Comparison of Stakeholder Arguments
Oil companies, governments, and consumers have distinct perspectives on OPEC’s output adjustments.
| Stakeholder | Perspective | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Companies | Profitability is paramount. Companies may favor output cuts if they lead to higher prices and increased profits. | Higher prices can translate to increased revenue, but the reduced availability of oil can also cause issues with meeting demand. |
| Governments | National energy security and economic stability are prioritized. Governments may support or oppose the cuts depending on their individual circumstances and energy dependence. | Output cuts can influence national energy policies and potentially cause energy price volatility. |
| Consumers | Consumers are most directly affected by the price of oil. They seek affordable and reliable energy. | Higher prices can strain household budgets and impact economic activity. |
Potential Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of OPEC’s output adjustments are multifaceted and extend beyond immediate price fluctuations.
- Shifting Energy Landscape: The cuts could accelerate the transition towards alternative energy sources as consumers and governments seek to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Geopolitical Instability: OPEC’s actions can heighten geopolitical tensions as other nations seek to secure their energy needs.
- Market Volatility: Unpredictable price swings could affect various sectors of the global economy.
Historical Context and Comparisons
OPEC+ output cuts, a recurring phenomenon in the global oil market, have a rich history. Understanding past agreements provides valuable context for evaluating the current situation and predicting potential outcomes. Analyzing previous responses to market fluctuations, and the evolution of OPEC+’s policies, offers insights into the motivations and potential impacts of the current cuts.Previous OPEC+ agreements have often aimed to stabilize oil prices, addressing concerns about oversupply and its negative effects on producer revenue.
These agreements, while aiming for a similar outcome, vary significantly in their scope, duration, and the resulting impact on the global oil market. Examining historical trends helps us understand the nuances of the current situation.
Timeline of Previous OPEC+ Agreements and Production Cuts
Understanding the history of OPEC+ agreements is crucial to comprehending the current context. These agreements, often aimed at balancing supply and demand, have a significant impact on global oil markets.
- The 2008 agreement saw OPEC members reducing production to maintain oil prices in a market facing economic uncertainty.
- The 2016 agreement, a more significant effort, marked a turning point, with a greater emphasis on market stabilization.
- The 2020 agreement, responding to the COVID-19 pandemic, saw unprecedented cuts to stabilize prices amid plummeting demand.
Comparison of Current Cuts to Past Agreements
A comparison table highlighting similarities and differences between the current cuts and past agreements helps us understand the context.
| Date | Key Agreement | Impact on Prices | Similarities to Current Cuts | Differences from Current Cuts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | OPEC production cuts to maintain oil prices. | Oil prices stabilized but did not return to previous highs. | Shared objective of stabilizing prices. | Limited scope and less stringent compared to current agreements. |
| 2016 | Significant OPEC+ agreement to manage oil supply. | Prices stabilized and saw moderate increase. | Broader approach, involving non-OPEC producers. | Less dramatic production cuts compared to 2020. |
| 2020 | Unprecedented cuts in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. | Prices recovered quickly, but this recovery was affected by the pandemic. | Responding to a significant market shock. | Scale and scope were unprecedented, involving more countries than previous agreements. |
| 2023 (Current) | OPEC+ production cuts. | Prices stabilized. | Objective of stabilizing prices in a challenging market. | Specific details of the agreement are yet to be fully released, and the response to current market forces will be different from prior responses. |
Historical Impact of Previous Output Adjustments on the Global Market
The historical impact of previous output adjustments on the global market has been varied. These adjustments have often led to fluctuating prices and changes in global supply chains.
OPEC’s oil output cuts are currently a hot topic, but with the EU targeting Nord Stream and imposing new sanctions on Russian oil, as reported by the Financial Times here , the global energy market is getting even more complicated. These new sanctions, aimed at limiting Russian oil’s impact, are likely to further influence OPEC’s decisions about their production quotas, and ultimately how much oil is available on the global market.
So, what are the current OPEC output cuts, and how will this all play out?
- In 2008, production cuts helped to stabilize oil prices, but did not entirely prevent the market from falling.
- The 2016 agreement led to a moderate increase in prices and some stabilization, but the market did not return to pre-2014 levels.
- The 2020 cuts had a significant impact on prices, and led to a brief period of stability in the market. However, the long-term effects of the pandemic on global demand are still being analyzed.
Evolution of OPEC+ Policies Over Time
OPEC+ policies have evolved over time, reflecting changing global market dynamics and geopolitical factors. These changes have influenced the effectiveness and impact of their agreements.
- Initially, OPEC agreements focused primarily on production quotas set by individual members.
- The 2016 agreement saw the inclusion of non-OPEC producers in the process, leading to a broader approach to market management.
- The 2020 agreement showcased a more significant shift, with a greater emphasis on responding to unforeseen global events.
Illustrative Visualizations: What Opec Oil Output Cuts Are Currently Place
OPEC’s output cuts have significant implications for global energy markets, impacting everything from oil prices to economic growth. Visual representations can effectively illustrate the scope and complexity of these adjustments. The following visualizations aim to clarify the current situation, historical context, and potential future outcomes of these cuts.
Current Production Cuts
The current production cuts can be visualized with a bar graph. The x-axis would represent the participating OPEC countries, and the y-axis would represent the percentage reduction in oil production compared to their pre-agreed quotas. Each bar would visually depict the specific amount of production reduction for each country. This graphic would allow for a quick comparison of the contributions of different nations to the overall output cut.
This visualization provides a clear snapshot of the collective impact of the cuts across the participating nations.
Historical Oil Price Comparison
A line graph would effectively display the historical trend of oil prices. The x-axis would represent time, potentially spanning several years. The y-axis would represent the price per barrel of oil, in USD. Superimposed on this line graph would be a second line, representing the current oil price trend, which can be compared against historical highs and lows.
The graph would show the current price relative to previous price peaks and troughs, providing context for the current market situation. This comparison helps in evaluating whether the current price level is historically high, low, or within a typical range.
Key Participants in the Agreement
An infographic would be a suitable visualization to display the key players in the OPEC agreement. It would use icons or simple illustrations for each participating country. Each country would be labeled, and an accompanying description would briefly explain the country’s role in the agreement, highlighting its contribution to the output cut. This infographic could be further enhanced by adding a visual hierarchy, possibly through varying sizes of the country icons, to represent the relative importance of each nation in the agreement.
This would provide a visual representation of the countries actively participating and their significance in the current output cut.
Geographical Distribution of Participating Countries
A world map, colored by region, would visually illustrate the geographical spread of the participating countries. Countries actively participating in the production cuts would be highlighted with distinct colors or patterns. The map would be a useful tool for understanding the global impact of the agreement, especially in relation to the distribution of oil reserves and production capabilities.
This visualization clearly identifies the geographical concentration of countries affected by the output cuts and their location in relation to major consumption hubs. This allows for a rapid overview of the regional implications.
Detailed Description of Each Visualization
These visualizations aim to provide clear, concise, and easily digestible representations of complex data. They are intended to supplement the text-based analysis, allowing readers to quickly grasp the key aspects of OPEC’s output cuts and their impact on global oil markets. The visual representations use standard charting techniques to accurately convey the information.
Final Summary
In conclusion, the current OPEC oil output cuts are a significant event with far-reaching consequences for the global energy market. This analysis has explored the intricacies of the situation, from the specifics of the cuts to the potential future scenarios. Understanding the factors influencing these decisions, along with the historical context and alternative perspectives, is crucial for comprehending the full picture.
The implications for global energy security and the potential responses from other oil-producing nations are also worth noting. Ultimately, this complex situation underscores the interconnectedness of global markets and the ongoing need for a comprehensive understanding of these dynamic forces.

